We all know the catastrophic effects of mass extinctions, but what we didn’t know until now is that the Late Devonian period (359 million to 416 million years ago) was even more catastrophic than previously thought. A new study by an international team of researchers has revealed that the Late Devonian mass extinction was far more severe than previously thought, with significant and lasting effects on marine life. The research also indicates that this extinction was caused by a combination of environmental changes, such as ocean acidification, and a series of major volcanic eruptions.

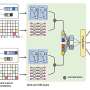
Introducing the new SUFEX-click modular platform: a revolutionary new way to conduct chemical reactions with ease! This platform utilizes click chemistry, a powerful tool that allows chemists to quickly and easily link together small molecules into larger, more complex structures. The SUFEX-click platform allows for reactions to occur with greater precision and efficiency than ever before, and offers both cost and time savings for those conducting chemical reactions. This revolutionary platform is sure to revolutionize the way chemists conduct research and experiments.
Iran today is making history as they have successfully launched a capsule containing animals into orbit around Earth. This is the first time an animal has been sent into space by an Iranian spacecraft. The animals, including a mouse, two turtles, and worms, were carefully chosen to be able to withstand the conditions of space travel. The capsule is expected to remain in orbit for several months and will transmit valuable data about the effects of space travel on the animals.

NASA is set to launch a spacecraft next year that will explore the asteroid Psyche, located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Last week, new images were released of Psyche by the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft, which has been orbiting the asteroid for the past two months. This is the closest we have ever been to Psyche, and the new images are providing valuable data about the asteroid’s composition and structure.

NASA has recently announced that its spacecraft, Osiris-Rex, will be undergoing a parachute deployment sequence in order to complete its mission to land on the asteroid Bennu. This sequence is expected to take place in the early hours of December 2023, and will be the first of its kind for a mission of this type. The parachute deployment sequence involves releasing two drogue parachutes to slow the spacecraft’s descent, followed by the deployment of the main chute and finally the separation of the spacecraft from the chute.

An exciting new breakthrough in technology has been made by researchers from the University of Sussex – they have developed the world’s first ‘supermirror’ that can reflect light in the mid-infrared range. This new development could have a major impact on things like medical imaging, environmental sensing, and spectroscopy.
The newly developed supermirror technology uses a unique combination of materials to create a highly reflective surface which is able to reflect light in the mid-infrared range.

We are living in an exciting time for scientific research. Recently, a research team has developed a new type of microscope that can directly measure the quantum state of individual electrons. This microscope is a significant breakthrough in the field of quantum technology, as it opens up the possibility of directly observing and manipulating the behavior of electrons. This microscope could be used to create quantum computers and develop new materials with novel properties.

A group of scientists have developed a new technology that promises to revolutionize the way lithium-ion batteries are used. The technology is called “functional micro-arrays” and it promises to make lithium-ion batteries more efficient and reliable. Functional micro-arrays are tiny, interconnected structures that are made up of billions of nanowires. These nanowires are able to transfer energy quickly and efficiently, meaning that lithium-ion batteries can be recharged at a much faster rate.
Scientists have discovered a new hormone that could revolutionize how we grow plants. By boosting the production of a particular growth hormone, researchers have been able to accelerate the growth of plants by up to 75%. This is an exciting breakthrough that could have a major impact on the agricultural industry. The hormone, which has been dubbed “Growth Hormone-3”, is believed to be responsible for the rapid growth of plants. By increasing the production of this hormone, scientists are able to stimulate growth at a much faster rate than ever before.
A new study has found that non-alcoholic beers contain higher levels of foodborne pathogens than traditional beers. The study, conducted by researchers from the University of Copenhagen, tested different types of beers for the presence of bacteria, yeast, and other contaminants. The results showed that non-alcoholic beers had significantly higher amounts of potentially harmful bacteria and yeasts than regular beers. The researchers concluded that the higher levels of foodborne pathogens in non-alcoholic beers could pose a risk to consumer health.
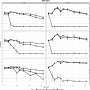
A new study conducted by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley has revealed that the environment can play a major role in the preparedness of bacterial communities against infectious diseases. By understanding how the environment shapes the composition of bacterial communities and affects their disease-fighting capabilities, the team hopes to gain insight into how to better protect human health.
The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, suggest that environmental conditions, such as temperature, pH, and nutrient availability, can significantly alter the composition of bacterial communities.
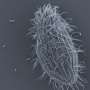
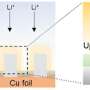
Today, scientists have discovered a new way to unlock the potential of neodymium compounds. By exploiting their magnetic properties, researchers have used neodymium compounds to create a variety of unique devices and applications.
The magnetic properties of neodymium compounds can be used to create materials with a wide range of properties. For example, they can be used to create materials that are electrically conductive, magnetic, or even piezoelectric. These materials can be used in a variety of applications, from sensors to energy storage devices.
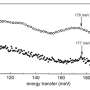
Do you ever wonder about the mathematical evolution of certain animals? New research suggests that chickens, fish and frogs could be linked in terms of their mathematical evolution. An international team of researchers has found that all of these animals have developed similar mathematical behavior in attempts to adapt to their environments. The researchers discovered that chickens, fish and frogs all use a mathematical strategy to find food in their environment and to avoid predators.
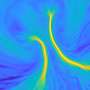
Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in the world of science. They have discovered a new way to control magnetism in colloids, with unprecedented precision and accuracy. This discovery has the potential to revolutionize many fields, from materials science to biology. With this new method, scientists can now finely tune the properties of a colloid, such as its magnetism, size, shape, and surface properties. This could lead to the development of new materials and technologies that could revolutionize the way we live, work, and play.

