
As the world continues to warm, the delicate polar ecosystems are facing a number of challenges that threaten their biodiversity. Scientists are warning of rapid decline in species that live in the Arctic and Antarctic regions due to melting ice, rising sea levels, and changes in the food web.
Recent studies have found that the rate of species extinction in the polar regions is alarming, with species such as polar bears, walruses, and seabirds suffering population losses of up to 40%.

A new generation of high power fiber lasers have recently emerged to revolutionize our technology. They are the most efficient and powerful lasers ever created, capable of emitting up to one terawatt of power, which is the equivalent of one trillion watts. These lasers are set to revolutionize fields such as defense, medical and industrial applications. They have applications in cutting, welding and drilling, as well as in laser therapy, laser imaging and laser spectroscopy.
In the US, election season is beginning to heat up and politicians are using culture war tactics to attract voters. A recent report from the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) has revealed that in the last decade, state legislatures have introduced over 500 bills that target the teaching of specific topics in public schools. These bills are intended to shape the education of students to align with a particular ideology, often times in favor of conservative values.

A recent study has revealed an effective new method for having a greater impact on scientific research. The method, which involves a combination of two different approaches, was developed by a team of researchers and has been tested with promising results. The approach focuses on increasing the visibility of scientific work by encouraging researchers to engage with their peers and the public. This involves actively promoting the research through various media outlets, such as social media and blogs, as well as by taking part in conferences and other events.

For too long, the employment prospects of people who have been incarcerated have been linked to their past. That’s why it’s so important to look at new ways to help those with criminal records get back on their feet and into the workforce. A recent study by researchers at the University of Louisville suggests that providing access to job training and support services can significantly increase the employment prospects of people with criminal records.

A new study has found that the universe could be much longer lived than previously thought. Researchers from the University of Cambridge have discovered that the universe is in a low-energy state, which could mean that it could last for much longer than the current estimates of 10 to 20 billion years. This means that the universe is in a kind of “Goldilocks zone” which is neither too hot nor too cold to support life.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have discovered that RNA molecules can act independently from their genetic code to influence cellular processes. This finding challenges the traditional dogma that only proteins are responsible for cellular regulation, and could open up a new area of research for understanding cellular behavior. This new development, reported in the journal Nature Communications, suggests that RNA molecules can act as a “solo” agent, dynamically altering their environment as needed.

In a major breakthrough, a team of international scientists have identified a comprehensive genetic profile of the bison, revealing a single gene responsible for the bison’s iconic humped shoulders. This discovery marks an important step forward in understanding the genetic basis of this unique species and could aid in its conservation efforts. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
Read Full Article Here
source: Phys.org

The microbiome, the collection of bacteria that live inside us, is responsible for many aspects of our health. Now, a new study from the University of California, San Diego, has shown that the microbiome can even shape the health of future generations. The study, published in the journal Cell, found that bacteria from a mother’s microbiome can be passed on to her offspring, and can influence the health of her descendants in the long term.

Recent research has highlighted the importance of exon splicing in isolation from other factors. Splicing is the process by which exons, or sections of a gene, are removed from the pre-mRNA and recombined to form the mature mRNA. This process is essential for creating proteins in the body, and a recent study has found that its role in gene expression is far greater than previously thought. The study, conducted by researchers at the University of Oxford, found that exon splicing has a much higher impact on gene expression than other factors, such as transcription and translation.
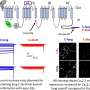
Recent advances in machine learning have enabled researchers to develop a new approach to studying the response of fungal genes to environmental changes. By combining machine learning with high-throughput genomic data, researchers have been able to identify key genes and pathways that can be used to predict how a fungal species will respond to changes in its environment. This new approach has the potential to provide insight into how fungi can interact with their environment, and may even lead to the development of new strategies for controlling fungal diseases.
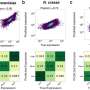
A team of scientists at the University of Toronto have developed a code that can accurately simulate the mechanics of tissues and cells in three dimensions. This breakthrough could have a huge impact on medical research, as it will allow researchers to model the behavior of cells in a more realistic and accurate way. The code, known as the Cell Mechanics Simulator, is capable of simulating cells and tissues within a three-dimensional environment, tracking the forces that are exerted on them.
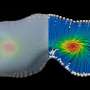
In a recent study, researchers have discovered a new species of butterfly created through crossbreeding. These butterflies are a combination of two different species and display a range of physical traits from each species, making them unique. The most remarkable discovery is that this new species is the result of multiple genes from both species being combined, rather than just one. This finding is significant as it proves that crossbreeding between different species is possible and that multiple genes are involved in the process.

