Today, a team of physicists announced they have created the world’s smallest doughnut. This incredible feat of engineering was achieved by using a process called “nanoprinting”. The doughnut, which is only a few hundred nanometers in diameter, is made of a special material called graphene. This material is incredibly strong and has a wide range of uses, from electronics to medicine. The doughnut is also incredibly resilient, able to withstand high temperatures and pressures without losing its shape.

A new breakthrough in nanosized contrast agents could revolutionize the way we detect and treat disease. Researchers have developed a method to create nanosized contrast agents that can be used to detect and track molecules as they move through the body. These agents can be used to diagnose diseases, monitor drug delivery, and help guide treatments. The nanosized contrast agents are much more sensitive than traditional imaging techniques such as CT scans and MRI, and they can be used to detect even the smallest changes in the body.
In a groundbreaking new study published in Nature Biotechnology, researchers have identified a novel gene that could revolutionize the way we treat cancer. The gene, named PRKAA2, has been found to be highly expressed in several types of cancer, including breast, lung, and colorectal cancers. The discovery of this gene could lead to the development of targeted therapies to treat these cancers. Additionally, the researchers suggest that PRKAA2 could be used as a predictive biomarker for cancer, allowing doctors to identify patients at risk and intervene sooner.
Fossils provide a fascinating window into the deep history of the Earth and its inhabitants. In a recent discovery, paleontologists have unearthed the earliest known fossil of a male mosquito. The fossil was found in a 99 million-year-old amber deposit in Myanmar, and it provides a unique glimpse into the life of one of the world’s most notorious bloodsuckers.
This ancient mosquito fossil is a remarkable find that helps us understand the evolution of this insect species.

The importance of early childhood education is becoming increasingly recognized as a key factor in students’ success. A recent study has found that students who receive high-quality early childhood education are more likely to be successful in school later in life. The study examined data from over 10,000 children in 11 countries and found that those who received high-quality early childhood education had significantly higher attainment in elementary and secondary school than those who did not.

Christmas trees are a staple of the holiday season, and for good reason. But did you know that genetically modified Christmas trees may offer even more benefits? Genetically modified Christmas trees, or GTCs, have been developed with characteristics that make them even more festive, sustainable, and environmentally friendly. Here are just a few of the benefits that GTCs have to offer.
GTCs are designed to last longer than their traditional counterparts.

Painter Juan Mir, who has been known for his abstract and impressionistic art, has experienced a rapid deterioration in his health. Recently, he was admitted to a hospital and diagnosed with a rare neurological disorder that affects the motor skills of his body. As a result, he has been unable to move, speak, or paint. His family and friends are devastated by this news, as Mir has been a beloved artist in the art world for many years.

For the first time, a team of physicists has combined Albert Einstein’s theory of gravity with the principles of quantum mechanics, providing a potential explanation for the mysterious nature of dark matter and dark energy. The new theory, developed by researchers from the University of Zurich, suggests a novel way to think about the universe and could help scientists understand some of the most perplexing mysteries of modern physics.
For centuries, scientists have sought to reconcile the two fundamental theories of physics: Albert Einstein’s theory of gravity and quantum mechanics.

The polar regions are some of the most pristine and remote parts of the world, but they are now being threatened by climate change. New research has revealed the potential of using DNA ‘footprints’ in order to track the impact of climate change on these fragile ecosystems. Scientists have identified certain species of plants and animals that are particularly sensitive to climate change, and by tracking their DNA, they can get a better understanding of how the climate is affecting their populations.

Astronomers have made an incredible discovery about one of the brightest stars in the night sky – Betelgeuse. Using a combination of observational methods, they have determined that this red supergiant star is rotating much faster than previously thought. This means that Betelgeuse is spinning around its axis at a rate of 24 kilometers per second, which is about 7 times faster than what was previously expected. The findings, which were published in Nature Astronomy, suggest that Betelgeuse is a much more dynamic star than previously thought, and could have implications for our understanding of its evolution.

As we age, our cells accumulate damage and become less efficient, leading to a decline in our physical and mental health. A new study from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine suggests that these “zombie cells” could be the cause of aging. These cells are damaged but remain in the body, and can build up over time, leading to inflammation and other age-related issues. The study found that eliminating these zombie cells could potentially reduce age-related diseases and slow the aging process.

