Today, scientists have made an incredible discovery: dozens of giant radio galaxies. These huge galaxies, located more than 10 billion light years away, are some of the biggest and most energetic galaxies in the entire universe. What makes these galaxies so special is that, unlike most galaxies, they produce extremely powerful jets of radio waves that extend for millions of light years. This is an exciting discovery, as these galaxies can help us to better understand the evolution of the universe and how galaxies form and develop over time.

Today marks a major milestone in the history of European space exploration. After years of development, the first Ariane 6 rocket, Europe’s newest launch vehicle, was successfully hot-fired. This is the final test before launch day and it means that the Ariane 6 is now ready to take flight. The Ariane 6 is an important part of Europe’s effort to become more independent in the field of space exploration. It is a powerful rocket that is capable of carrying heavier payloads than its predecessor, the Ariane 5.

The effects of climate change on the environment and the organisms that inhabit it are vast and diverse. One of the most important effects is on the abundance and diversity of bacteria. A new study has found that life history traits of bacteria are strongly influenced by climate, and that greater changes in temperature are associated with greater abundance and diversity. The study, conducted by an international team of researchers, used data from the Global Ocean Sampling Expedition to analyze the life history traits of over 300,000 bacteria species.
Recently, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery in the realm of bacterial communication. It has long been known that bacteria communicate using specialized chemical languages, but a team of researchers has now been able to decode and untangle the intricate relationships between different bacteria species. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of how microbes interact and could lead to the development of new treatments and therapies to combat harmful bacteria.

The future of space exploration has been thrown into question as a result of the recent discovery of a satellite death spiral. In short, this phenomenon occurs when two satellites orbit too close to each other and their gravitational pull causes them to spiral closer and closer until they eventually collide. This has the potential to create a chain reaction of debris that could seriously damage or destroy other satellites in the vicinity, thus endangering the future of space exploration.

As scientists continue to explore the potential of jellyfish as a biomaterial for medical purposes, recent research has shown that it could be used to help treat a variety of diseases and conditions. A team of researchers from the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) has been investigating the potential of jellyfish to produce proteins that could be used to treat cancer, heart disease, and other illnesses. The team has been able to isolate proteins from jellyfish that they believe could be used to help fight cancer, repair damaged heart tissue, and even help reduce inflammation.
Biohybrid microrobots are a new class of autonomous robots that are able to move in aquatic environments. These robots are composed of a combination of biological materials and micro- or nano-plastics, creating a hybrid system that is able to move in a fluid environment. These biohybrid microrobots have the potential to revolutionize the way we explore and interact with the aquatic environment. They have been designed to swim autonomously through water, allowing them to survey and monitor the ocean, rivers, and other aquatic environments.

Astronomers have recently discovered a group of extreme stars with unique properties that link them to the early universe. The findings, published in the Astrophysical Journal, suggest that these stars have existed for billions of years and could help us learn more about the evolution of the universe.
These stars, dubbed “ultra-metal-poor” stars, have a much lower metallicity than other stars in the Milky Way. This means they contain only a tiny fraction of the metals that are commonly found in other stars.

The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has been a pioneering tool in the field of astronomy. Recently, a team of astronomers used it to make a groundbreaking discovery about the origin of gamma rays. The team was able to trace a number of gamma rays back to their origin, ultimately discovering that they originated from a supermassive black hole located in the center of a distant galaxy. This discovery is incredibly important as it helps shed light on the nature of supermassive black holes and their impact on the universe.
In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have discovered a way to make invasive species less harmful by introducing a genetic mutation that makes them poisonous. This technique, which is being termed ‘gene poisoning’, is a promising new tool for controlling invasive species that are wreaking havoc on natural ecosystems.
The study, which was published in the journal Nature, was conducted by a team of scientists at the University of California, Berkeley.

Astronomers have made a major breakthrough in our understanding of supernovae with the help of a powerful telescope located in India. The Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) at Hanle, Ladakh has been used to observe and collect data on a rare type of stellar explosion known as a Type Ia supernova. This is the first time that a telescope in India has been used for such a purpose. Type Ia supernovae occur when a white dwarf star in a binary system accretes mass from its companion star, pushing it past the Chandrasekhar limit and triggering the thermonuclear explosion.

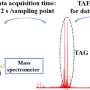
High-throughput mass spectrometry (HTMS) is a powerful tool for analyzing large datasets quickly and accurately. In a recent study, researchers have developed a novel platform that enables HTMS to be used in a variety of applications, from drug discovery to protein analysis. This new platform, called the Rapid High Throughput Mass Spectrometry (RHTMS) platform, promises to revolutionize the way scientists analyze complex data sets.
The RHTMS platform allows for the rapid analysis of large data sets, due to its ability to quickly and accurately analyze hundreds or thousands of samples in a single run.
Venice, the romantic floating city, is now offering tourists the opportunity to enjoy its beauty while supporting its economy. Starting in November 2023, visitors to Venice will be able to purchase tickets for a set price that will cover both the cost of admission to the city’s attractions as well as the cost of the environmental measures that are needed to protect the city. This is a great way for tourists to enjoy the city without putting extra strain on its fragile infrastructure.

