In a recent breakthrough, a team of researchers from the University of Tokyo have discovered a new way to create optical logic gates using graphene nanoribbons. These optical logic gates are made from two-dimensional (2D) materials such as graphene, and can be used to control light instead of electricity. This opens up a range of potential applications, from ultra-fast computing to optical signal processing. The team’s research is a major step forward for the development of future-generation photonic devices.

A research team has recently made a discovery that could lead to improved absorption and fluorescence properties in certain molecules. By using a combination of computational and experimental techniques, the team was able to create “antiaromatic” molecules, which have a unique structure that was found to enhance the properties of the molecules. This could be a game changer for many applications, from medical treatments to industrial processes. The team’s research is an important step forward in understanding how antiaromatic molecules can be used to improve properties in various molecules.

In a breakthrough study, researchers have discovered a new way to create artificial dual-center systems with a proximal cofactor like module. This module allows for the integration of two independent machines or systems into one entity, creating a new and exciting form of intelligence. By combining two systems, the researchers have (for the first time) demonstrated the potential for greater efficiency and performance in artificial intelligence (AI). This new technology could have a wide range of applications, from robotics to autonomous decision-making.

Science fiction has become reality. Researchers have recently revealed a breakthrough in which they have successfully extracted and sequenced the DNA of a new species, an alien-like creature found in a far-off galaxy. This is the first time that scientists have ever been able to sample the genetic material of an extraterrestrial species. The implications of this discovery are huge. Not only does it open the door to further exploration of the universe, it also provides an unprecedented opportunity for researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the evolution of life in the universe.

A new study published in Nature Communications has revealed an important discovery about the way infections are treated. Researchers from the University of Michigan have found that a different type of immune response is required for therapeutic treatment of viral infections. This new insight could have a huge impact on the way treatments are designed and administered for diseases such as HIV, influenza, and other viral infections. The team was able to show that a particular type of immune response, known as the type I response, is necessary to activate the body’s own antiviral defense mechanisms.

Grapes have been a staple of the human diet for centuries, but the science behind their growth and development has remained relatively mysterious. That is, until now. Scientists have recently discovered a way to decode the molecular phenology of the grapevine, a process which can help us better understand the physiology of the grape and how it is affected by environmental conditions. This new research has the potential to revolutionize the way we grow grapes and make them more resilient to climate change.

It’s official: the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is set to make a huge discovery in the field of planet formation. Using its powerful infrared vision, JWST has detected a large population of newborn planets located in the NEOWISE-NEO3 region of space. This region is believed to be one of the most active areas of planet formation, and what JWST has seen provides exciting new insights into the process.
This discovery is especially exciting for scientists because the NEOWISE-NEO3 region is so far away from Earth.

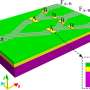
One of the most important decisions in urban planning is understanding how to manage the flow of traffic. To assist with this, researchers have developed a way of visualizing traffic cell movements on a 3D map. By utilizing a method called particle tracking velocimetry, they are able to measure the speed and direction of traffic flows over time. This gives urban planners a better understanding of the dynamics of traffic flows, allowing them to plan more efficient road networks and better manage traffic.
Today, researchers revealed a revolutionary finding that could change our understanding of the universe: an alternative cosmic source of gold! Gold, a precious metal that has been valued for centuries, is usually formed in neutron star collisions. However, the researchers demonstrated that gold can also be produced in a previously unknown process involving a white dwarf star and a neutron star. This discovery has exciting implications for our understanding of the universe, and may provide new insights into how gold is formed and distributed throughout space.
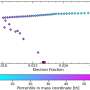
A group of astronomers have discovered an unprecedented series of flares from a stellar corpse, suggesting the possibility of life existing around it. Using a combination of ground-based and space-based telescopes, the team was able to detect extremely brief, but powerful flares that occurred on a regular basis. The regularity of these flares suggested to the researchers that they may be caused by something orbiting the stellar corpse, such as a planet or asteroid.

Screening Urine Samples Reveals Previously Unrecognized Disease
A new study has revealed that screening of urine samples can reveal previously unrecognized diseases in individuals. The research, conducted by a team of scientists from the University of California, San Francisco, has shown that screening of urine and other bodily fluids can detect multiple diseases which have previously gone undetected. This new approach could revolutionize the way diseases are diagnosed and treated, by offering an early, accurate, and cost effective screening method that can be used to diagnose and treat a wide range of diseases.

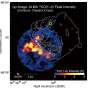
Today, astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have made an incredible discovery: molecular clouds are forming in the supernova remnant G350.3-0.3. This supernova remnant is located in the Milky Way, about 11,000 light years away from Earth. This is the first time that molecular clouds have been found in a supernova remnant, and it could provide valuable insight into the formation of stars and planets. ALMA’s high-resolution images have allowed astronomers to detect dense clumps of gas and dust, which are just beginning to form new stars and planets.
Recently, scientists have discovered an ancient species of insect preserved in amber from the Lower Cretaceous period, approximately 99 million years ago. This stunning discovery provides an unprecedented glimpse into the evolution of insect behavior and morphology during the Mesozoic Era. The insect, now named Burmomyrmex bohemicus, is the earliest known species of its kind, and provides a window into the ancient world of insect behavior. Its complex jaw and mouth parts suggest that it was an early forager, and its body size and shape suggest that it was adapted to an arboreal lifestyle.

