
We’ve all heard of the Milky Way, our home galaxy in the universe. But did you know that there are many other galaxies out there in the cosmos? According to a recent study published in the journal Nature Astronomy, there are over 100 billion galaxies in the observable universe! This is an incredible number that we are only just beginning to understand. This research team used a new method of measuring galaxies from their extragalactic stars, which are stars that lie outside of a single galaxy.

In a breakthrough study published in Nature Chemistry, researchers from the University of Cambridge have discovered a new way of recycling polyethylene, the most common plastic on the planet. The team has developed a process that can break down polyethylene into its original chemical components, allowing it to be recycled into new polyethylene products. This process could have huge implications for the global plastic waste crisis, providing a way to reduce the amount of plastic in the environment and save billions of dollars.

Today, December 17th, 2023, an international group of scientists and scholars have announced the dawn of a new epoch in lunar exploration: The Age of the Moon. This is a major milestone for lunar exploration, as it marks the beginning of a new era of collaboration and exploration of the Moon. The Age of the Moon will bring together scientists from around the globe to collaborate on lunar research and exploration.
Scientists have recently announced that an asteroid will pass in front of the bright star Betelgeuse, and we couldn’t be more excited! On December 28th, 2023, the asteroid will block out Betelgeuse’s light for an estimated five seconds, allowing us to get a glimpse of the star’s size, shape and brightness. This event will be visible to the naked eye and will be the first of its kind in over 600 years.

Scientists have recently discovered a new vein pattern in rice that could help boost crop yields. This vein pattern, known as “C4-like”, could be the answer to increasing a rice plant’s photosynthesis, and thus its yield, by up to 40% in some varieties. This discovery could revolutionize the way we grow rice and benefit millions of smallholder farmers around the world. This new vein pattern was discovered by a team of researchers at the University of Tokyo who identified the key genetic mechanism that controls the development of the veins in rice.
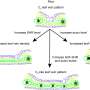
In an exciting new breakthrough, scientists have discovered a way to convert the corrosion from lime kilns into a viable biofuel source. This new technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce energy, creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy source for the future. By utilizing the corrosive waste from lime kilns, we can efficiently and safely convert it into a biofuel which can be used in a variety of applications, from powering vehicles to generating electricity.

A new breakthrough in the field of superconductivity has just been made by scientists at the University of Cambridge. They have successfully created a superconducting junction between two-dimensional (2D) materials. This means that the electrons in the junction can now flow without resistance. This could lead to a wide range of applications, from faster and more energy-efficient electronics to the potential for a new type of quantum device. The team was able to demonstrate that these junctions can work at room temperature, which is a major advancement in the field.

In a recent study, scientists have discovered that certain genetic mutations in reproduction can tend to shorten lifespan. The researchers analyzed data from the genomes of more than 400,000 people and identified 12 genetic mutations in reproductive genes that are linked to shorter lifespans.
It’s no secret that the aging process can be affected by genetic factors, but this new discovery sheds light on the potential role of genetic mutations in reproduction and how they can contribute to a shorter lifespan.

Scientists have discovered a new way to engineer and process 2D materials which could one day lead to the creation of a new generation of safe, durable, and reliable devices. The process, called ‘Fragile-2D’, uses a combination of laser irradiation, electric fields, and chemical treatments to create structurally robust 2D materials which can be used in a variety of applications. The researchers believe that this method could revolutionize the way in which 2D materials are processed and used in device fabrication, as it eliminates the need for harsh chemical treatments and heat processes.

The world of nutrition is constantly evolving, and a new research paper is set to revolutionize the way we think about plant-based pretreatment methods. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, outlines the findings of a team of scientists who have developed a novel, plant-based pretreatment method that could potentially reduce the environmental impact of food production. The method involves using plants to break down the cell walls of food crops, resulting in increased nutrient content, improved digestibility, and reduced energy inputs.

In the near future, classrooms could be filled with Artificial Intelligence (AI) math teachers that are able to teach students important math skills. AI math teachers are able to interact in real-time with students and provide personalized instruction. This technology is designed to recognize student’s strengths and weaknesses and tailor their instruction to the individual. With AI math teachers, students will be able to learn math in an engaging and personalized way.

Today marks a breakthrough in the field of nanotechnology with the development of a new bimetallic alloy nanocatalyst. This alloy has been found to boost the efficiency of chemical reactions in a way that has never been seen before. By combining two different metals, scientists have created a nanocatalyst that is more effective in catalyzing reactions than either of the original metals. This new nanocatalyst has the potential to revolutionize the field of chemistry and provide previously unattainable levels of efficiency.
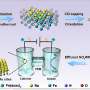
A revolutionary new class of drugs could be hitting the market as soon as 2023, and it could revolutionize the way we take medication. These drugs, called catalytic drugs, are designed to minimize the side effects of existing drugs while still providing the same benefits. This means that even the most potent medications can now be taken with fewer negative reactions from the body. Catalytic drugs work by interacting with the body’s existing enzymes, allowing the drug to pass through without causing any harm.

