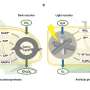
We are living in an age where renewable energy is becoming more and more accessible and efficient. A new breakthrough in solar energy technology could revolutionize the way we power our homes and businesses. Scientists have developed a new all-weather solar panel called Co8322, which is capable of mimicking natural solar energy capture. This panel is able to capture and store energy from both direct sunlight and indirect light, meaning it can generate energy even on cloudy days.

Recently, scientists have developed advanced AI techniques to visualize citrus fruits in 3D. Their research combines data from a variety of sources, including 3D imaging, machine learning, and computer vision. By combining these technologies, scientists are able to create a detailed 3D representation of citrus fruits. This can be used for a variety of applications, including providing a better understanding of citrus fruit characteristics and helping growers and retailers identify fruit species.

Recent research has found that an extra blending letter can help struggling readers in the early stages of learning to read. In a study published in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers from the University of Sussex and St. George’s University of London investigated the impact of adding a fourth letter (or letter cluster) to words that are typically composed of three letters.
The results of the study showed that adding an extra blending letter to words such as ‘cat’ or ‘map’ made them easier for children to read.

A new discovery in the field of plant biology could revolutionize the way we measure crop yields. Researchers at the University of Virginia have discovered that sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) can be used to accurately measure crop yields. SIF is an optical phenomenon in which plants absorb sunlight and re-emit some of the light energy as fluorescent radiation. The researchers found that measuring the SIF of a crop can accurately predict its yield.

Recent research has uncovered a method to hijack solar cell technology and use it to power everyday devices. By using an external nanostructure, the researchers were able to create a simple and inexpensive device that captures the sun’s energy and converts it into electrical power. This breakthrough could have a huge impact on our ability to access renewable energy. Imagine being able to power your phone or laptop with nothing more than the light of the sun!

The human gut microbiome is a complex and diverse microbial ecosystem that plays a vital role in human health. Recent advances in technology have enabled scientists to begin to understand the microbial features that are causative of health and disease. In a new study, researchers have used a novel approach to identify microbial features that are causative of health and disease in the gut microbiome. The team used metagenomic data to infer causative microbial features in the human gut microbiome.
NASA is feeling the urgency to get to Mars, and Idaho scientists are contributing to the mission. This is the first time that Idaho scientists have taken part in a mission to explore the Red Planet, and their research is expected to have a major impact on our understanding of the planet. The research team is headed by Dr. Michael Meyer, a professor at Idaho State University, and includes seven graduate and undergraduate students from across the state.

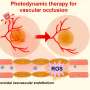
New research has revealed a possible breakthrough in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). A team of scientists have developed a nanomedicine treatment using photoactivatable nanocarriers, which could be used to deliver drugs specifically to damaged areas of the eye. By using light to activate the nanocarriers, the drugs can be released directly into the targeted area, reducing the risk of side effects. This method of treatment could revolutionize the way AMD is treated, providing a safer and more targeted approach.
NASA’s mission to explore the surface of Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, has taken a leap forward with the development of a new technology to safely land a spacecraft on the moon’s geologically active surface. The new technology, designed by a team of NASA scientists and engineers, uses a combination of radar, computer vision, and a novel propulsion system to land a spacecraft directly on the surface of Titan, which has been described as a “cold and dangerous place”.

For years, scientists have worked together to develop new technologies that help us reduce our carbon footprint and tackle climate change. A new study from researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, shows that collaboration between scientists can play a major role in driving the development of new clean energy technologies. In the study, the researchers examined the impact of scientific collaboration on the development of clean energy technology, and the results are encouraging.

Revolutionizing Disease Diagnosis: Pre-trained AI Outperforms Human Physicians
In a breakthrough study, researchers have found that AI can outperform human physicians when it comes to disease diagnosis. The research team from the University of Southern California developed a pre-trained AI system that can diagnose diseases from medical scans more accurately than doctors. The AI system was trained on hundreds of thousands of patient scans and was able to detect diseases with an accuracy of over 90%.
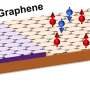
In a major breakthrough, scientists have discovered a way to combine graphene and magnetic materials to create a new low-power electronic device. The breakthrough could pave the way for the development of a new class of electronics which are more energy efficient and can be used in a variety of applications.
Graphene is a two-dimensional material made of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. It is a highly conductive material and has great potential for use in many electronic applications.
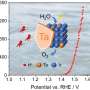
Today, scientists have discovered a new form of amorphous iron oxide, or iROX, that is doped with high-valence metals and has a stable structure. This new form of iROX has the potential to be used in numerous applications, such as electrochromic windows and electrochemical sensors. The new material is composed of a network of iron oxide nanocrystals, with high-valence metals such as cobalt, manganese, and nickel, which are added to the material as dopants.
Have you ever wondered how scientists are able to observe the behavior of individual atoms? A new breakthrough from scientists at the University of California, Berkeley has allowed them to observe the jiggling and wiggling of individual atoms in a molecule. Using an atomic force microscope, the scientists were able to detect the tiny motions of the atoms, which can reveal key information about the molecule’s stability and properties. This could have major implications for understanding a number of chemical and physical processes.

