Today, a team of scientists have announced the discovery of a new enzyme, made possible by Artificial Intelligence (AI). This enzyme, created by AI, could revolutionize the production of a wide range of medicines and chemicals, from antibiotics to plastics.
This discovery is the result of years of research and development, and is made possible by a combination of machine learning and robotics. By training a neural network to identify patterns in chemical reactions, the team of scientists were able to identify a new enzyme that could dramatically improve the efficiency of certain chemical processes.

A revolutionary new method for peptide sequencing based on nanopore technology has been developed by a team of researchers at the University of Toronto. This breakthrough could revolutionize the field of proteomics, allowing for faster, more accurate and cost-effective analysis of proteins. The team developed a novel technique that involves the use of nanopores—tiny openings in a nanoscale membrane—to determine the sequence of a peptide. By using a combination of electrical and chemical signals, the researchers were able to detect the order of amino acids in a peptide, as well as other functional groups.

In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have discovered an early epigenetic gene-regulating mechanism that could be key to developing new treatments for blood cell-related diseases. The research, conducted by a team of scientists from the University of Toronto and funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, examined how epigenetic gene-regulating enzymes, called histone methyltransferases, interact with the DNA in blood cells. They found that these enzymes regulate gene expression in a way that is distinct from how it is regulated in other cells.

Scientists recently discovered a new family of proteins that are similar to human immune receptors. These proteins, called “immunoreceptors,” are found on the surface of cells and help the body recognize invading pathogens, like viruses and bacteria. The discovery of these proteins could help scientists better understand how the human immune system works and potentially lead to new treatments for immune-related diseases.
Read Full Article Here
source: Phys.org
Recent research from the University of Oxford has revealed a broad bean ion channel that is hyperactive. This hyperactive ion channel, named ABCB19, could be the key to developing more effective treatments for neurological diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. The research team used genetic engineering techniques to make a point mutation in the ABCB19 channel, which resulted in an increased activity of the channel. This increased activity could prove to be beneficial in treating neurological diseases.

Seafood is a staple of many diets around the world, but it can often be difficult to determine which types of seafood are ethically sourced. A new study published in Nature Communications has identified 11 types of seafood that can be considered more morally and ethically sound than other types. The study evaluated the sustainability of different types of seafood based on factors such as fishing practices, impacts on marine habitats, and level of bycatch.

Today, scientists have found a new way to self-assemble colloidal particles into a 3D structure. This breakthrough was made possible through bio-inspired techniques, and has the potential to revolutionize the field of nanotechnology. By using a combination of DNA-guided self-assembly and electrostatic interactions, the scientists were able to create a 3D lattice structure with precise control of the particles’ positions. This technique could be used to create new materials for use in a variety of applications, including medical diagnostics and drug delivery.

We’ve all heard about artificial intelligence (AI) and the incredible progress that has been made in recent years. But did you know that AI is now being used to help scientists understand the earliest stages of embryonic development? A team of researchers has recently developed a new AI-based system that can analyze the tempo of different stages of embryonic development. This AI system is providing new insights into the complex processes that occur during early embryonic development.
Astronomers have recently discovered a remarkable system of two hot Jupiters orbiting a red giant star, in what is thought to be a very rare occurrence. The two exoplanets, named WASP-180b and WASP-180c, are orbiting a star 500 light-years away in the constellation of Cetus.
In an exciting new discovery, astronomers have found a system of two hot Jupiters orbiting a red giant star! This is a rare occurrence, and these two exoplanets, named WASP-180b and WASP-180c, are located 500 light-years away in the constellation of Cetus.
Today, researchers have unveiled fresh insights into the landscapes of antibiotic resistance. By delving deep into a strain of staphylococcus aureus, they have unlocked new secrets about how this bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics. The findings can help doctors and scientists understand how antibiotic resistance develops and inform treatment strategies.
The research focused on a strain of S. aureus called ST398, which is an important cause of infections in both humans and animals.

Recent studies have revealed a fascinating phenomenon in the plant kingdom - phototropism. Phototropism is the process by which plants respond to light, growing towards it in order to maximize their exposure. Scientists have now discovered that this process is mediated by the presence of air channels inside the stem of the plant. These channels allow the light to reach the plant’s cells, triggering the phototropic response. This new research has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of plant growth and behavior.

In a groundbreaking discovery, physicists have found evidence of an exotic new quantum material. This material, called a quantum spin liquid, forms when electrons in a magnetic substance interact in a way that prevents them from settling into a single state. Instead, the electrons remain in a disordered state, similar to a liquid. This state is so unusual and hard to observe, that it has remained purely theoretical for decades. Now, physicists have found evidence of the quantum spin liquid in a material called chromium.

