
Recent research has revealed the potential limits of ozonated sanitizer when it comes to killing bacteria on raw vegetables. While the sanitizer was effective in removing some pathogens from the surface of the produce, it did not completely eliminate them. This means that while ozonated sanitizer may be a good option for reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses, it is not a substitute for proper washing and other food safety practices.

Today, a team of researchers from the University of California, Davis unveiled a new type of thermoacoustic loudspeaker that uses a material called MXene. This material has been hailed as a revolutionary discovery in the world of materials science, as it has the unique ability to shape-shift and reconfigure itself to suit different applications. The team’s research is poised to revolutionize the way we think about loudspeakers and acoustics, and bring a new level of flexibility to the field of acoustic engineering.

Today, a professor of science proved something that many of us have thought for years: science doesn’t have to come with a price tag. Professor Peter Cohen of the University of California proved that science can be free, and that many of the assumptions made about the cost of science are mistaken. He demonstrated that with a combination of open access journals, publicly available research materials, and a commitment to making science more accessible, anyone can access the latest scientific knowledge without paying a penny.

It’s been long known that Earth is vulnerable to intense solar storms, but now scientists have quantified the largest magnetic storms in history. In a new study, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Germany have identified the 11 biggest solar storms on record, some of which date back to the 19th century. The findings could help scientists better prepare for future storms.
The largest magnetic storm took place in 1859, during what is known as the Carrington Event.

A new study from a team of scientists has revealed two methods that can be used to isolate DNA from a photolyase enzyme. This enzyme is used in a variety of organisms to repair damage to their DNA that has been caused by exposure to ultraviolet light. The two methods, using a combination of chemical and chromatography techniques, offer a reliable way to extract and purify the photolyase enzyme for use in further research.

In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers have uncovered a trove of information about life in medieval England. By analyzing the bones of individuals from the era, they have unearthed a wealth of data that provides unprecedented insight into the lifestyle and health of these individuals. This new “bone biographies” approach has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the Middle Ages and is helping us to paint a more vivid picture of life in medieval England.

Today, scientists announced a breakthrough in plasma physics that has the potential to revolutionize the way we power our world. Researchers at the University of Chicago have discovered a way to create a new type of cold plasma from a single particle. This discovery could open the door to a whole new form of energy production that is cleaner, more efficient, and more powerful than existing methods. This new form of cold plasma could be used to generate electricity, provide heating, and even power large-scale applications such as picnics and other outdoor events.

Recent research has revealed that life may exist in molecular clouds, regions of interstellar gas and dust found in space. This exciting new finding has opened up the possibility of discovering extraterrestrial life in places once thought to be inhospitable. Scientists believe that these clouds, which are rich in complex organic molecules, may provide the necessary ingredients for life to form and flourish. In addition, the clouds provide a unique environment that could potentially be hospitable to microbial life.

A new study published in Nature Communications has revealed that an ancient form of DNA can be used to decode the potential of aqueous amino acids. By decoding the potential of these amino acids, scientists have been able to better understand how life could have started on Earth.
The study used ancient DNA sequences to simulate the conditions in which the first amino acids could have formed. This allowed the researchers to analyze the potential of the aqueous amino acids in the environment.
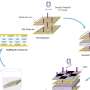
“Scientists have just developed a new photonic chip that can be used as a kind of ‘Lego door’ for semiconductors. This chip is capable of manipulating and controlling light with unprecedented precision, allowing scientists to manipulate and control the flow of light into semiconductor devices. This could drastically reduce the amount of energy needed to power these devices, making them much more efficient and allowing them to be used in a variety of applications.
In a breakthrough study, researchers have developed a new technique for high-resolution microscopy using molecular rulers. The new technique is capable of measuring distances down to the nanoscale, making it possible to study the fine details of biological structures and processes. The technique works by using fluorescent molecules as “rulers” to measure the distance between two points. The fluorescent molecules are attached to the points of interest and then illuminated with light, allowing the researchers to measure the distance between the two points.

Scientists have recently made a breakthrough in understanding how life on our planet originated. After years of research, they have discovered a way to synthesize the building blocks of life from simple sugars. This new method has enabled them to create the building blocks of proteins and nucleic acids, which are essential components of life. It is a huge step forward in our understanding of how life began on Earth and could lead to many exciting possibilities in the future.

As the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the life sciences continues to grow, many researchers are beginning to explore how this technology can be applied to study complex biological systems. AI has already been used to analyze large datasets and identify patterns in disease and drug development. Now, researchers are exploring ways to use AI to understand the complexity of biology at a deeper level, such as predicting gene expression patterns, drug interactions, and disease subtypes.

