Today, scientists have developed a new technology that makes sound diffraction resistant profiles that are highly elastic. This new technology could revolutionize the way we use sound in everyday life.
Using a combination of nano-structured materials and acoustic metamaterials, the team of researchers developed a unique structure that allows sound waves to be bent around an object without diffracting. This effect is achieved by incorporating an array of nano-structures into the profile, which creates a series of waveguides that guide the sound waves.

Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in today’s world, and the demand for recycling and biobased polycarbonates is no exception. Researchers at the University of Oxford have recently developed a new method to recycle and biobased polycarbonates in a sustainable manner. By breaking down the material into its constituent parts, they are able to create new materials that can be used for a variety of applications. The process is energy efficient and does not require toxic chemicals.

A new framework developed by researchers at the University of Toronto aims to make STEM learning more effective and engaging for students. The framework, called STEM-AR, is based on the idea that students should be given access to a range of resources that are relevant to their learning needs and experiences. This includes access to interactive tools, simulations, and other web-based materials that can help them explore different topics in more depth.
The search for new methods to extract content from water-soluble compounds has been a long and difficult one. But, a new breakthrough from researchers at the Technical University of Munich has changed the game. The team has developed a new method that uses a combination of pulsed electric fields and ultrasound waves to extract the content from water-soluble compounds in a much more efficient and effective way. This new method is expected to revolutionize the extraction of water-soluble compounds and allow for new, more efficient ways to extract content from them.
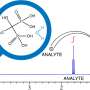
In a revolutionary discovery, scientists have developed an effective approach to creating supramolecular polymers with high stability and repeatability. This new method enables the creation of polymers with more precise and controllable structures than ever before. These polymers could be used to create materials with diverse properties, such as greater strength, improved optical properties, and more. This discovery could lead to a vast array of new applications, such as stronger and more durable materials, higher-quality optics, and more.

A new molecule developed by scientists could help tackle the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance. The molecule, called bismuth polymethylene, is a combination of two existing antimicrobial agents and is designed to target bacteria that are resistant to traditional antibiotics. It works by interfering with the bacteria’s ability to produce essential proteins and enzymes, making it much harder for them to survive. In laboratory tests, the molecule showed promise in killing some of the most resistant bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).

As antibiotic resistance continues to be a growing issue, scientists are continually looking for new and improved methods of fighting bacteria. In a breakthrough discovery, a team of scientists have developed a quick and easy method for producing antimicrobial peptides, an important type of antibiotic. Using this method, the scientists were able to produce a promising class of peptides that have been effective in killing both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in laboratory tests.

In a major breakthrough, scientists have developed an Artificial Intelligence (AI) system that can detect antibiotic resistance in bacteria in minutes. This provides a powerful new tool for clinicians to quickly identify and treat bacterial infections. With this new AI system, antibiotic resistance can be detected in as little as five minutes, compared to the days it traditionally takes with traditional methods. This could revolutionize the treatment of bacterial infections, giving physicians the ability to quickly and accurately identify the best course of treatment.
A new satellite to monitor the Arctic’s ever-changing weather patterns is on its way to Germany! The satellite, named “Arctic Weather Explorer,” is a joint venture between the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the European Space Agency (ESA). The satellite will provide unprecedented data on the Arctic’s weather and climate conditions, giving scientists and decision-makers the information they need to better understand and predict changes in the region. The satellite is expected to launch later this year, and will be equipped with advanced instruments to measure temperature, winds, and cloud cover.

In a new study, scientists have discovered that climate change is likely to lead to a reduction in beneficial microbes in the oceans. This could have a severe impact on marine ecosystems, as these microbial populations are essential to the health of the oceans. The study found that higher temperatures and increased carbon dioxide levels, both of which are expected to result from climate change, are likely to reduce the abundance of beneficial microbes in the oceans.
A recent study conducted by scientists at the University of Alberta has revealed a potential new treatment for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. The unlikely source? Coffee grounds! The researchers found that, when applied to cells, used coffee grounds contain compounds that can protect against the damage caused by these diseases. The team believes that the compounds, like caffeine and antioxidants, found in coffee grounds may be able to protect neurons from the damage caused by these diseases.