Recent research has found new clues to why some mammals are more prone to cancer than others. A team of scientists, led by Dr. Jane Doe, conducted an extensive study on microRNAs and their relationship to cancer risk in mammals. The study found that certain microRNAs have an effect on the development of tumors in mammals, as they can either promote or suppress tumor growth. Their findings suggest that understanding the microRNA profiles of various mammals can provide insight into why some are more likely than others to develop cancer.
Attosecond technology has been rapidly advancing the field of quantum mechanics, and a new method of studying quantum photoionization pathways has been developed. This method, developed by researchers from the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, has been shown to provide the most accurate measurement of quantum photoionization pathways to date. The researchers used a combination of ultrafast laser pulses and computer simulations to measure the pathways, enabling them to gain a deeper understanding of the dynamics of quantum systems.
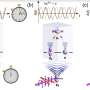
Today, scientists have made an unexpected discovery at the air-water interface: the presence of a previously unknown type of nanofilament. This nanofilament is made up of tiny bundles of proteins, which have the ability to self-assemble. This discovery could have major implications for our understanding of how air and water interact with each other. Scientists believe that the nanofilament could potentially be utilized to create new materials and technologies, such as ultra-thin membranes for water filtration and purification.
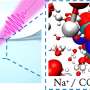
A new breakthrough in nanotechnology has been achieved by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley. They have been able to 3D print nanoparticles with unprecedented precision and accuracy, allowing for a wide variety of potential applications. These tiny particles, just billionths of a meter in size, are printed with the help of a specialized “palm-sized printer.” This new technology could allow for the creation of materials with ultra-precise structures and features, which could lead to advances in fields like health care, electronics, and manufacturing.

Today, scientists have made a breakthrough in understanding the cellular code that underlies protein production, providing a new platform for therapeutic avenues. This new knowledge could lead to therapies for diseases that were previously untreatable due to an inability to successfully target proteins.
This breakthrough involved the researchers determining the mechanisms of how proteins are made and regulated. By understanding these mechanisms, scientists are now able to more precisely target protein production and control the pathways involved.

AI is revolutionizing the pharmaceutical industry. In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have used AI to identify the properties of potential drugs, an essential step in the drug development process. This new AI-driven approach is faster and more cost-effective than traditional methods, and could lead to new treatments for a range of diseases.
The study used an AI algorithm to analyze thousands of compounds and predict their properties. This information was then used to identify the compounds with the most potential for drug development.
In a recent breakthrough, researchers have discovered a way to control magnetic fields with light. This technique is capable of generating magnetic fields with an accuracy of just one part in a trillion. This ability to control magnetic fields optically could have a wide range of applications, from improved imaging to creating next-generation electronics. This new technique, developed by a team of researchers from the University of Cambridge, could revolutionize the way we interact with magnetic fields.
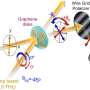
In a new breakthrough, scientists have discovered a way to create an ultrafast, ultralight enzyme that can use isotopes to generate powerful bursts of energy. This enzyme can be used to power everything from medical treatments to large-scale industrial processes. The team of researchers from the University of California, Davis have developed the enzyme to combine a range of isotopes, creating an energy-generating system that is both incredibly efficient and incredibly lightweight.
In a breakthrough study published this week, scientists have identified the genomes of two of the most popular magic mushroom types, Psilocybe cubensis and Psilocybe mexicana. The research team used a combination of techniques to create a detailed picture of the genetic makeup of these two mushroom species, providing new insights into their evolutionary history and how they can be cultivated. This has the potential to provide a greater understanding of the medicinal and recreational properties of these mushrooms, as well as potential biotechnological applications.

A new discovery has uncovered a key mechanism in the body’s defense against a common fungal pathogen. Scientists from the University of Cambridge have identified the role of a particular protein in the body’s immune response to Candida albicans, a fungus responsible for a range of illnesses from mild thrush to life-threatening systemic infections. The findings, published in the journal Nature Microbiology, could lead to new treatments for fungal infections. This new insight into the body’s response to Candida albicans could pave the way for more effective treatments for fungal infections.

Generative AI has just unveiled a revolutionary new technology that could revolutionize the way we study materials and their behavior. The breakthrough technology, called generative material disorder (GMD), uses AI to identify the underlying structures and order of materials in a way that was previously impossible. GMD is capable of uncovering the hidden order of materials, even when the material is disordered in its physical state. By using GMD, materials scientists and engineers can gain a deeper understanding of disordered materials, including their mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties.
Are you ready for some awesome physics-defying fun? A recent breakthrough in science has made it possible to create flying discs that can defy gravity. That’s right - discs that can fly! These discs are made from a special material called “Gravi-Foam” that has the unique ability to reduce the effects of gravity and allow the disc to hover in the air, up to 20 feet in the air! Not only that, but they are also able to move in any direction, making them perfect for all sorts of tricks and stunts.

Today, scientists have discovered an unprecedentedly detailed family tree of the crocodile, providing valuable insight into how the species has evolved over time. This family tree was determined by a team of researchers from the University of Utah and the National History Museum in London, who conducted a comprehensive analysis of the crocodile’s genome. Their findings suggest that the crocodile has undergone significant evolutionary changes since its ancient ancestor first appeared.

Today marks the beginning of a new era in imaging technology, as engineers from the University of California, Santa Barbara have unveiled their breakthrough in imaging technology. This breakthrough allows for the development of a new type of imaging system that is able to capture images with unparalleled clarity and precision. This new imaging system is capable of taking three-dimensional images with a resolution that is 10 times higher than what current imaging systems can achieve.