In a breakthrough discovery, scientists have developed a new method to observe a catalytic reaction in real-time. This new principle, which was recently published in Science Advances, reveals the dynamics of the reaction at an atomic-level. This means that researchers can now observe how the reaction occurs, and the catalysts used to speed up the reaction. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize catalysis research, and could have far-reaching implications for the chemical industry.
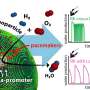
A new study published this week in Nature Communications has uncovered a new tool for pest control: the dung beetle! Researchers from the University of Valencia have identified a type of dung beetle, Idna, that is capable of destroying pests such as cockroaches, mites, and flies. This species of dung beetle has the unique ability to break down the proteins and carbohydrates found in the waste of these pests. The study found that the beetles have a strong appetite for the waste of these pests, and are highly efficient at breaking it down and eliminating them.
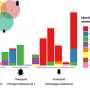
A recent breakthrough in synthetic biology has combined both artificial intelligence and synthetic biology to create a new method for engineering living cells. This new method, developed by a team of researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, promises to revolutionize the way scientists engineer cells. By automatically and intelligently designing genetic circuits, this new method can be used to create cells that are specifically tailored to perform any desired task.
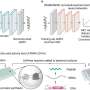
In recent years, scientists have been uncovering the secrets of chimerism, a phenomenon in which two genetically distinct organisms form a single organism. Now, researchers have discovered plastid genes associated with chimerism, which could lead to a greater understanding of this remarkable process. By examining genetic data from the plastids of plants, scientists were able to identify specific genes that are associated with the formation of chimeric organisms. This research could be beneficial to the study of evolution, as it could help us to better understand the adaptation of organisms to their environment.

A recent breakthrough in quantum physics has opened up the possibility of understanding the relationships between genes and their function. Scientists at the University of Cambridge have developed a new method which can measure the quantum properties of genes, providing new insight into how genes interact and function in living organisms. The new method uses a technique called ‘quantum tunneling’, which allows scientists to measure the energy levels of a gene, giving them a better understanding of its properties.
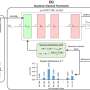
In a groundbreaking new study, physicists have discovered a phenomenon that they are calling a “boomerang-like quantum backflow.” This phenomenon occurs when particles of light—also known as photons—travel through two-dimensional materials and appear to flow in the opposite direction. This phenomenon has implications for the developing field of quantum computing, as it could allow for extremely fast and efficient data transfer. The researchers believe that this discovery could lead to a new era of quantum computing technology.

The crocodile is one of the most ancient and iconic creatures on Earth. In a new study, researchers have unveiled a complex and fascinating look into the evolutionary history of the crocodile. The team used genetic analysis of modern crocodiles to identify the major evolutionary events in the history of this remarkable animal. The findings provide new insight into the evolution and diversification of crocodiles, and could help in their conservation.

A new study has revealed something unexpected about the universe’s youngest galaxies: they’re unusually hot! Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international team of scientists has discovered that the interstellar medium of extremely young galaxies, those born in the early universe, is much hotter than expected. This could have a major impact on our understanding of the early universe and the formation of galaxies.
Read Full Article Here
In a groundbreaking experiment, scientists have used artificial intelligence (AI) to guide the reshaping of a protein’s function. This is the first time AI has been used to manipulate protein function, and the results could have far-reaching implications for the advancement of biotechnology. The team of researchers used AI to identify the key amino acids of a protein and then used a technique called protein engineering to modify the protein’s structure and function.
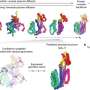
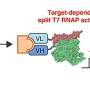
Scientists have discovered a way to use single antibodies as a tool for controlling bio-circuitry. This means that researchers can now create and control biological circuitries that can be used to better understand the human body and the environment around us.
The research team, led by Professor Shuichi Takayama from the University of Michigan, has developed a method that combines several antibodies to create a “bio-circuitry” that can be used to construct complex networks and systems.
Today, SpaceX announced their latest project—the Starship booster, a fully reusable rocket system designed to transport people and cargo to the Moon and beyond. The Starship booster system consists of two stages: the Starship, a 160-foot-tall rocket, and the Super Heavy, a booster rocket that will provide the extra power needed to launch the Starship into deep space. Together, these two stages will provide the most powerful rocket system ever built, capable of carrying 100 metric tons to low Earth orbit and beyond.

Are you a whisky enthusiast? If so, then you’ll want to check out the world’s priciest bottle of whisky, which is hitting the auction block in London. The bottle is a 1926 Macallan Fine and Rare 60 Year Old Single Malt Scotch Whisky, and it’s estimated to fetch a whopping £700,000 (nearly $900,000). The bottle is the only known one in existence, and it’s an incredibly rare find. It was distilled in 1926 and bottled in 1986, making it the oldest single malt whisky ever bottled.