This week, the Vera Rubin Telescope was officially commissioned, and it’s sure to generate some mind-boggling discoveries! This revolutionary telescope is named after the late astronomer Vera Rubin, who was a pioneer of galaxy rotation and dark matter research. The telescope is located in Chile’s Atacama Desert, and it has a primary mirror that is 27 feet in diameter. It will be the world’s largest telescope dedicated solely to surveying the sky for visible light.

The Moon is set to make a rare appearance in the night sky this January. On January 28th, the Moon will be in its closest point to Earth since it was first discovered 11 years ago. This event, known as a supermoon, will be the closest and brightest full moon to date! It will appear up to 14% larger and 30% brighter than a typical full moon, making it a sight to behold.

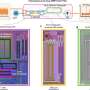
Todays’ electronics are limited by their ability to modulate light for communication systems, but a new approach to polarization-independent liquid crystal (LC) phase modulation may be the key to unlocking higher data transmission rates. Developed by a team of researchers from the Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, this approach can be used to modulate the phase of an incident light beam with a wide range of angles of incidence, making it extremely useful for communication systems.
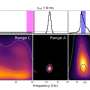
Astronomers have made a remarkable discovery that could revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos. They have detected a gravitational wave signal from the merger of two binary black holes. This is the first time a gravitational wave signal has been observed from a binary black hole merger, and it could provide important new insights into gravitational physics and the formation of black holes. The discovery could also help us unravel the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, and could even lead to the detection of primordial gravitational waves from the early Universe.
Astronomers have recently discovered a giant stream of stars and galaxies spanning across the observable universe, providing a glimpse into the history of our cosmic neighborhood. This stream is made up of over half a million galaxies, and it stretches for an impressive 3.5 billion light-years. Researchers believe this structure is the result of an ancient collision between two massive galaxies, and it could provide new insight into the formation and evolution of our universe.

We have exciting news from the world of astronomy! Astronomers have just announced the discovery of a gigantic planet orbiting a star much bigger than our sun. The planet, known as TOI-1231 b, has a mass that is 18 times that of Jupiter, making it one of the largest planets ever discovered. It orbits its host star at a distance of only 0.15 astronomical units (just 14 million kilometers) – closer than any other planet of similar mass.

A new strain of bird flu has been discovered in poultry in the United States. This strain, labeled H7N3, is a low pathogenic avian influenza (LPAI) and is similar to other strains of bird flu that have been found in the US in the past. However, what makes this strain of particular interest is that it can cause more severe symptoms in some birds, making it a potential threat to poultry production.

Have you ever wanted to capture the beauty of a sunrise in an image? Now, thanks to a new imaging technique developed by scientists, you can! Using a combination of computer vision and machine learning algorithms, researchers have developed a way to capture the beauty of a sunrise in an image. This technique allows scientists to capture the changes in light and color that occur as the sun rises, and to create a vivid, detailed image of the sunrise.

In a major breakthrough for astrophysics, a team of researchers led by Dr. Lillo and Dr. Mike Farmer has successfully validated their new model for large-scale cosmic structure. This model, called the “Farmer-Lillo model,” is a revolutionary approach to understanding the evolution of galaxies, stars, and gas in the Universe. This work could lead to new insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies and stars, as well as the nature of dark matter.

Recently, a new study conducted by a group of astronomers has revealed that contact binary asteroids are much more common than previously thought. Previous observations suggested that only 5-10% of all asteroids in the main asteroid belt were contact binaries, however this new study shows that this figure may be as high as 40%. This means that contact binary asteroids are four times more common than originally thought. The implications of this discovery are huge, as contact binary asteroids can give us insight into the formation and evolution of asteroids in the main belt.
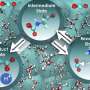
For years, scientists have been fascinated by the unique environment of hydrothermal vents. Now, researchers have discovered a new species of bacteria that lives in these extreme conditions. The team of scientists identified a new species of bacteria, named Chlorobaculum venti, that live in hydrothermal vents found in the Pacific Ocean. This bacteria is the first of its kind to be discovered in the deep-sea vents of the Pacific Ocean, and it is the first species of Chlorobaculum to be discovered in the region.

In a study published in the journal Science, researchers have found that the ocean’s large apex predators are in an exceptionally vulnerable state due to human-driven activities. The research team used an unprecedented global data set to analyze the abundance of apex predators such as sharks, tuna, and marlins, across the world’s oceans, and found that their populations have decreased drastically in the past 50 years. They conclude that the depletion of large apex predators could have a serious impact on the health of marine ecosystems.

