
Astronomers have used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to obtain the highest resolution image ever in radio astronomy. The image, generated from data collected over a period of seven months, shows the radio emission from the galaxy M83, also known as the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy.
Astronomers have achieved an amazing feat using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA): the highest resolution image ever taken in radio astronomy! The image shows the stunning radio emission from the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy, also known as M83.

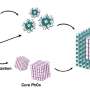
A recent breakthrough in synthetic biology has opened up the possibility of bacteria being able to biosynthesize intricate protein complexes. This exciting development could lead to many potential applications in healthcare, food and other industries. Researchers at the University of Cambridge have developed a method to engineer bacteria to produce large and complex protein complexes, which are essential for many cellular processes. This could potentially be used to create novel drugs and therapeutic proteins, as well as new materials, such as bio-plastics.
In a landmark move, Australia has become the first nation to pass a law requiring companies to pay for carbon dioxide emissions. The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme, which was passed by the Senate on Wednesday, requires companies to pay a fee for every tonne of carbon dioxide they emit. The fees will be collected by the government and used to fund clean energy projects and other initiatives to reduce emissions. This new law marks a major shift in how Australia is addressing climate change, and is expected to have a positive impact on the country’s economy and environment.

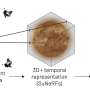
Today, CERN announced a new milestone in particle physics research. Scientists have successfully shifted gold nuclei, a heavy nucleus made up of 79 protons and 118 neutrons, to the center of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). This is the first time such a heavy nucleus has ever been accelerated in a particle accelerator. This breakthrough gives us a glimpse into the inner workings of the nucleus and could help us understand the origin of the universe.

Animal-to-human transmission of viruses has been a major concern in recent years, with the emergence of the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus being the most prominent example. Now, a new study has shed light on the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in animals, highlighting the potential gap in understanding the full scope of the virus.
The study, published in the journal Science, found that out of over 18,000 animal samples tested, only 0.1% were positive for SARS-CoV-2.

The COVID-19 virus has been a source of great concern for the global population since its emergence in late 2019. Recently, a study conducted by scientists at the University of Michigan revealed that the virus may be more infectious than previously thought. The study revealed that the virus is capable of surviving on surfaces and in the air for up to three days, and possibly longer. This news is concerning as it means that individuals must take extra precautions to protect themselves from infection.
A new deep artificial intelligence (AI) tool could help ecologists learn more about rare species and their habitats. Developed by researchers at the University of Washington, the tool uses machine learning to find patterns in the data that would be difficult to detect with traditional methods. The tool could be used to identify rare species and their habitats, and to better understand the complex relationships between species and the environment. The research team tested their tool on data from the San Francisco Bay Area, and found that it was able to accurately identify rare species.

We all know that physical activity is important for healthy development in children, but what about the skills necessary to move? New research has found that the ability to move in a coordinated and efficient manner is essential for children to reach their full potential. Researchers from the University of Toronto studied the development of movement skills in children aged 2-5 and found that those with higher levels of movement competency had better physical, mental, and social development.

In a major announcement, the European Union (EU) declared that the coming decade will be a ‘Quantum Decade’, a time of intense research and development in the field of quantum computing. With the goal of making Europe a global leader in this cutting-edge technology, the EU is investing €1 billion into the initiative. This investment will create new quantum technology hubs, support research into quantum computing, and provide resources for start-ups.

A new study recently published in the journal Nature Sustainability outlines a potential solution for reducing methane emissions. Scientists suggest harnessing the power of microbes, specifically methanotrophic bacteria, to help reduce the amount of methane released into the atmosphere. This could provide a viable alternative to current methods of reducing methane emissions, such as capturing and flaring or simply reducing the amount of livestock.
Methanotrophic bacteria are a type of microbe that feeds on methane.

A recent study has revealed that the atmosphere of ice giant planets like Neptune and Uranus have a unique fall season. Scientists from the University of California, Santa Cruz, studied data from the Hubble Space Telescope to determine that the atmosphere of Neptune and Uranus experience seasonal changes. During the fall season, these planets experience a dramatic decrease in temperature and an increase in atmospheric pressure. This leads to a unique atmospheric phenomenon that has never been seen in other planets or moons.

NASA’s Roman Space Telescope is set to launch in 2023 and will be the first of its kind to chronicle the history of the universe. This telescope will be able to see further into the universe than ever before and provide new insights into the evolution of galaxies, dark matter, and dark energy. With its unprecedented sensitivity and resolution, the Roman Space Telescope will be able to detect the faint light from distant galaxies, study the atmospheres of exoplanets, and search for evidence of the first stars and galaxies in the universe.

