NASA’s Earthcare mission is an ambitious project that looks to revolutionize our understanding of how clouds and aerosols interact with Earth’s climate. Scheduled to launch in 2023, the mission will use a suite of advanced instruments to collect data on the radiation balance of the planet, aerosol particles, and clouds. With this data, Earthcare aims to provide us with a greater insight into how these elements interact to affect global climate.

For thousands of years, flowering plants have been the backbone of the world’s ecosystems. They have been providing food, shelter, and oxygen to life on Earth for millions of years, and yet, in the last few million years, their diversity has exploded. A new study has found that the flowering plants of today are more diverse than ever before, with over 300,000 species that have evolved in the last million years.

NASA’s Zhurong rover has discovered mysterious polygons beneath the Martian surface. The polygons appear to be composed of basaltic rocks, and are thought to be evidence of an ancient lava flow. Scientists believe that these polygons were formed as the lava cooled, with cracks forming along the boundaries of the polygons. The discovery of these polygons has opened up a new window into Mars’ geological history and could provide new insight into its evolution.

A new study recently published in the journal Science Advances has reexamined the phylogenetic and biogeographic history of trees. By using a combination of genetic and fossil data, researchers were able to demonstrate that trees have a more complex evolutionary history than previously assumed, and that they have adapted and diversified in order to survive in a wide range of habitats. This research has implications for conservation efforts, as it provides insight into how tree species have evolved and adapted to different environments.

A research team from Spectrum has recently made a major breakthrough in the potential for vaccine adjuvants. The team has discovered new adjuvants, which are substances added to vaccines to enhance their effectiveness. This could be a major step forward in the development of future vaccines, allowing them to better protect the public from a range of infectious diseases. The team’s research has the potential to revolutionize the way vaccines are administered.

NASA has just announced an exciting new mission to the Sun-Earth L2 (SEL2) Lagrangian point in 2023! The mission will involve the deployment of a new, advanced space station to this unique location, which is the point in space that is located between the Earth and the Sun, and is used as a stable point for spacecraft to observe the Sun.
The new space station, named the Sun-Earth L2 Observatory (SEL2O), will be equipped with instruments to observe the Sun and measure the effects of solar activity on Earth’s atmosphere.

Today, NASA announced their newest mission: the Lucy Mission, set to launch in 2023. This mission will send a spacecraft to explore a unique group of asteroids in our solar system, known as the Trojan Asteroids. This is a first-of-its-kind mission, as the spacecraft will be the first to explore asteroids that are located in Jupiter’s orbit. The Lucy Mission aims to learn more about the origin of our solar system, including the formation of planets and the delivery of organic compounds to Earth.

NASA recently announced a new mission for the Hubble Space Telescope that will extend the telescope’s scientific capabilities for the next decade. The mission, called “Hubble Science 2020-2030,” will focus on exploring the universe’s most distant galaxies, studying the evolution of the cosmos, and searching for planets beyond our solar system. The telescope’s instruments have been upgraded to enable new observations that may reveal previously unseen phenomena. With its new capabilities, Hubble will be able to make significant advances in our understanding of the universe and its evolution.

Recent research has revealed that the world is more suitable for diversified farming than previously thought. This is a major finding for the future of sustainable food production.
Diversified farming involves the planting of multiple crops in a field. By combining different crops, farmers are able to increase their yields while also being more resilient to climate change. Additionally, diversified farming helps to reduce the need for chemical inputs such as herbicides and pesticides.

In a study led by the University of Lincoln, scientists have found that pickier dogs have larger brains than their less picky counterparts. The research team discovered that dogs that are pickier about the food they eat have an enlarged hippocampus, a region of the brain associated with decision making. This suggests that pickier dogs can make more complex decisions when it comes to choosing their food, and that they are more cognitively developed than their less picky relatives.
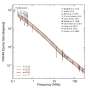
A new study by the University of California has opened up a new understanding of the turbulence in the sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona. Using high-resolution data from the Solar Dynamics Observatory, the team was able to observe anisotropic density turbulence in the corona, which had not been observed before. This new discovery could help us better understand the solar wind and how it affects Earth’s atmosphere. It could also lead to more accurate models of the corona’s dynamics and a better understanding of the sun’s magnetic field.
A new satellite is set to revolutionize transportation in Japan. The satellite, developed by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), will be used to provide remote wide-area transpiration services for the country. This unique technology is capable of providing real-time data on transportation conditions across the country.
This technology will help to improve the efficiency of transportation by providing detailed information on traffic congestion, any road construction, and other relevant factors. By utilizing this data, it will be possible to reduce traffic jams and provide more efficient routes for users.

This summer, nature and technology will be in perfect harmony! Researchers have discovered a unique phenomenon that will be occurring this summer–periodical cicadas emerging and singing in perfect synchronization with the frequency of fiber optic cables. This phenomenon is incredibly rare, and has only been observed in a handful of locations around the world. Researchers believe that this could be linked to a process known as “resonance”, where the cicadas’ chirps resonate with the frequency of the fiber optic cables.

