
Recent research has found that ice cores from Antarctica may be a potential source of new antimicrobial compounds. In a study published in Frontiers in Microbiology, researchers from the University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) collected ice cores from Antarctica and analyzed the microbial communities they contained. The researchers found that the communities contained a range of compounds with potential antimicrobial activity, including compounds with activity against multi-drug resistant bacterial strains.

“Scientists have made a breakthrough in the search for extraterrestrial life, discovering a previously unexplored region of the universe which could contain alien life. The region, called the “Galactic Habitable Zone”, is located at the outer edge of the Milky Way and is believed to have conditions that are suitable for the development of life. Scientists believe that this region could contain planets that are capable of hosting aliens, and that further exploration is needed to determine if this is the case.

In a groundbreaking study published today in the journal Nature, researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have revealed a new approach to nuclear fragmentation induced by gamma rays. Using the Spagins method, the researchers were able to study the effects of gamma rays on the behavior of a nucleus, and the resulting fragmentation of the nucleus. This research could have far-reaching implications for our understanding of the behavior of matter at the nuclear level.
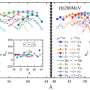
In a breakthrough discovery, researchers at the University of Bundengan have uncovered a new type of photovoltaic material that could revolutionize the way we create and use solar energy. The new material is based on a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite formula and has the potential to create cheaper, more efficient solar cells, making solar energy more accessible and affordable to people around the world. The material’s unique properties also make it more stable and durable than traditional photovoltaic materials, meaning it can stand up to the elements and work for longer periods of time.

It’s official: space exploration is a good idea. According to a new study published in the journal Nature, space exploration has been found to be beneficial for humanity as a whole. The study found that space exploration has a positive effect on our economy, our culture, and our environment. It has also been found to help boost our technological advances, increase our scientific knowledge, and even provide us with new sources of energy.

NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has just released a breathtaking image of a distant cluster of galaxies, located in the constellation of Serpens. Spanning an area of approximately one million light-years, this cluster contains some of the earliest known galaxies in the Universe, making it a remarkable sight for astronomers and enthusiasts alike. In the image, we can see the galaxies’ bright cores, as well as the faint tendrils of gas and dust that stretch across the cosmos.

Today marks a milestone for scientists, as they have discovered a way for bacteria to hijack and use advanced mechanisms. This process, known as ‘bacterial infamy’, has been uncovered by a team of researchers who have found that certain bacteria can gain access to sophisticated biomolecular machinery in order to gain an evolutionary advantage. This process is achieved by introducing a gene into the bacterial genome, allowing them to hijack the machinery for their own benefit.
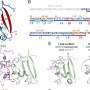
A new study published in the journal Nature Communications has revealed an exciting new way to explore the depths of asteroid crater lakes. Using seismic imaging, researchers have been able to discover the characteristics and limitations of these unique environments. The research team found that the crater lakes are formed by large impacts, resulting in a bowl-shaped depression. These lakes are often filled with water, but the amount of water they contain is limited due to the impact’s size.

Didgeridoo playing is an ancient Aboriginal tradition, but it turns out that it can also be used as a tool to teach physics! A recent study published in the journal Physics Education found that playing the didgeridoo can help students understand the physics behind sound waves.
The study was conducted by researchers from the University of Huelva in Spain, and involved a group of undergraduate physics students. The students were taught about sound waves and then asked to play a didgeridoo.

Recent advances in additive heterostructures have incredible potential for biomedical applications. By combining different materials at the nanoscale, scientists can create structures that are stronger, more efficient, and more versatile than ever before. These complex, layered architectures can be tailored to specific applications, such as drug delivery, biosensing, and tissue engineering. Furthermore, they are biocompatible and biodegradable, making them ideal for biomedical applications. With these exciting advancements, the possibilities for biomedical applications are endless.
The days of dealing with pesky water stains and other residues from drying dishes may be a thing of the past thanks to a new technology developed by researchers at the University of Tokyo. In a breakthrough study published in the Nature Communications journal, the team has demonstrated advances in the use of a built-in electric field assisted photocatalytic dry process. This method uses a photocatalyst that reacts to ultraviolet rays emitted from LEDs to break down water droplets into smaller molecules, thereby avoiding the formation of water stains.
Exploring the Possibility of Habitability on Europa: NASA's Europa Clipper Mission to Jupiter's Moon
Exciting news out of NASA: the agency has confirmed its plans to launch the Europa Clipper mission to Jupiter’s moon Europa in 2023. Europa is thought to be one of the most likely places in our solar system to host life, and the Europa Clipper mission will seek to provide more information about the moon’s habitability. The mission will take a close look at Europa, studying its icy surface and the ocean that lies beneath it in unprecedented detail.

The silver bullet theory, which suggests that one single factor, such as the use of the herbicide glyphosate, is responsible for the decline of biodiversity, has been debunked by a new study. The research, conducted by an international team of scientists, concluded that the silver bullet theory is too simple to explain the loss of biodiversity around the world.
The study, published in Nature Communications, found that the decline of biodiversity is a result of multiple factors, including land-use change, climate change, and pollution.