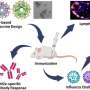
A revolutionary new nanoparticle flu vaccine has been developed that could potentially make the need for flu shots a thing of the past. The new vaccine, developed by researchers at Harvard Medical School, utilizes a combination of nanoparticles and proteins to create a long-lasting, highly effective immunization against the flu virus. This vaccine has been shown to remain effective for more than a year, meaning that people may no longer need to get yearly flu shots.
A scientific breakthrough could pave the way for imaging devices with 10 times the resolution of today’s technology. Researchers from the University of California, San Diego have developed a new process that uses “Fourier Ptychographic” microscopy, enabling far higher resolution imaging than previously possible. This new technique uses a combination of laser beams and computational algorithms to increase the resolution of images, allowing researchers to capture far more detailed images. This technique could revolutionize a wide range of scientific fields, from medical imaging to materials science.
Recently, scientists have been reassessing the role of peptides in disease. Peptides, which are small proteins, have long been overlooked as a potential cause of some of the world’s most common diseases. However, new research is suggesting that peptides could be a major factor in the development of diseases such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and even cancer. By understanding the function of peptides, researchers may be able to develop more effective treatments and preventative measures for these diseases.
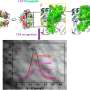
In a groundbreaking new study, scientists have engineered a conjoined racetrack of optical devices that could revolutionize the field of optics. This new device consists of two nested optical racetracks that are linked together and can be used to manipulate light in new ways. The conjoined racetracks allow for the efficient control and manipulation of light in a way that was previously impossible. This new device could be used to create more powerful lasers, improve optical communications, and develop new optical computing technologies.
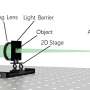
As medical technology continues to evolve, scientists are discovering groundbreaking new ways to identify stem cells. In a recent breakthrough, researchers at the University of California, San Diego have identified a new mechanism for stem cell identity. This new mechanism sheds light on how stem cells are able to maintain their identity and how they can be used in regenerative medicine. This discovery will open the door to new possibilities in stem cell research, including potential applications in tissue engineering and drug discovery.

A team of researchers from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich (ETH Zurich) have developed a new method for quantifying the onset of turbulence in a curved pipe. By analyzing the flow of a fluid through a curved pipe with a camera-based technique, the researchers were able to accurately determine the onset of turbulence and the speed at which it occurred. This method could enable engineers and scientists to better understand turbulent flow in curved pipes, enabling them to design more efficient and safer systems.

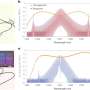
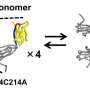
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have discovered new insights into how antibodies aggregate and what this might mean for therapeutic treatments. By analyzing the structure of a monoclonal antibody, they were able to see how it changes shape when exposed to different environmental conditions. They found that the antibody can form a variety of aggregates, such as dimers, trimers, and tetramers. These aggregates can be used to improve the efficiency of drug delivery or enhance the immune response to certain diseases.
Do you ever wish you could just get a little extra energy boost for medical procedures? Well, now you can! Scientists have recently discovered a way to use caffeine molecules to help make medical procedures easier and more efficient. Caffeine molecules are small enough to be injected directly into the body and provide an immediate energy boost to help patients get through medical treatments. This revolutionary breakthrough could help to make medical treatments less uncomfortable and more efficient.
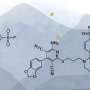
A new study published in the journal Nature Chemistry has successfully characterized the role of enzymes in forming NN bonds, a type of bond that is essential to many antibacterial molecules. The study, conducted by researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, used a combination of synthetic chemistry and molecular biology to explore the structure of the enzyme that forms NN bonds. The results of the study have important implications for the development of new antibiotics and other drugs that target NN bonds.
A new study out of the Philippines has revealed a potentially groundbreaking discovery in the marine life of the Philippine Sea. Scientists from the Philippine Institute of Marine Science and Technology have identified a species of sea cucumber that may have biomedical applications. This species, called the Holothuria scabra, has been found to contain a compound known as “echinoside A” which has anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. The potential implications of this discovery are far reaching, as this compound has the potential to be used as a basis for new treatments for a variety of diseases.

A new study conducted by researchers at the University of Toronto has revealed key insights into how muscle cells regulate the production and release of the hormone IGF2. IGF2, which stands for Insulin-like Growth Factor 2, is an important hormone for skeletal muscle growth and development. The research team used a combination of advanced imaging techniques and molecular genetics to gain insight into the IGF2 secretory pathway in muscle cells. They found that the secretory pathway of IGF2 is cell-specific and involves the calcium-dependent release of IGF2 from the cell.

Recent research has uncovered the central component of the human immune system. Scientists have identified a special type of immune cell that’s responsible for orchestrating the body’s defense against infection. This new discovery could lead to the development of more effective treatments for a range of diseases, including cancer.
Our bodies are constantly under attack from pathogens such as bacteria and viruses, and it’s our immune system that’s responsible for defending us from these invaders.