Today, Michigan is leading the way in transforming the lives of high school students by introducing a new program: the Transitional High School. This school is designed to help students who have fallen behind in their education, and are at risk of dropping out, to stay in school, graduate, and become successful. With this program, Michigan is hoping to provide students with the skills and resources they need to transition into further education or the workplace.

NASA has just unveiled a revolutionary new way to explore the universe: packing mini satellites in a suitcase-sized container, ready to launch at a moment’s notice. The new system, called CubeSats, consists of a 12-inch-by-12-inch box containing up to 20 smaller satellites. Each CubeSat is only about the size of a shoebox, but contains all the necessary components to send back important data to scientists on Earth. This technology has the potential to revolutionize space exploration, allowing us to send miniature probes to explore new worlds faster and more efficiently than ever before.

NASA is taking another huge step forward in its mission to return to the Moon and explore the cosmos. On November 2023, the agency announced that it had successfully tested in-flight refueling capability for the Artemis lunar mission. This development marks a major milestone for the mission, as it will allow the spacecraft to travel farther and stay in space for longer periods of time. This will allow for longer and more ambitious missions to the Moon and beyond, and will open up a wealth of opportunities for exploration and scientific discovery.

Scientists have recently made a major breakthrough in the fight against plastic pollution. The team from the Institute of Polymer Science and Engineering developed an innovative new plastic that is both durable and easily degradable. This new plastic is designed to be a solution to the global plastic pollution problem, and it could revolutionize the way we handle plastic waste. The team has already tested the plastic under various conditions and found that it can degrade in a matter of weeks.

Scientists have made a major breakthrough in understanding how ionizing radiation affects our DNA. In a recent study, published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Tokyo have elucidated the mechanism of ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage.
This breakthrough could pave the way for better treatments and therapies for cancer patients, as well as a better understanding of the long-term effects of radiation exposure.
We are excited to share the news that scientists have made a major breakthrough in understanding how ionizing radiation affects our DNA!
Two-photon lithography is revolutionizing photonic packaging, offering a more precise and efficient solution than conventional methods. By harnessing the properties of light, this technology enables smaller and faster components to be produced with greater accuracy than ever before. The technology is being used to create ultra-small components for applications in the telecommunications, medical, and automotive industries. Two-photon lithography has the potential to revolutionize the way we package and deploy components, allowing us to create components with higher performance and lower costs.
Dutch astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery that could help us better understand how galaxies are formed. By studying the gas flow in the vicinity of two galaxies, the research team was able to trace a previously unknown form of gas feedback. This newly discovered feedback mechanism could significantly impact our understanding of how gas is used to form stars and galaxies.
This discovery was made possible by combining data from several telescopes, including the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile and the Hubble Space Telescope in the United States.

Today marks a major milestone in the field of particle physics: the successful testing of a prototype of the DUNE Detector Technology, a cutting-edge facility designed to detect and study neutrinos. This technology could revolutionize our understanding of the universe and the matter within it. The DUNE Detector is a large, complex system that consists of an array of particle detectors, digital electronics, and other components. This prototype was tested at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory in Illinois and the results of the test were promising.

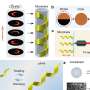
In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have developed shape-changing helical microswimmers that may revolutionize biomedical research and treatment. These micrometer-scale swimmers move through fluids in a unique wave-like pattern, allowing them to cover a much larger area than traditional microswimmers. This breakthrough could enable researchers to more easily target hard-to-reach areas of the body for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. With further development, these microswimmers could revolutionize biomedical research and treatment, providing an efficient and precise method of delivering drugs and other substances to specific locations inside the body.
A new study has revealed that the dwarf planet Eris, located in the distant Kuiper Belt, may be much squishier than expected. This discovery could provide us with valuable information about the formation and evolution of our Solar System.
Using computer models, researchers have found that Eris may be composed of a soft, icy mantle made up of frozen nitrogen and methane, surrounded by a rock and dust core. This would make Eris much more malleable than previously thought, and could explain why it has a much less elliptical orbit than other large Kuiper Belt Objects.

Today, astronomers are excited to announce a groundbreaking discovery in the far reaches of space. Using the Chandra X-ray Observatory, astronomers have discovered a cluster of pulsars, or rapidly spinning neutron stars, that are destroying a nearby interstellar cloud. This is the first time pulsars have been found to have such a dramatic effect on their environment.
The pulsars, dubbed the “Chandra Spider”, are located about 25,000 light-years away from Earth in the Milky Way.

3D printing technology has just taken a leap in precision and functionality. Researchers have developed a new 3D printing method that allows for the precise control of material properties. The method uses a custom-built, light-based 3D printing system, which can produce 3D printed materials with unprecedented levels of control and accuracy. This new method could revolutionize the production of 3D printed items, from medical implants to industrial components, allowing for the precise control of material properties.