Astronomers have recently discovered a new stellar cluster in the Southern Hemisphere, known as the “Southern Beehive.” Located in the constellation Carina, the cluster contains a large number of stars estimated to be less than 300 million years old. This makes it one of the youngest stellar clusters in the Milky Way.
The Southern Beehive is an exciting new discovery for astronomers, as it is the first cluster of its kind to be found in the Southern Hemisphere.

Have you ever been walking around with a full cup of coffee, only to have it suddenly jump out of your hands and onto the floor? It may seem like a random occurrence, but a new study has found that the phenomenon of coffee splashing out of a cup is actually due to static electricity! This intense static charge builds up between the cup and the liquid, leading to a powerful repulsive force that can cause the liquid to suddenly leap out of the cup.

Black holes have long been a source of fascination and mystery for scientists, but now researchers have discovered a new population of them that could provide some insight into the early universe. A team of astronomers has identified a group of black holes from the earliest stages of the universe that are much larger than those previously seen. The findings could help us better understand the formation and evolution of the universe, as well as the nature of dark matter.

In a breakthrough discovery, scientists have developed a new bioinformatics tool called ‘SexyMarkers’ that is revolutionizing the way we look at gene expression. This tool helps researchers analyze and compare gene expression levels across different species in order to better understand the evolution of gene expression. It is based on a novel algorithm that takes into account the individual gene expression data of each species in order to accurately compare gene expression levels between species.

Are you ready for a stunning new discovery in the field of physics? A team of international researchers have recently uncovered a strange and unusual behavior in certain stars, which could be classified as ‘super stars’. The team believes this behavior could be the result of a number of complex physical processes, and they are determined to uncover the mystery. The team’s findings could revolutionize our understanding of the universe, and even help us unlock the secrets of dark matter.
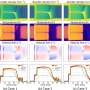
Recently, scientists have discovered the genes that make humans more cognitively advanced than other primates. In a study published in the journal Nature, researchers at the University of Edinburgh and the Wellcome Sanger Institute have identified several genes that are responsible for the cognitive differences between humans and our primate relatives. The researchers believe that these genes are likely to have been selected for during human evolution, allowing us to develop advanced cognitive skills such as language, problem-solving, and abstract thought.

Scientists have made a major breakthrough in the field of synthetic biology, achieving the successful synthesis of artificial cells. These cells, created from scratch, are the first of their kind and could potentially pave the way for the development of new medicines, materials, and other applications. The results of this groundbreaking research are published in the journal Nature Chemistry.
A team of researchers from the University of Cambridge has made a major breakthrough in the field of synthetic biology - the successful synthesis of artificial cells.
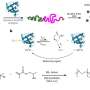
Today, scientists have discovered a revolutionary way to accurately edit human genes using an enzyme and CRISPR technologies. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize gene editing, making it easier, faster, and more accurate than ever before. The enzyme, called Cas12, works by binding to specific DNA sequences, allowing scientists to precisely edit the gene associated with a particular disease or trait. This could lead to treatments for conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and genetic disorders.
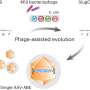
Atomically precise two-dimensional (2D) materials are like Lego blocks—they can be used to construct complex structures that could revolutionize the way we think about building materials. A team of researchers from the University of Cambridge have now developed a way to precisely control the size and shape of 2D materials, paving the way for the creation of advanced materials with unique properties. The team used a combination of scanning tunneling microscopy and atomic force microscopy to precisely control the size and shape of 2D materials, enabling them to create complex structures that can be used for a variety of applications.
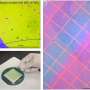
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have developed a new photocatalyst that could revolutionize mercury (Hg) removal from wastewater. This photocatalyst has an unprecedented conversion efficiency of up to 99.7%, and could potentially be used in commercial wastewater treatment plants. The new photocatalyst was developed with a combination of two different metals, gold and palladium, along with a unique nanostructure that increases its surface area for effective absorption of light. This combination of metals and nanostructure enables the photocatalyst to create reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are able to break down Hg in wastewater into harmless by-products.
A new deep learning framework has been developed that can accurately predict drug-drug interactions and drug-target interactions. This framework, named DeepDDI, was developed by researchers at the University of Minnesota and aims to provide powerful insights into drug-drug and drug-target interactions. DeepDDI is based on a deep learning network architecture that combines the prediction power of Convolutional Neural Networks and Recurrent Neural Networks. This deep learning network is used to integrate information from a wide variety of sources, including drug-drug interaction databases, biological databases, and drug-target interaction databases.