In a groundbreaking study, scientists have developed a new type of nanoparticle that is propelled by a miniature propeller. The propeller-shaped nanoparticles, which measure around 200 nanometers in diameter, can move quickly in water and are capable of carrying drugs or other substances. The scientists suggest that these particles could be used to deliver drugs directly to cancerous tumors or other specific parts of the body. The study, which was published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, could revolutionize the field of drug delivery.

A new breakthrough in rice phenotyping was announced recently by a team of researchers, led by Dr. Li Jiang from the National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement in China. The team developed a novel deep panicle phenotyping system that is capable of accurately and quickly detecting multiple growth traits in rice, such as leaf angle, panicle length, panicle weight, and grain number. This advanced system could help researchers and breeders to quickly identify and select desirable rice varieties.
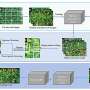
Today we have exciting news from the world of science! Researchers have developed a new machine that can optimize production of volatile fatty acids (VFAs). This machine is set to revolutionize the food and beverage industry, as VFAs are important ingredients in many products such as cheese and yogurt. The machine uses a combination of AI and biochemical engineering, allowing it to identify and harness specific VFAs to optimize their production.
It’s been a great year for the cabbage white butterfly, and the end of 2020 has seen a dramatic increase in its population. According to recent research, the UK has experienced an explosion of cabbage white butterfly numbers, with up to 10 times the amount seen in 2019. This is great news for gardeners, as these butterflies are a key pollinator in many gardens. Not only do they help to produce beautiful flowers and vegetables, but they can also help to fend off pests, as they feed on caterpillars and other insects.

In a breakthrough discovery, scientists at the University of Washington have developed a new display technique based on electro-microfluidic particles. This technology uses tiny particles, suspended in liquid, which are electronically manipulated to create visuals. The particles are charged with an electrostatic field, which causes them to move and change shape in response to the applied electric field. The result is a dynamic display that can be used for a variety of applications, including digital signage and augmented reality.
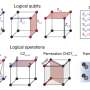
Today marks an exciting milestone in the development of quantum computing: researchers have reported that they have achieved logical qubits with the ability to correct quantum errors. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize how we use quantum computing, allowing us to store and process information more reliably than ever before. This is a major step in our journey towards a quantum-based future, as quantum computing is poised to revolutionize fields from healthcare to finance.
A new study has found that antibiotic resistance genes are now widely distributed among bacteria worldwide. This means that bacteria are increasingly able to resist the effects of antibiotics, making it harder for healthcare professionals to successfully treat infections. The findings of this new study are concerning because it suggests that the spread of antibiotic resistance is much more widespread than previously thought. This could have serious implications for public health, as the ability to effectively treat bacterial infections is essential for keeping people safe from harm.

Astronomers have made a remarkable discovery using data from the Kepler space telescope: 12 large exomoons orbiting distant planets. Exomoons are moons orbiting planets outside of our solar system, and this discovery is the first time astronomers have observed large exomoons with masses similar to Earth’s moon. This is a major breakthrough in the field of astronomy since it gives scientists a better understanding of planetary formation and evolution in other solar systems.

Today, a team of astronomers announced an amazing breakthrough in the search for exoplanets. After years of searching, they have finally discovered two Earth-like planets orbiting a star that is 40 light-years away. This discovery marks a major milestone in the search for potentially habitable worlds beyond our own solar system. The two planets are both about the size of our own Earth, and they are orbiting a star that is similar to our Sun.

Today, a groundbreaking new technology has been announced that could revolutionize the field of radar and lidar. Researchers have created a coherent two-photon lidar rangefinder that can accurately measure distances up to 10 meters away with incredible precision. Unlike conventional lidar, this new technology uses two-photon absorption to detect the distance between objects, allowing it to measure distances with accuracy down to the millimeter. This new breakthrough could dramatically improve the accuracy of autonomous vehicles, drones, and robots, as well as many other applications.
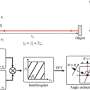
Scientists have developed a new technique that enables X-ray imaging with micron-level resolution. This new method is an important breakthrough that could revolutionize the way we use X-rays for imaging and medical diagnoses. The technique uses a specially designed X-ray detector that can detect tiny features with unprecedented clarity. This new method could be used to image cells and tissues that are too small for conventional X-ray techniques, providing researchers with a powerful tool for understanding the structure and function of objects on the micron scale.

Today marks a milestone for India’s space exploration program. After 10 years of research and development, the Chandrayaan Propulsion Module has successfully been launched into Earth’s orbit. This marks the first time that India has been able to send a spacecraft into an orbit around our planet and is an exciting step forward in India’s space exploration journey. The Chandrayaan Propulsion Module, an advanced and complex spacecraft, is equipped with advanced navigation and guidance systems that will allow it to reach its destination.