Today scientists from the University of Washington made a groundbreaking discovery that could revolutionize our understanding of electricity. After years of researching electric eels, they have discovered that the source of their electricity is actually a genetic adaptation! This is the first time that scientists have been able to pinpoint the source of electricity in an animal, and it could lead to a variety of new developments in the field of electricity.

Have you ever wondered what a black hole’s breakfast might look like? A team of scientists recently shed some light on this question by discovering an “afterglow” that was left behind after a black hole feasted on a star. The afterglow, a bright X-ray emission from the black hole, was the first of its kind to be observed and provides insight into the mysterious nature of black holes. The findings were published in Nature Astronomy and could lead to a better understanding of how black holes interact with their surrounding environment.
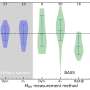
A new nanomaterial has been developed that could revolutionize the treatment of bacterial infections. This nanomaterial has the ability to kill both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, making it a potential game-changer for antibiotic-resistant infections. The nanomaterial is composed of two different polymers, both of them small enough to slip through the cell walls of bacteria and disrupt their internal structures. This means that it is effective against even the most resistant bacterial strains, offering a new avenue of treatment for infections that are resistant to traditional antibiotics.
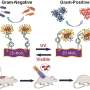
In a recent study, researchers have uncovered a new mechanism by which a pathogenic bacterium can use molecular mimicry to compromise the body’s immune system. By producing molecules that mimic those of the body’s cells, the bacterium is able to fool the immune system into thinking that it is a harmless part of the body, allowing the bacterium to spread and cause infection. This new mechanism could be used to develop more effective treatments to combat bacterial infections.
A recent breakthrough in the study of neutron stars has shed new light on the mysterious rotation anomalies exhibited by the ultra-dense stellar objects. Researchers have discovered that these anomalies can be explained by two distinct physical phenomena that arise from the extreme conditions in the neutron star’s interior. The findings provide new insights into the physics of neutron stars and could lead to a better understanding of the evolution of these objects over time.

As the summer months approach, it’s important to be aware of the potential spread of diseases due to mosquitoes. Japanese encephalitis is one of the most serious diseases that can be spread by mosquitoes and is especially common in parts of Asia. It is caused by a virus, and the symptoms can range from mild headaches and fevers to seizures, paralysis, coma, and in extreme cases, death. It is important to take precautions to prevent the spread of Japanese encephalitis, such as wearing protective clothing and using insect repellent.

NASA has recently announced a new initiative that will limit their focus in the field of physics research. The agency will now be focusing on three main areas of research in order to “refocus and reinvigorate” their work in the field. These areas are: gravitational wave detectors, dark matter, and exoplanet research. By narrowing their research focus, NASA hopes to make more significant advances in these three key areas. This shift will enable NASA to make more efficient use of their resources and personnel, as well as make sure that the research they do is relevant and up-to-date.

NASA has announced they are set to launch a groundbreaking interstellar probe in 2023. The historic mission will explore a nearby stellar system and gather data on the possibility of extraterrestrial life. This unprecedented mission will be the first of its kind and will be a major advancement in space exploration. The probe will be launched with the help of a powerful rocket and will take approximately a year to reach its destination.

Today, Physicist X has made a groundbreaking discovery that X-Rays shouldn’t have any effect on cold plasmas. This could have a huge impact on the field of plasma physics and our understanding of how charged particles react with light. X-Rays are usually absorbed or scattered by plasmas at elevated temperatures, but Physicist X has shown that this doesn’t happen when the plasma is cold. This is due to the fact that when the plasma is cold, the effect of the electric field on the charged particles is decreased, leaving the X-Rays to pass through the plasma unaltered.

Recent research has revealed that polyoxometalates (POMs) may be an effective drug for treating cancer cells. POMs are metal-oxide clusters that are composed of metal ions and oxygen atoms. They have been found to be effective in killing cancer cells without damaging healthy cells. This new discovery could revolutionize the way cancer is treated and lead to more successful treatments. POMs have the potential to become a crucial tool for treating cancer in the near future.
In a recent study, researchers from Takah University discovered a curious relationship between humans, rats, and dogs. The study, conducted in the Fiordland of New Zealand, observed that when humans, rats, and dogs interact, they all seem to benefit. The researchers found that the presence of humans reduced the stress levels in both rats and dogs, while the presence of rats or dogs tended to reduce the stress levels of the humans.
Today, a major breakthrough is revolutionizing biorefineries and advancing us towards a more sustainable third-generation biofuel industry. Researchers have developed a new process that utilizes enzymes to convert biomass to sugar-based compounds, which can then be used to produce fuels. This breakthrough has the potential to drastically reduce the environmental impact of traditional petrochemical-based fuels and could lead to a more sustainable future. With this new process, the cost of producing biofuels could be reduced significantly, making it more accessible and affordable for consumers.