NASA’s Ingenuity helicopter has made history by completing its fourth successful flight on Mars, becoming the first aircraft to fly on another planet. On Wednesday, the miniature four-pound chopper flew to an altitude of 16 feet and stayed aloft for 39.1 seconds, covering a distance of 98 feet from its takeoff spot. This marks the longest and highest flight in the Martian atmosphere, a feat that could have implications for future space exploration.

In a groundbreaking study, scientists have discovered successful substitutes for the traditional ivory billiard balls that are commonly used in the popular game. The study, conducted by an international team of researchers, found that a number of materials, including polymers, polystyrene, and even glass, could be used as a substitute for the ivory billiard balls. This is great news for those who are looking for a more sustainable way to enjoy the game of billiards, as the use of these substitutes eliminates the need for the harvesting of ivory.

A recent study published in the journal Photonics Research has revealed a potential breakthrough in the world of high-energy lasers. Scientists have discovered that tapered fiber, an unconventional type of optical fiber, could be a viable candidate for producing higher-energy, more efficient lasers. This discovery could revolutionize the way lasers are used in a variety of applications, from communications to aerospace.
The tapered fiber is made by manipulating the structure of the optical fiber itself, creating a waveguide that is tapered into a smaller, more focused beam.
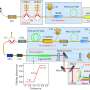
In a recent study, scientists have discovered a new way that bacteria can defend themselves against plasma. According to the findings, bacteria can use the generated electricity from an electric field in the plasma to form a protective barrier around themselves. This barrier helps to keep the bacteria from being damaged by the high temperatures of the plasma. The researchers believe this could have implications for the development of new treatments for bacterial infections.

A new study has revealed the presence of ultralight dark matter in the Milky Way. This discovery has been made possible through the constraints placed on the properties of dark matter particles. The findings of this study have implications for our understanding of the structure and evolution of galaxies.
This study has shown that the presence of ultralight dark matter is essential for the formation and evolution of galaxies. This is because dark matter is the major component of the universe and it plays a critical role in the gravitational interactions between galaxies.

Scientists have recently developed an algorithm that can identify different kinds of CRISPR systems in bacterial genomes. This breakthrough is an exciting development in the field of gene editing and has the potential to revolutionize the way we understand and manipulate the genomes of bacteria. The algorithm is called DecipherCRISPR and it can identify different types of CRISPR systems quickly and accurately. By recognizing different CRISPR systems, this algorithm could help determine the function of these systems in bacteria and allow scientists to better control and manipulate them.
Today marks an incredible milestone in the history of human genetics: the completion of the sequencing of a human gene cluster. This cluster, located on the X chromosome, contains more than 500 genes and has been a major focus of genetic research for decades. Our understanding of the function and relationship of these genes has increased significantly, and this sequencing is a major step forward in our knowledge of human genetics.

For centuries, scientists have studied the physics of oscillations and the circular motion of hydraulic systems. Now, a new study is shedding light on a fascinating new phenomenon: stillness. In this study, researchers have discovered that under certain conditions, hydraulic systems can spontaneously enter a state of stillness - without any external force or control. This finding could have major implications for the design and operation of many industrial and consumer hydraulic systems.

Recent advances in the field of nanotechnology have opened up new possibilities for the use of bio-distribution functions in polymer-DNA origami nanostructures. Polymer-DNA origami nanostructures are a type of nano-scale structures composed of short strands of DNA that are folded into complex 3D shapes. These nanostructures have been used for a wide variety of applications, including drug delivery, imaging and sensing, and tissue engineering.
Now, researchers at the University of Oxford have developed a novel method to control the bio-distribution of polymer-DNA origami nanostructures.
A new study has revealed the earliest stages of the universe’s formation, allowing scientists to uncover new details about the universe’s history. Using a combination of two independent methods, researchers have been able to pinpoint the universe’s earliest stages with unprecedented accuracy. By combining two different types of data—the cosmic microwave background and measurements of the universe’s large-scale structure—the team was able to identify fluctuations in the universe that correspond to the earliest stages of formation.

In a new study published this week, researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison have identified a group of genes in soybeans that could be used to increase soybean yield. By manipulating the expression of these genes, the researchers were able to increase the yield of soybeans by up to 17%. The researchers found that the genes are involved in the uptake of molybdate, an essential nutrient for soybean growth. The findings suggest that manipulating the expression of these genes could be used to improve soybean productivity in a sustainable way.

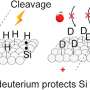
The potential of hydrogen and deuterium-based materials has long been explored in the scientific community. In a recent paper published in Nature Communications, a team of researchers revealed new insights into the properties of silicon-hydrogen-deuterium surfaces. By combining high-resolution electron microscopy and theoretical calculations, the team was able to identify new properties of these surfaces, such as the presence of an additional hydrogen bond and an unexpected mobility of the hydrogen and deuterium atoms.