
A recent study published in Nature Astronomy has revealed the discovery of an incredibly rare solar system with six planets orbiting a distant star. This system is particularly unique in that the planets are all in perfect synchrony, meaning that they all orbit the star at the same rate. Researchers believe that this phenomenon is the result of the planets having formed very close to one another, and then having been pushed further outwards over time as they interacted with each other.

A key protein responsible for the growth of new blood vessels has been identified by scientists. The protein, known as EphA2, acts as a “master switch” to control the formation of new vessels in the body. The discovery could pave the way for new treatments for diseases such as cancer and heart disease, as well as conditions like stroke and diabetes.
Scientists from the Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB) in Singapore have made a groundbreaking discovery that could have major implications for the treatment of a range of diseases.
Today, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery about the building blocks of life in the universe. By studying stars and planets, they have identified 11 chemical elements that are essential to the formation of life. These elements are carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, magnesium, calcium, iron, sodium, potassium, and hydrogen. This discovery has enabled us to better understand how stars and planets form, and how life arises in the universe. It’s an exciting step forward in our understanding of the universe and its potential for life.

A recent study has shed new light on the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the virus responsible for the global pandemic. Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco have discovered that the virus’ ability to cause disease is linked to its dynamic behavior. Rather than the virus’ physical structure, the researchers found that the virus’ ability to cause disease is due to its dynamic behavior - how it interacts with the human body.

A new study has found that bee venom could be a potential target for the treatment of certain types of cancer. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a method to sequence the entire genome of bee venom, providing new insights into the compounds and proteins that make up the venom. The results of the study could lead to the development of new treatments for cancer that target the venom rather than the tumor.

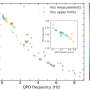
Recently, scientists have made an exciting breakthrough in understanding high-frequency X-ray binaries. A team of researchers at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, has discovered a new X-ray binary, GX 339-4, that is emitting high-frequency X-ray signals. This new discovery could provide valuable insight into understanding the mysterious phenomena of X-ray binaries, which are composed of a neutron star and a companion star that orbit around each other. GX 339-4 is the first high-frequency X-ray binary to be discovered, and its properties could offer insight into the dynamics of these binary systems.
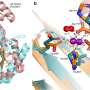
A new study from researchers at the University of Copenhagen has uncovered the mechanism of an enzyme that acts like a pair of scissors in the intestines of humans and other mammals. This enzyme, called Cdx2, is essential for the proper functioning of the intestinal microbiome, and its discovery could lead to new treatments for gastrointestinal diseases. The researchers used a combination of genetic and biochemical techniques to elucidate the molecular mechanism behind Cdx2’s function.
Scientists have recently made a breakthrough in the field of electrocatalysis, which could potentially revolutionize the way we generate energy. A team of researchers from the University of Twente in the Netherlands have developed a laser-induced hydrothermal growth approach that can be used to produce high-performance electrocatalysts. This new method could be a major step forward for renewable energy technologies such as fuel cells and electrolyzers.
The hydrothermal growth approach uses laser pulses to induce a chemical reaction that creates a highly porous material with a high surface area.

Scientists have discovered a new group of algal strains that are incredibly rich in phosphorus, a key element for life and growth. The findings were recently published in the journal Nature. According to the researchers, these new algal strains are capable of producing hundreds of times more phosphorus than traditional sources of the element, making them a potentially valuable resource for agriculture and other industries. The discovery could also help reduce the cost of fertilizers and other phosphorus-containing products.

Recent advances in technology have enabled us to apply a sophisticated approach to spectral energy synthesis, known as Bayesian spectral energy synthesis (BSES). This method has revolutionized the way we analyze and interpret observations of galaxies and other astronomical objects. BSES uses a Bayesian statistical approach to analyze the spectra of galaxies and other objects, allowing us to better understand the physical structure and evolution of these objects. By allowing us to combine the data from multiple observation frequencies, BSES can provide a more comprehensive picture of the physical processes driving the evolution of galaxies.

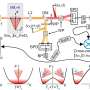
Scientists have recently developed a new method to detect ultrafast magnetic noise in magnetic memories. This breakthrough technology promises to revolutionize the way that magnetic memories are used and stored in our increasingly digital world. The new technique uses ultrafast lasers and a special type of detector to measure the magnetic noise of the memory more accurately than ever before. This new technology could lead to faster and more efficient memory storage and retrieval, which would benefit a variety of applications including computing, artificial intelligence, and data storage.
In a recent study, researchers at the University of Tokyo have discovered how chloride ions play a critical role in the stability of blue-colored perovskite semiconductors. These materials are widely used in the development of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and solar cells, which have the potential to revolutionize the way we generate energy.
This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize the way we use energy. The researchers found that chloride ions can stabilize blue-colored perovskite materials, which are used in LEDs and solar cells.
The future of quantum physics just became a little bit brighter. Scientists have developed a new quantum tool that could open the door to exploring uncharted phenomena and discovering new physics. The tool, known as a “quantum simulator,” uses a combination of lasers and magnetic fields to create a highly controlled environment, which can be used to model the behavior of quantum systems. By studying these simulated systems, scientists can gain a better understanding of the complex interactions between particles in nature.