Today, scientists have made a breakthrough in the field of geochemistry. For the first time, they have succeeded in dissolving dolomite in a lab, a process that has been thought to be impossible for many years. This achievement opens up the possibility of further research into the formation and properties of dolomite, an important mineral found in sedimentary rocks. This could lead to a better understanding of the geological processes behind the formation of rocks, and the development of new technology to extract resources from them.
A new study from researchers at the University of Cambridge has revealed that the loss of tropical forests due to rubber plantations is more substantial than previously thought. The study, published in Nature Communications, found that the loss of biodiversity associated with rubber plantations is particularly pronounced in Southeast Asian countries like Vietnam and Thailand. The researchers used satellite imagery to examine the extent of forest loss and identified areas where rubber plantations are the primary cause.

Forensic anthropologists are playing an increasingly important role in uncovering the truth behind human remains. In the last decade, forensic anthropology has become an integral part of the investigation process, allowing us to delve into the mysteries of our past. Through the analysis of human skeletal remains, forensic anthropologists are able to provide invaluable information about the identity of the deceased, the cause of death, and the time and place of death.

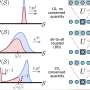
Recently, a team of researchers from the University of Cambridge has developed a universal framework for understanding how quantum information scrambles in isolated quantum systems. The framework provides a way to measure how quickly a quantum system scrambles information, as well as providing a tool for analyzing how information is encoded in a quantum system. This could have implications for how quantum computers process information, and could help to further develop the field of quantum computing.
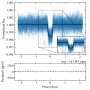
Today, scientists have announced the completion of a powerful telescope array that will allow us to observe the second highest energy cosmic rays ever recorded. This new telescope array, located in the High Andes Mountains in Peru, will give us unprecedented access to these mysterious cosmic rays. The telescope array consists of 30 telescopes that are designed to detect and measure the energy of the cosmic rays. This data will help us better understand the origin of these mysterious particles, and potentially shed light on the nature of the universe itself.

Recently, a startup called Osium AI unveiled a groundbreaking technology that could revolutionize the way materials innovation is done. Osium AI uses artificial intelligence (AI) to speed up the process of discovering new materials with desirable properties, such as increased strength or electrical conductivity. The company’s proprietary AI-driven platform is capable of rapidly scanning large datasets of materials to identify notable patterns and correlations that can be used to help engineers and scientists make informed decisions.

A Bay Area scientist has created a revolutionary new product that could help save the bees! Dr. Mary Jones has developed a bonnet that is designed to provide protection against pesticides and other environmental hazards for honey bees. This bonnet is made from a special material called “nano-fiber” that is lightweight and breathable, yet strong enough to block out most environmental threats. Dr. Jones believes that her bonnet could help to reduce honey bee deaths due to pesticide exposure and other environmental hazards.

A new discovery by astronomers has just been announced - the first ever nova in the constellation of Andromeda, located approximately 2.5 million light-years from Earth. This nova, formally known as Nova Andromedae 2023, is the brightest nova seen in the Andromeda constellation in over 70 years. This nova is particularly special because it provides a rare opportunity for astronomers to study the evolution of a nova over time.
Read Full Article Here

Today, Colossal Biosciences is making history with their groundbreaking new project. For the first time ever, they are developing a way to bring extinct species back to life. With the help of teams of knowledgeable scientists, Colossal Biosciences is using the latest technology to sequence DNA from extinct species and attempt to recreate them. This bold new venture is sure to revolutionize the field of genetics and create a new wave of possibilities.

In a world-first, two chemists have used oxygen and copper to make scissors that are cheaper and more environmentally friendly than traditional scissors. The new scissors were developed by Dr. Sarah Kowal and Dr. David Reid from the University of Victoria in Canada. The two chemists combined oxygen and copper to create a new type of scissors that are both cheaper and more sustainable. The scissors are made from a combination of copper and oxygen, which are both relatively cheap and abundant materials.

Recently, astronomers have made a remarkable discovery with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST): the spectrum of methane in the atmosphere of an exoplanet. With this observation, astronomers are able to gain an unprecedented understanding of the chemistry in an exoplanet’s atmosphere. The exoplanet is called Wasp-107b and is located about 200 light-years away from Earth. This exoplanet is the size of Jupiter, but orbits very close to its host star.

Today, researchers from the University of Chicago have announced the first experimental evidence of the existence of a new type of particle called a Hopfion in three dimensions. The recent findings could help explain the behavior of quasiparticles, which are collective excitations of a system made up of many particles. Most importantly, the findings could help scientists develop innovative new technologies based on quasiparticles. According to the study, the Hopfion can be thought of as a magnetic vortex, with the magnetic field of the particle arranged in a helical pattern around a central axis.

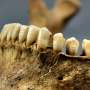
An exciting new study conducted by researchers from Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich is revealing what life was like for children in medieval Bavaria. Using the teeth of children from the time period, the team was able to gain an unprecedented view of their diets and health. The study showed that children from the 8th to 11th centuries were consuming a high-fiber cereal-based diet, and were overall pretty healthy with few signs of malnutrition.