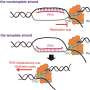
DNA Curtain technology is an exciting new development that promises to revolutionize the way scientists monitor and visualize DNA changes in real time. This technology allows scientists to observe the intricate changes that occur in DNA strands as they are altered and manipulated. By taking advantage of the unique properties of DNA, this technology can provide scientists with a powerful tool to accurately monitor changes in DNA in real time. With this technology, scientists can observe changes that can be used to better understand the complex mechanisms of genetic diseases and provide insight into potential treatments.

Recent research has revealed an extraordinary discovery that could unlock the secrets of our galaxy: the first solar system with six planets in perfect synchrony. This discovery was made by scientists at the University of the Milky Way, who used a combination of ground-based and space-based telescopes to observe the system, located approximately 5,000 light years away. Through careful analysis, the researchers were able to confirm that each of the six planets were orbiting their star in perfect harmony, a phenomenon never before seen in any other planetary system.

Astronomers have recently uncovered a massive exoplanet orbiting a star similar to our Sun, located about 320 light-years away. The exoplanet, known as NGTS-4Ab, is almost as large as Jupiter and orbits its star in only 2.6 days. This discovery provides astronomers with a unique opportunity to understand the physical properties of an exoplanet in an environment very similar to our own Solar System.
Astronomers have made a remarkable discovery - a massive exoplanet orbiting a star much like our own Sun!

In a recent study, researchers have presented a possible explanation to the ‘Hubble tension’ - the discrepancy between the two estimated values for the Hubble constant, a fundamental measure of the universe’s expansion rate. The study suggests that the tension can be explained by the presence of a new particle, known as a ‘sterile neutrino’, which interacts only through gravity and is difficult to detect. This particle could account for up to 5% of the universe’s total mass-energy density.
In a landmark study released this past Saturday, researchers discovered a surprising correlation between citations of adorable kittens and violent content in academic articles. The study, conducted by a team of researchers from institutions around the world, found that articles containing references to both kittens and violent content were cited more often and for longer periods of time than those containing references to either kittens or violent content alone.
This study has significant implications for the academic community.

Nanomaterials are becoming increasingly important to a wide variety of industries, from medical technologies to renewable energy. But with the complexity of nanomaterials, it can be difficult to keep up with the latest developments. Now, a new chatbot technology is helping bridge the gap between nanomaterials and the people working with them.
The new chatbot, called NanoExpert, is a natural language processing system designed to help scientists, engineers, and other professionals stay up-to-date on the latest developments in nanomaterials.

Botany is set to become a featured subject in school curriculums around the world starting in 2023. This exciting development is the result of a collaboration between several leading botanists and educational experts. The aim is to introduce students to the wonders of the plant kingdom and to foster a greater understanding of the importance of plants in our lives. The new curriculum will cover topics such as plant anatomy and physiology, plant genetics and evolution, and plant ecology.

Today, researchers have discovered an exciting new phenomenon that could have huge implications for our understanding of the universe: anomalous relativistic emission from an intense interaction between two energetic particles. This discovery could open up new possibilities for studying the properties of high-energy particles and their interactions with matter. The emission appears to be caused by the particle-particle collision producing a shockwave that generates a beam of light with unique properties.
Scientists have recently discovered that a strange fluid, known as “Oobleck-like” fluids, can be used to create smart materials. Oobleck-like fluids are made up of particles suspended in a liquid, and have the unique ability to transition from a liquid-like state to a solid-like state when a force is applied. This means that when pressure is applied, the particles bind together and the material will become firmer. The potential applications for this are vast, and researchers believe it could be used to create materials that could be used in everything from wearable technology to aerospace engineering.
Recent research has revealed that meteorites most likely played a significant role in supplying nitrogen to the early Earth. Scientists believe that meteorites provided Earth with a source of nitrogen, an essential element for life. This is the first time that meteorites have been associated with nitrogen delivery to Earth.
The study was conducted by a team of scientists from the University of Manchester. They studied meteorites from the early Solar System and found that they contained nitrogen-bearing minerals that would have been delivered to Earth.
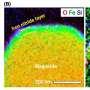
Europe is gearing up to become the first space power to construct a multi-purpose habitat on the moon. The European Space Agency (ESA) is close to finalizing a contract with the French space firm Thales Alenia Space to build the habitat as part of the agency’s plans to establish a permanent presence on the moon.
The habitat will be used as a research facility and will provide a safe environment for astronauts to live and work while carrying out experiments and exploring the moon.

Scientists have discovered a new approach to synthesizing three-dimensional covalent frameworks derived from organic linkers. This groundbreaking research could have a huge impact on materials science, as it could lead to the creation of new materials with tailored properties for a range of applications. The research team used a combination of theoretical and experimental methods to develop a new strategy for synthesizing three-dimensional covalent frameworks, which are materials that are made up of covalently-bonded organic linkers.
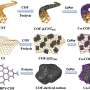
For centuries, British otters have been an integral part of the British wildlife and landscape. Now, a team of British scientists have used genetic technology to uncover the genetic history of these beloved creatures. By studying the DNA of over 500 otters, the team was able to trace the genetic history of the species back thousands of years. The results revealed a previously unknown picture of the origins, diversity, and population structure of otters in the British Isles.