The future of particle physics is looking brighter than ever with the potential for the world’s next big collider: the Electron-Ion Collider (EIC). Scientists believe that the EIC would be able to provide a much deeper understanding of the structure of matter and the interactions between particles, allowing us to further explore the fundamental building blocks of our universe. The EIC would collide beams of electrons and ions at extremely high energies, allowing us to explore the quarks and gluons that make up the protons and neutrons in atomic nuclei.
In a breakthrough study, researchers have developed a new nanotechnology-based platform that could potentially tackle a range of diseases. The platform, which consists of thermostable nanoparticles, has the ability to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells without damaging healthy cells. This could revolutionize the way diseases are treated, as it offers an efficient and safe way to deliver drugs directly to the site of the disease. The nanoparticles are made of polymers that have been engineered to withstand high temperatures, making them highly stable and able to maintain their structure over long periods of time.

This year is set to be a solar peak year, with the most solar energy capacity ever installed around the world! According to a new report from the International Energy Agency, global solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity is expected to grow by 18% in 2023, reaching a record level of about 690 GW. This will be the first time in history that solar PV capacity has surpassed the 600 GW mark. This is a huge milestone in the global energy transition, as solar energy is now one of the most cost-competitive sources of electricity in many countries.

We are excited to share a groundbreaking new invention that will make cleaning your toilet a breeze. Scientists have developed a slippery to bowl treatment that is designed to make it easier to keep your toilet clean and free of bacteria. The treatment works by coating the surface of the bowl with a slick coating that prevents bacteria from adhering to it. This makes it much easier to clean, as the bacteria is not able to stick and form a film.

Scientists have unveiled a new and effective vaccine for a cow parasite that has evolved to become resistant to existing treatments. The research was published in Nature Communications and could be a game-changer for farmers struggling to keep their cows healthy. The vaccine, developed by a team of researchers at The University of Nottingham, uses a novel technique to modify the parasite’s genetic code and make it vulnerable to the vaccine.

Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery that could help revolutionize the field of astrophysics. After over a decade of study, they have detected the first gamma-ray pulsar beyond the Milky Way. This is a major milestone in the field of astrophysics as it could lead to a better understanding of the universe and how it works.
The gamma-ray pulsar was detected by the Large Area Telescope (LAT) aboard the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope.

Astronomers have discovered three new planets, all orbiting a star about 380 light-years away from Earth. The planets are located in a tilted plane, unlike most planets in the solar system which orbit mostly in a flat plane. This discovery could shed light on the formation of our own solar system and the conditions necessary for life to exist.
Astronomers have just made an exciting new discovery! Three new exoplanets have been found in a previously unknown tilted plane, orbiting a distant star 380 light-years away!

Scientists have long sought to develop a method to create a novel type of crystallization, one that involves the co-crystallization of COOH (carboxylic acid) functionalized gold. This process, known as biomimetic crystallization, has the potential to revolutionize the way materials are created, providing a means to control the size and shape of nanostructures with unprecedented precision. In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have finally achieved this goal, creating a novel form of gold nanostructures using the biomimetic crystallization process.
Recently, a new study has found that girls with special needs have a much higher chance of success in the future than boys with special needs. This study, conducted by researchers from the University of Maryland, found that girls with special needs are more than twice as likely to complete high school and three times more likely to complete college than their male counterparts. This is a groundbreaking discovery, showing that girls with special needs can succeed in ways that boys with special needs cannot.

A new method of measuring biodiversity from space has been developed by scientists at the University of Maine. The breakthrough uses lidar (light detection and ranging) technology to measure the unique characteristics of forests and other ecosystems, allowing researchers to accurately assess their biodiversity from space. This innovative technique promises to revolutionize the way that scientists monitor and measure biodiversity, giving us a much better understanding of the health and dynamics of different ecosystems.
A team of physicists has discovered a new exotic atomic nucleus that could provide insight into the mysterious world of quarks. The nucleus, which has two protons and three neutrons, was created in an experiment at the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams at Michigan State University. The results of the experiment, which were published in Nature Physics, suggest that the nucleus could provide a unique window into the behavior of quarks, the fundamental particles that make up all matter in the universe.

A new study has revealed a surprising connection between piglet gut bacteria and statistical models. Researchers from the University of Tennessee found that by blending statistical models and data from piglet gut bacteria, they were able to predict the health of the piglets more accurately than either method alone. This could lead to the development of new techniques to monitor the health of piglets, as well as other animals. The findings have been published in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology.