Recent studies have uncovered a previously unknown process of genetic exchange between cells: the transfer of genetic material via extracellular vesicles. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny bubbles of membrane enveloping proteins, lipids, and other molecules. They are released by cells and can travel between cells, allowing them to exchange genetic material. This process, known as intercellular communication, has been found to be essential for normal cellular functioning. Scientists believe that EVs play a key role in this process and may even be able to transfer genetic information between distant cells.

A team of physicists and astronomers have made a startling discovery: the universe is expanding faster than theory predicts! In a recent study, the researchers used data from the Hubble Space Telescope to measure the rate of expansion of the universe and found that it was about 9 percent faster than that predicted by the standard theory of cosmology. This mismatch could force scientists to rethink their understanding of the universe and its origin.

A new study has revealed that aquatic crocodiles have undergone multiple evolutionary trajectories over time, which have resulted in a variety of adaptations to the aquatic environment. The research, published in the journal Nature, suggests that multiple lineages of aquatic crocodiles have been present since the Early Cretaceous, which is approximately 145 million years ago. The study also indicates that the various aquatic crocodile species have independently evolved several adaptations to the aquatic environment, such as paddle-like forelimbs, webbed feet, and a streamlined body shape.

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has just achieved a major breakthrough in its mission to explore the Solar System. Scientists have successfully used the JWST to detect vaporized sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere of a distant planet. This suggests that the planet may be covered in sand-like particles. This discovery is a crucial step forward in understanding the atmosphere and environment of a planet beyond our own. It will also help in the search for potential habitable planets in the universe.

Scientists have achieved a world-first: a quantum chemistry experiment in space! The experiment, conducted on board the International Space Station (ISS), marks a huge milestone in the development of quantum-enabled technologies for space exploration and beyond. The experiment, led by a team of researchers from TU Delft in the Netherlands, involved the use of trapped ions to study the behavior of atoms and molecules in a microgravity environment. This is the first time that an experiment of this kind has been conducted in space, and the results could have major implications for the development of future quantum technologies.

For the first time in human history, scientists have discovered evidence of ice on the moon! This incredible revelation has opened up the possibility of hosting missions on the moon, and the possibilities for these missions are nearly endless. This discovery could be the start of a new era of space exploration and science.
The ice was found in dark, permanently shadowed craters near the moon’s poles, and the scientists believe that the ice could be hundreds of millions of years old.

Scientists have developed an incredible new technique using acoustic lenses to create a futuristic material that is extremely impact-resistant. This new material could be used for a variety of purposes, from aerospace and automotive applications to protective armor.
The technique involves using acoustic lenses to create tiny waves in a material that have the same healing properties as a human bone. This allows the material to absorb the shock of an impact and dissipate it, making it much more impact-resistant than traditional materials.
In recent years, the demand for green hydrogen gas has been steadily increasing as the world moves toward a more sustainable future. Now, researchers from the University of Cambridge have developed a new reaction that could revolutionize the way green hydrogen gas is produced. This reaction is highly efficient, using only a small amount of energy to produce hydrogen gas from water. In their study, the researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of the reaction with a prototype reactor, which was able to produce hydrogen gas with an energy conversion efficiency of 86%.

In a groundbreaking article published in the journal Nature, researchers from the University of California, Berkeley have unveiled the groundbreaking discovery of a new kind of quark, dubbed the “personal perspective quark.” This quark is the first of its kind to be discovered in the realm of particle physics, and has the potential to shake up the way we understand the universe.
The personal perspective quark is a subatomic particle that is believed to be responsible for the emergence of individual identities within the universe.

NASA has just announced a major breakthrough in space exploration! In 2023, they will be launching two unmanned rovers to explore the surface of Mars. These rovers will be equipped with the latest in robotic technology which will allow them to traverse the landscape and collect data that could help us better understand the red planet. This is an exciting step forward in our efforts to explore the solar system and uncover the secrets of our universe.

We are excited to announce the launch of the world’s first Virtual Observatory of the Solar Poles! This innovative space observatory will provide unprecedented access to the poles of the Sun, allowing scientists from around the world to observe and study the behavior of solar activity and its potential effects on Earth. The project is the result of a collaborative effort between the European Space Agency, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and the European Southern Observatory (ESO).
In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers have discovered the underlying molecular basis of the Terroir effect in grapevines. Terroir is a French term referring to the unique combination of environmental factors such as climate, soil, and geography that affects the flavor and quality of wine grapes. By studying the transcriptional profiles of grapevine leaves, the research team was able to uncover a set of genes that could explain the Terroir effect and explain the differences between different vineyards.
A feathery surprise has been found in New Zealand! A fossilized footprint of the extinct moa bird, which lived in the country until the 1400s, was discovered in an area of the country known as the Catlins. The footprint is estimated to be 500 years old and is the first of its kind found in the region. The discovery of this ancient footprint provides a unique insight into the behavior of the moa bird and gives us a glimpse of life in New Zealand long ago.