Scientists have made a breakthrough discovery in understanding friction on both small and large scales. By studying the behavior of nanorods, the researchers were able to determine that friction behaves differently at different scales. On small scales, friction occurs at the atomic level, while on large scales, friction is caused by surface roughness. This finding could help to improve the design of materials and machines, as well as reduce energy consumption.
A team of scientists have made a remarkable discovery in fish immunology. After spending months studying the immune system of the Epinephelus coioides (or orange-spotted grouper) they have made several new discoveries that will help in the understanding of fish immunology. The team found that the grouper has a unique and complex immune system that is capable of activating a range of genes that allow it to respond to a variety of different pathogens.
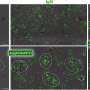
Scientists have recently discovered a new way to harvest solar energy from two-dimensional supercrystals - a revolutionary advance in solar technology! Supercrystals are an advanced type of semiconductor material that has the potential to revolutionize energy production. Supercrystals are composed of layers of two-dimensional materials that are stacked and arranged in a three-dimensional lattice. This unique structure allows for the efficient conversion of sunlight into electrical energy. By utilizing the properties of these supercrystals, scientists have been able to achieve an unprecedented level of efficiency in the solar energy harvesting process.

Climate change is having a dramatic effect on the insect populations that play an essential role in the growing of fruits and nuts in California, with some species surging and others declining. This is according to new research from the University of California, Davis, which found that the populations of some insects responsible for pollinating almonds, peaches, cherries and walnuts have increased dramatically over the past decade. The study highlights the importance of climate change mitigation and the need for further research into the effects of climate change on pollinators.
Today, the global health crisis has had a significant impact on women and girls around the world. Access to safe and affordable menstrual hygiene products has become an even greater challenge, especially in developing countries. A group of students at the University of Colorado Boulder have come up with a creative solution to this problem - re-purposing menstrual pads into planters for succulents! This initiative, known as the Menstrual Pads for Succulents Project, is a simple and cost-effective way to provide access to sanitary products.

Today, scientists have discovered that a type of prion protein called PrPC plays a major role in orchestrating the delicate balance between physics and biology. PrPC is known to exist in every living organism, and has the ability to change the shape of its molecules in order to interact with other proteins. Researchers believe that this interplay between physics and biology is essential for the functioning of cells, and PrPC is one of the key players in this process.
A new study from researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles, has revealed a new mechanism by which the sun is able to survive for billions of years. The study, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, found that the sun is able to regulate its own energy production by adjusting its internal pressure and mass. This process, known as “self-regulation,” helps to ensure that the sun’s energy production is stable and not too high or too low.

Today marks a major milestone for the Japanese experimental nuclear fusion reactor, JT-60SA. After more than five years of construction, the reactor has been completed and is now ready to begin its testing phase. JT-60SA is the world’s largest tokamak-type fusion reactor and is a joint effort between the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the European Union, and the United States. This reactor is designed to replicate the same process that takes place in the sun, using a strong magnetic field to contain and control the fusion reaction.

Astronomers have just spotted a mysterious, ghost-like galaxy that disappeared for nearly a century, only to reappear in 2021. The galaxy, known as AGC198691, was first discovered by American astronomer Harlow Shapley in 1923. Since then, it has been a mystery as to its whereabouts until now. By using the powerful James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have been able to find the galaxy and map its structure. What they found was quite remarkable - the galaxy is composed of vast amounts of dust, stars, and gas, with a mass estimated to be around 3 million times the mass of our Sun.

Today, science has made a breakthrough that will revolutionize the world of natural dyes. Researchers have discovered a way to use fermentation to create a new palette of color options that are natural, sustainable and environmentally friendly. This breakthrough could revolutionize the fashion industry and all industries that rely on dyeing natural products. This new method could lead to the production of more vibrant colors, longer lasting colors, and colors that are more consistent and reliable.

Scientists have sounded the alarm on a type of bacteria that has been linked to the mass deaths of fish, coral, and other marine organisms. The bacteria, called Vibrio coralliilyticus, has been found in coral reefs around the world and has been linked to a variety of diseases in marine life. In a joint study conducted by the University of Hawaii and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), researchers found that V.

Astronomers have been left scratching their heads after discovering a giant void in the universe that has left them puzzled about the rate of expansion. The void, which is located in the distant universe and is about 1.8 billion light years across, is the largest ever discovered and has been dubbed the “KiDS-450” void after the Kilo-Degree Survey (KiDS) which discovered it. The discovery of this void has thrown a wrench into the current understanding of the universe’s expansion rate, as it appears to be expanding faster than expected.