Today, China made history as the country became the first to successfully land a spacecraft on the far side of the moon. The Chang’e 4 spacecraft touched down at 10:26 am Beijing time, and the event marks a major milestone in China’s ambitions to become a global space superpower. The mission is the latest in a series of ambitious space exploration efforts by the Chinese government, and its success proves that China is now a major player in the race to explore the moon.

A recent study has revealed the existence of an avian supergene that may help explain a long-standing evolutionary paradox. The paradox, known as the “paradox of the plankton,” questions how highly specialized species can persist in an environment that is constantly changing. By studying a species of finch in the Galapagos Islands, researchers have discovered a gene that is responsible for the finch’s ability to adapt quickly to changing environments. This gene, dubbed the “supergene”, is believed to be a key factor in the finch’s ability to survive a variety of environments.
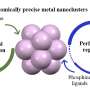
A research team from the University of Tokyo has just announced a new breakthrough in nanocluster synthesis. They have developed a technique for producing metal nanoclusters using an external ligand to induce the formation of the clusters. This is the first time that phosphine ligands have been used in this way, and the results are promising. The technique offers the opportunity to create nanoclusters with well-defined structures, sizes, and compositions, which could be used in multiple applications ranging from optical devices to fuel cells.
Exploring the advances of waveguide-based augmented reality (AR) is an exciting step forward in the study of augmented reality technology. In this blog post, we will be discussing the different advancements made in this technology, and how they are being used in various applications. Waveguide-based AR technology utilizes waveguides, which are material layers that can guide and contain light, to create an augmented reality experience. These waveguides allow for a much higher visualization quality than traditional AR technology, with improved image clarity and brightness.
A new type of surface material has been developed by scientists that could revolutionize the way we think about everyday objects. The material, which is made up of tiny, flat particles, is designed to be extremely resistant to dirt, dust, and other contaminants, while also being extremely easy to clean and maintain. The surface material is also able to repel water and oil, while still being able to absorb impact, making it perfect for items that come into frequent contact with the environment.
3D stacking has the potential to revolutionize photonics. A new study from scientists at the University of Connecticut shows that by stacking photonic crystals on top of each other, the thermal impact of the crystals can be significantly reduced. The research, published in the journal Optics Express, suggests that 3D stacking of photonic crystals can be used to reduce the heat energy generated by the crystals, and therefore, reduce their temperature.
If you thought sending a message from space was weird, just wait - soon, we’ll be communicating with relativistic spacecraft! According to recent research, scientists have developed a method for sending and receiving messages from spacecraft travelling at close to the speed of light. This method uses the Doppler effect to shift the frequency of the signal, allowing messages to be sent and received even when the spacecraft is travelling at relativistic speeds.

Have you ever wondered what happens to your old clothes after you donate them or throw them away? Well, thanks to a recent breakthrough in textile recycling, we now have a solution! Scientists have developed a new type of elastane, which is a type of synthetic fiber used in clothing such as yoga pants and swimsuits, that can be recycled and reused for up to ten times. This means that the lifespan of textiles can be significantly extended, reducing the amount of waste created by the fashion industry.

A potential new treatment for a rare and devastating bone disorder has been identified by scientists. The disorder, known as Von-Hippel Lindau (VHL) disease, is caused by a genetic mutation that leads to the growth of tumors in various parts of the body. The new treatment, a viral gene therapy, has been found to be effective in a small trial of patients with VHL. The results of the trial, published in Nature, showed that the gene therapy was able to reduce the symptoms of VHL and slow the progression of the disease.
The world’s agricultural soils are one of the most important reservoirs of carbon, accounting for approximately one third of the total carbon stored on land. In a recent study, researchers from the University of Illinois have demonstrated that the world’s agricultural soils have the potential to be used for storing even more carbon, making them one of the world’s largest carbon stocks. The team found that if agricultural practices were optimized to promote carbon storage, the extra carbon could offset a significant amount of global emissions.

The future of high school education is here! In a revolutionary move, schools across the country are beginning to incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) into their chemistry curriculum. AI-based virtual labs will provide students with an interactive learning experience, enabling them to explore complex chemical reactions and topics in a safe and engaging environment. This cutting-edge technology will not only revolutionize the classroom environment, but also provide students with a deeper understanding of chemistry and its applications.
It’s no secret that the definition of an entrepreneur has evolved over the years. The traditional definition of an entrepreneur is someone who starts and runs their own business. However, in recent years, the term has broadened to include people who work in nontraditional roles, such as freelancers, contractors, and remote workers. A new study by the University of Cambridge has found that ex-entrepreneurs are now playing a vital role in the workplace as employees.

Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in the fight against antimicrobial resistance. A new Ramanome-based technology is able to accurately identify and differentiate mycobacteria, shortening the time it takes to detect and treat antimicrobial resistance. This new cutting-edge technology uses Raman spectroscopy, a form of vibrational spectroscopy, to identify the unique molecular signature of mycobacteria in a fraction of the time it would take to identify the bacteria using traditional methods.