In a groundbreaking new study, bioengineers have successfully grown cardiac muscle samples in space! This exciting news brings hope for new discoveries in the fields of space exploration and medical research. The experiment, conducted by a team of scientists from the University of Texas Medical Branch, involved sending samples of cardiac muscle cells into space and then monitoring them over the course of a month. The samples were found to be healthy and viable when they returned to Earth.

Today marks a momentous day in the history of space exploration. For the first time in human history, a satellite has launched into orbit around the Earth with the purpose of exploring and studying the planet in greater detail than ever before. The satellite, known as Trailblazer, was developed and launched by a team of scientists and engineers from around the world. This ambitious mission is expected to provide groundbreaking insights into the Earth’s atmosphere and climate, and its data will be used to develop better models and predictions of future climate change.

In a remarkable feat of citizen science, astronomers have discovered a boundary between comets and asteroids using only images taken from amateur telescopes. This boundary, known as the ‘froggy line’, marks the separation between small icy bodies and rocky asteroids. It was discovered by a team of international scientists, led by amateur astronomer Gianluca Masi from the Virtual Telescope Project in Italy. The team’s findings have been published in the November 2021 issue of the Astrophysical Journal.

Climate mutation has enabled flour beetles to survive and thrive in the face of a changing climate. Scientists at the University of Arizona have discovered a gene mutation in the flour beetle that has allowed them to adapt to warm temperatures that were once deadly to them. The gene mutation provides the beetles with an evolutionary advantage that has enabled them to survive and even thrive in hotter climates. This adaptation has given the species a leg up in the face of climate change, and could have implications for other species’ ability to survive the effects of global warming.

Today, an innovative chemists is leading the way to create an environmentally sustainable solution to the global plastic crisis. Dr. Carol Yang is developing biodegradable plastics made from proteins derived from food scraps. Through her research, she is revolutionizing the way we think about plastics and creating an accessible solution that is both affordable and renewable. Dr. Yang’s plastics are made from proteins from food waste and other organic materials, meaning that we can reduce our dependence on petroleum-based plastic products and drastically reduce plastic pollution.

The need for safer spaces is becoming increasingly important in our everyday lives. With the rise of hate speech, discrimination, and other forms of violence, more and more people are looking for ways to create and maintain safe environments. Recently, researchers have been working on ways to make public spaces safer, particularly in urban areas. This research focuses on developing technologies and methods that can be used to create a sense of safety and security in public spaces.

In a groundbreaking study, researchers have successfully decoded the cascade genome, offering a unique insight into the evolution of species. The analysis of the cascade genome reveals an ancient evolutionary network, with the network’s structure and complexity providing clues as to how various species have adapted and developed over time. The team of researchers has identified a set of genes that are essential to the cascade genome, which could help explain the diversity of species and their respective evolutionary pathways.

A major Dutch company has recently announced their plans to enter the space industry. Royal Dutch Shell, a global energy and petrochemical company, has announced their plans to begin investing in the space sector. This is an exciting development that could shape the future of the space industry.
Shell plans to focus on the development of new technologies and services that will help increase their presence in space. This includes developing new energy storage capabilities, investing in space-based communication systems, and researching new materials and methods that could be used to manufacture products in space.

Scientists have recently developed a new way to deliver mRNA to cells and potentially treat autoimmune diseases. This new method uses lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to safely transport mRNA into cells. This could provide a new way to treat autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, using gene therapy. The method is non-invasive and could potentially be used to target certain types of cells in the body. By delivering mRNA to cells, the cells can produce therapeutic proteins that can fight off the autoimmune response and reduce inflammation.
NASA is now using supercomputing to revolutionize how they approach space missions. With the power of supercomputers, they are able to bring more complex mission concepts to life. Here are 11 ways NASA is using supercomputing to revolutionize their missions:
Simulating how spacecraft will interact with space debris. Predicting the most efficient route for a mission. Developing autonomous systems and algorithms for robotic exploration. Modeling and predicting the behavior of complex systems like the Earth’s atmosphere.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have developed a new type of supramolecular hydrogel that can mimic the behavior of the extracellular matrix found in the natural environment. This new material is composed of the supramolecular assembly of two polymers, poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). By combining these polymers, the researchers have created a material that is capable of absorbing large amounts of water and can be used to create 3D structures.

Today, scientists have discovered a phenomenon that could potentially change the way we think about our Solar System. For the first time ever, scientists have observed an eclipse on Saturn that was caused by its own moon! This rare event was observed by the Cassini spacecraft and is the first of its kind to be seen up close. The eclipse lasted for about 7 minutes and provided scientists with valuable information about the atmosphere of Saturn and its moons.

