Today, scientists are exploring a new approach to improving the effectiveness of vaccines and immunotherapies. This approach involves the use of machine learning to develop more precise treatments tailored to each individual patient. Through the application of machine learning, scientists are able to analyze large datasets of patient data to better understand how the immune system responds to different treatments. In doing so, they can develop more effective and targeted treatments tailored to each patient, boosting the efficacy of vaccines and immunotherapies.

SpaceX is poised to launch the world’s largest rocket, the Starship, into space. The Starship is a reusable two-stage rocket that stands at nearly 400 feet tall and can carry up to 100 tons of cargo into orbit. Its immense size and power promise to revolutionize the space exploration industry by reducing the cost of launching satellites and other payloads into space. The first test flight of the Starship is scheduled for November 2023, and SpaceX is confident that the rocket will be ready to go by then.

SpaceX, the aerospace company founded by tech entrepreneur Elon Musk, is set to launch its latest and most ambitious mission yet: a giant rocket and a pair of explosions. On November 30th, the company will launch its Falcon Heavy rocket from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, sending the rocket into space carrying a payload of 24 satellites. The launch will be the most powerful since the Saturn V rocket used by NASA during the Apollo missions, and will be the first time a private company has attempted a launch of this magnitude.

The Jurassic Period, which occurred from 199.6 to 145.5 million years ago, has long been an iconic era of Earth’s history. New research reveals that the environment during this period was not as stable as previously thought, and that the dinosaurs that roamed the planet were actually struggling to survive.
In a new paper published in the journal Nature Communications, an international team of researchers used a combination of fossil evidence and climate simulations to reconstruct the Jurassic environment.

The recent discovery of a 4,000-year-old bronze axehead in the village of Zengpiyan, in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of south-east China, has highlighted a significant development in the understanding of gender roles in the Bronze Age. The axehead, which dates from around 2,000 BCE, was inscribed with the characters for “man” and “woman,” suggesting that the society of the time had a developed sense of gender representation. This is believed to be the oldest example of gender representation in a material object ever discovered.

In today’s higher education system, having cultural capital is becoming increasingly more important for college students. According to a recent study, cultural capital—defined as the knowledge, skills, and experiences acquired through exposure to cultural activities such as music, art, literature, travel, and museums—was found to be a key factor in determining college outcomes. The study found that students with higher levels of cultural capital, such as those from higher socioeconomic backgrounds, had higher grades, greater involvement in extracurricular activities, higher graduation rates, and were more likely to receive honors and awards.

A PhD student from the University of Queensland is making waves in the bioengineering world with their latest project: a potato that can produce gamma radiation. The student, Skylar Chase, has been working on the project for the past three years. The potato is modified to contain a gene that activates the production of gamma radiation when a certain wavelength of light is shined on it. This could have major implications for medical imaging, as it could potentially replace X-rays in certain applications.
California scientists recently made a significant breakthrough in their quest for higher pay days. After years of campaigning to increase the wages of their academic and research colleagues, their efforts have finally paid off. A new salary structure has been approved by the state legislature that will raise the wages of California scientists by up to 10%. This means that after years of consistent hard work and dedication, many of these esteemed scientists will finally be receiving the pay that they deserve.

Today, scientists announced a groundbreaking development in the exploration of space - a Chinese booster rocket will be used to launch an impactor to the Moon. This is the first time a Chinese booster rocket has been used for such a mission. The Lunar Impactor, which is expected to be launched in 2023, will be deployed from the Chinese booster rocket, and will be used to study the composition of the Moon’s surface.
A group of scientists from the University of Minnesota have developed a new type of bandpass filter made of proteins. This filter is capable of selectively separating out certain frequencies of electromagnetic waves, allowing only a certain range of frequencies to pass through. This could be a major breakthrough in the development of a wide range of new technologies, from improved wireless communication to medical imaging. The filter works by using a combination of two proteins, one of which blocks certain frequencies while the other allows them through.

Recently, a team of researchers from the University of Cambridge have made a groundbreaking discovery in Africa. Through the analysis of ancient DNA, they have found evidence of widespread transmission of viruses in Africa over the last 10,000 years. This finding sheds light on a critical period in human history, providing us with insight into how viruses spread and evolve.
The study, which was published in Science, looked at the DNA of ancient human remains from across Africa.
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have discovered the promise of a new approach to treating genetic insufficiency. This approach, known as “gene addition,” involves the insertion of a healthy gene into a person’s cells to replace a defective gene. This technique has shown to be an effective treatment for diseases caused by a single gene defect, such as hemophilia, cystic fibrosis, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. It has also been used to treat certain types of cancer.
Today we had the pleasure of speaking with Professor Andrew Smith, one of the leading researchers in quantum computing, about the various approaches to quantum computing. Professor Smith discussed the promise of quantum computing and the various approaches to building a quantum computer. He described how quantum computers could potentially solve complex problems that are too difficult for classical computers to handle. He also discussed the challenges that must be overcome in order to make quantum computing a reality.