A new report has revealed that a deadly pathogen and toxic chemicals have been found in a river near a small town in France. The pathogen is a bacteria called Yersinia pestis, which is the same bacteria responsible for the plague. The toxic chemicals, which are believed to have been released from a nearby industrial plant, include mercury, lead, and cadmium. These chemicals have been linked to a number of serious health issues including cancer and neurological damage.
A new breakthrough in quantum cryptography has been made! Researchers from the University of Oxford have created a device-independent quantum cryptographic protocol that uses zero-knowledge proofs. This protocol enables the secure exchange of information between two parties without relying on the trustworthiness of their devices. This is a major step forward in quantum cryptography, as it allows for secure communication without the need for any trust in the devices being used.
Humans have long been fascinated by the complexity of their feet and the incredible range of motion it provides. Now, researchers have uncovered new insights into the evolution of the human foot, providing clues as to how it became so complex.
Using 3D scanning technology, scientists were able to create a detailed picture of the anatomy of the foot of the earliest human ancestors. They found that the foot structure of these ancestors was surprisingly complex, with a range of features that were not seen in other primates at the time.
CRISPR-Cas technology is revolutionizing the medical diagnostics industry. According to a new study published in Nature Medicine, researchers have demonstrated the efficacy and efficiency of using CRISPR-Cas to diagnose diseases. The study focused on the ability of CRISPR-Cas to detect genetic variants associated with several blood disorders. The results showed that CRISPR-Cas could accurately detect these variants with high sensitivity and specificity. In addition, the technology was able to detect variants across a range of allele frequencies, making it suitable for both rare and common diseases.
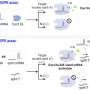
A recent study has uncovered new insights into the genetic basis of anthocyanin, a key pigment in many plants. Anthocyanin gives plants their distinctive colors, from bright purples to deep reds. The study, led by researchers at the University of Toronto, mapped a network of genes and pathways in plants that control the production of anthocyanin.
This research is important for understanding how plants respond to their environment and helps us better understand the genetic basis of plant color.
We live in a time of unprecedented understanding of our global environment, and a new study published in Nature reveals a fascinating insight into the connection between volcanoes and the tidal forces of the moon and sun. The research, conducted by an international team of scientists, shows that the interplay between volcanic activity and tidal forces affects the behavior of Earth’s interior in a manner that will provide a new global view of Io, one of Jupiter’s moons.
A new way of looking at the universe may provide insight into the mysteries of dwarf galaxies. For decades, astronomers have studied the Milky Way and its satellite galaxies, but a new study shows that when viewed using a different framework, these galaxies appear differently. By studying the dwarf galaxies in relation to the Milky Way, astronomers can gain new insight into their properties and mysteries. This could provide new understanding of how these galaxies form and evolve.

When it comes to solving crimes, science is on our side. A new study has uncovered a revolutionary way to analyze bloodstains that could have a significant impact on criminal investigations. Researchers have developed a technique called “written blood” that can be used to read bloodstain patterns left behind at crime scenes. With this technique, scientists can determine the direction of the force that caused the bloodstain, the type of weapon used, and other key details.

Today, wastewater treatment is becoming more sustainable thanks to the development of supramolecular photocatalysts that use the power of sunlight to purify water. These new photocatalysts, developed by scientists, can break down pollutants in water more efficiently than traditional wastewater treatment methods. They can also be used to break down organic pollutants such as dyes, phenols, and pharmaceuticals that are commonly found in wastewater. The photocatalysts are composed of two parts: a porous material that can absorb light and a photosensitizer that is activated by the light.

A recent breakthrough in the world of microbiology has allowed us to witness the amazing process of how bacteria use their genetic material to defend themselves against viruses. Researchers from the University of California San Francisco have discovered that bacteria can be caught in the act of using their genes to defend themselves against viral attacks. This is the first time such a process has been observed, and it is a major step forward in our understanding of how bacteria protect themselves.

Astronomers have just made a groundbreaking discovery that could revolutionize our understanding of stellar evolution: a triple star system! This is the first of its kind, with two stars orbiting each other and a third star orbiting them both from a distance. The discovery was made using the Very Large Telescope in Chile and is an exciting development in the field of astronomy. This finding could lead to a better understanding of how stars form, develop, and die.

NASA recently announced the launch of a new climate science spacecraft, PACE, which will provide an unprecedented level of detail on the health of Earth’s ocean ecosystems. PACE stands for the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem mission and it is scheduled to launch in 2023. Its goal is to significantly improve our understanding of the ocean’s role in global climate processes. This mission will provide critical data to improve our ability to predict the impacts of climate change and develop strategies to mitigate them.

In a major breakthrough, scientists have discovered a way to create switchable metastable discrete chiral materials. These materials could revolutionize the way we think about and utilize certain substances, and could lead to a wide variety of new applications. This new discovery could have far-reaching implications for the fields of science and engineering - from advanced materials to medical instruments. The research team was able to create and manipulate these new materials using a combination of optical, electrical, and magnetic forces.
A team of scientists has made a breakthrough in tackling chronic infections caused by the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is responsible for many severe illnesses, such as cystic fibrosis. The team, from the University of Sheffield in the UK, has developed a new method for studying the infection that could lead to new and more effective treatments. The method combines advanced imaging and data analysis techniques to better understand how the bacterium interacts with the human body, and how it changes as the infection progresses.