Recent advances in medical technology have paved the way for faster and safer T-cell therapy. T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that utilizes a patient’s own immune cells to fight cancer and other diseases, and is a promising field of research in the medical community. Scientists have developed a new method of T-cell therapy that is more efficient and less risky than traditional methods. This new technology, called the “T-cell Expansion Platform,” is capable of producing billions of specialized T-cells in a matter of days, rather than the weeks or months it typically takes with traditional methods.

A new report has revealed that people with disabilities are still being underpaid and underrepresented in academia, even though laws and regulations have been enacted to help protect their rights. The report, published by the National Science Foundation, shows that PhD students with disabilities are paid an average of $3,000 less than their peers without disabilities. This is in spite of the fact that they often have to work harder than their colleagues to attain the same level of success.

In a world looking for more sustainable sources of energy, Brazil is leading the pack in their production of biofuels from sugarcane. A new study from the University of Sao Paulo reveals that the country is responsible for two-thirds of the total global production of ethanol fuel from sugarcane. This is due to the many advantages the crop offers, such as its high yields, low production costs, and the fact that it is a renewable resource.

A team of researchers from the University of Toronto have recently discovered the role of a certain protein in cell differentiation. The protein, known as PIF4, is responsible for controlling the activity of genes that regulate the process of cell differentiation. Through their experiments, the research team has determined that PIF4 plays a crucial role in the differentiation of stem cells into specialized cells with distinct functions. This discovery has the potential to provide new insights into the development of stem cell therapies and other treatments that use cell differentiation.

Recent studies have revealed that solar storms can cause locally generated currents in the ocean and atmosphere that can be larger than those caused by tsunamis or earthquakes. To better understand these currents, scientists have developed an instrument to measure them in real time. This new instrument is designed to measure the size and direction of the currents created by solar storms, and to provide essential information for predicting the potential impacts of these events.

In a groundbreaking development, scientists have successfully used CRISPR-powered optothermal nanotweezers to precisely manipulate single molecules and cells for the first time. This revolutionary technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of nanomedicine, offering unprecedented control over the manipulation and delivery of drugs to targeted cells. The nanotweezers are incredibly precise and can be used to accurately manipulate single molecules and cells without damaging them. This technology could revolutionize the way we diagnose and treat diseases, allowing for unprecedented control over the delivery of drugs to specific cells.

In a monumental breakthrough, physicists at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) have simulated the creation of a new element, marking a major milestone in the field of particle physics. By smashing together the nuclei of two atoms, the researchers were able to generate an entirely new element, which has been named “Ununpentium” after its atomic number of 115. The discovery has been described as a “tremendous achievement” and could potentially pave the way for new technologies and advancements in the field of nuclear physics.

In a new study published in the journal Molecular Pharmaceutics, researchers have explored the potential of silica-based nanocarriers for oral drug delivery. Using a combination of synthetic and natural polymers, the team has developed a novel system that can be used to transport drugs directly into the gut, allowing for more effective treatment of a wide range of conditions. The nanocarriers have been designed to be resistant to digestive enzymes, allowing them to survive the stomach’s harsh environment and reach the target site.

A new platform could be the key to solving a number of problems in drug delivery. Researchers from the University of Manchester have developed a platform which allows drugs to be delivered to specific areas within the body with unprecedented accuracy. This could revolutionize the way drugs are delivered and could result in fewer side effects for patients. The platform is based on a combination of nanomaterials and an electric field.
In an exciting new breakthrough, scientists have discovered that Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used to boost the strength and temperature resistance of nickel-aluminum alloys. This could revolutionize the production of materials used in a variety of industries, from aerospace to automobiles. The team of researchers trained a deep learning algorithm on a large amount of data to identify the best combination of nickel and aluminum for a given application. The AI-optimized alloys showed an increase in strength and temperature resistance of up to 50% compared to existing alloys.

In recent years, researchers have made great strides in understanding the principles of evolution and how it affects cancer. Now, the National Cancer Institute has released 11 principles of cancer evolution, a comprehensive list of the mechanisms scientists believe can make cancer cells more resistant to treatment. These principles provide a roadmap for researchers to better understand how cancer evolves, allowing them to develop more effective treatments and improve patient care.