NASA recently announced the development of a revolutionary new form of communication that could revolutionize humanity’s connection to deep space. This new form of communication is known as Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC). Instead of relying on radio waves, DSOC uses laser beams to transmit data over vast distances. This will allow NASA to transmit large amounts of data back and forth with remarkable speed and accuracy. DSOC could also be used to send images and video from deep space probes, giving us a real-time glimpse into the unknown.

Today, the Hubble Space Telescope released some of the most stunning images of NGC 6814, a spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Cygnus. This galaxy, which is located approximately 55 million light-years away from Earth, consists of a bright yellow-white core surrounded by vast, intricate swirls of blue-and-red-tinged stars. The image captures the beauty of the galaxy’s star-forming regions, dust lanes and other features. Every spiral arm is densely packed with young, blue stars that are nestled in a matrix of dark, dusty lanes.

Today scientists have uncovered a new and revolutionary understanding of the universe and our cosmos. A team of researchers has discovered echoes of the universe’s first inflation, just after the Big Bang, in the cosmos we observe today. This remarkable discovery could help us better understand the origin and evolution of the universe.
The study, published in the journal Nature Physics, was led by Dr. John Webb of the University of New South Wales in Australia.
Recent research has found that adding antimicrobial silver nanoparticles to tea can reduce the risk of pathogens. This study was conducted by scientists from the University of Malaya and published in the journal Food Control.
The scientists found that adding 0.1% silver nanoparticles to tea successfully reduced the presence of E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella typhimurium. This is an important discovery, as these three pathogens are known to cause a range of foodborne illnesses.
A new study has found a unique way to reduce the number of malaria-carrying mosquitoes: using soap! Researchers from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that washing hands with soap before bedtime can significantly reduce the number of mosquitoes carrying the malaria-causing parasite. This is a welcome breakthrough, as malaria is a major global health problem, with an estimated 219 million cases and 435,000 deaths in 2017 alone.

We live in a fascinating universe, and now a team of international researchers have discovered the existence of the earliest Earth-like planets. By studying data from a nearby star, the researchers have managed to deduce the existence of three planets that have the potential to potentially support life. These planets are located in the “habitable zone” of the star, where temperatures are just right for liquid water and other forms of life to potentially thrive.

A new robotic arm is poised to reach new heights in quantum technology. Developed by researchers at the University of Bristol, this robotic arm is capable of manipulating single atoms with unprecedented precision. By placing individual atoms in specific positions and orientations, the arm will enable the construction of ultra-precise quantum devices. These devices could be used to generate extremely accurate measurements of physical phenomena, leading to a greater understanding of the quantum world and its potential applications.
Scientists have recently unraveled a decades-long mystery surrounding a common damselfly species in Central Europe. The species, known as the Variable Damselfly, has been puzzling researchers since it was first discovered over a century ago due to its unusually large range of colors and patterns.
After years of research, a team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and the Natural History Museum in London have finally cracked the case. Through lab experiments and fieldwork, they discovered that the Variable Damselfly’s wide range of body patterns and colors is due to a single gene that controls pigmentation.

It looks like we’ll have to wait a little longer to see SpaceX’s Starship launch to space. The company has announced that the launch, which was scheduled for Saturday, has been postponed due to “unexpected movements” in the rocket’s upper stage. SpaceX CEO Elon Musk stated that the movements were detected during a propellant loading sequence, and that the team is now working to identify and resolve the issue. In the meantime, the launch has been postponed until further notice.

In a recent paper published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour, an expert panel is calling for stronger standards in the courts when it comes to accepting scientific evidence. The panel, which included legal experts, psychologists, and other academics, discussed the current standards used by courts to evaluate scientific evidence and argued that they are often too lax. The experts argued that the current standards do not sufficiently protect against the potential for bias and error, leaving courts open to misuse of scientific evidence.

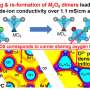
A recent breakthrough by researchers at the University of Manchester has revealed a unique mechanism behind the success of perovskite oxide materials. Perovskite oxide materials are a key component in the development of next-generation electronic devices, such as solar cells and fuel cells. The research team discovered that the materials can form a unique type of bond, which is known as a “polar bond”. This bond not only helps to boost the performance of the materials, but also helps to stabilize them.
We’ve all heard of cancer and the devastating effects it can have on individuals and families. But did you know that scientists have recently discovered a new way to inhibit the growth and spread of cancer?
A new study has found a novel way to slow the growth of cancer cells by targeting the cells’ weakness. Researchers have identified a particular gene, known as “FAM20C,” that plays an important role in the growth and development of cancer cells.