
Are you struggling with weak bones? Bisphosphonates might be a potential solution! A recent study has found that bisphosphonates, a drug commonly used to treat weak bones, could be an effective way to maintain bone strength. Bisphosphonates have been used for over two decades to help treat osteoporosis, a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The study found that bisphosphonates help to reduce bone turnover and increase bone mineral density, leading to improved bone strength.

The Geminids meteor shower is one of the most spectacular events of the year, and it’s almost here! This year’s Geminids will peak on Monday, December 14th, making it the best meteor shower of the year for the United States and Canada. During this time, the sky will be filled with shooting stars, streaking across the night sky in a dazzling display. While the peak of the shower will be on the 14th, the Geminids will be visible in the night sky up until December 17th.
This week, scientists revealed their latest breakthrough in atmospheric imaging technology. With this new technology, scientists can now take images of the atmosphere with unprecedented clarity and detail. This is a major breakthrough as it will allow researchers to better understand the effects of climate change and other environmental phenomena. By studying the atmosphere in this way, scientists can better inform us of the potential consequences of global warming and other climate-related issues.

The strange behavior of cuprates, a class of materials known as high-temperature superconductors, has long been a mystery. But new research from an international team of scientists has revealed a novel explanation for this behavior, with potentially far-reaching implications. The team’s findings, published in Science Advances, suggest that cuprates may be able to act as a form of “superconductor” - a material that can conduct electricity without resistance. This could have a major impact on the development of advanced technologies such as quantum computing and energy storage.
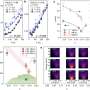
Nanopores are much more than just tiny holes. A new study has revealed the amazing ability of nanopores to selectively permeate ions and molecules, an ability that could be used to create a new generation of sensors and separators. This technology could allow researchers to create highly specialized nanopore membranes that can be used to selectively sort various molecules and ions with remarkable precision. The research team used a combination of advanced molecular dynamics simulations and experimental techniques to analyze the dynamics of the nanopore membrane and how it can selectively permeate molecules and ions.

Seaweed farming is becoming increasingly popular as a sustainable source of food and biofuel, but the effects of this booming industry on the environment are still largely unknown. A new study published in the journal Nature Communications has provided a glimpse into how seaweed farming can affect the environment. The researchers found that farmed seaweed can promote increased diversity and function in nearby marine environments.
This exciting new research shows that seaweed farming can be a beneficial activity for the environment.
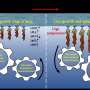
The future of renewable energy is looking brighter than ever! In a recent study, scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles, revealed a new highly efficient way to reduce carbon dioxide. This new method involves using light energy from the sun to convert CO2 to fuel, creating a renewable energy source with the potential to help reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. The research team used a combination of two photosensitizer molecules to convert CO2 molecules into carbon monoxide, a valuable fuel, at an efficiency rate of 10%.

In a breakthrough for medical research, scientists have developed a new technology for microscopy analysis that allows for extremely precise cell analysis. The new technology, called “light sheet fluorescence microscopy,” is capable of capturing incredibly high resolution images of single cells. This technology could revolutionize the way cells are studied and analyzed, leading to new discoveries in the field of medicine. With this new technology, researchers will be able to observe how cells respond to different treatments and environments, which could potentially lead to more effective treatments for diseases and other medical conditions.
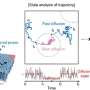
Soybean oil production is about to get a major upgrade! Researchers have developed a new process for turning the residue left over from soybean oil production into a valuable product. This new process not only increases the efficiency of soybean oil production, but it also opens up new possibilities for using the residue. This could lead to new uses for the residue, from biofuels to animal feed supplements. The researchers are excited to see what other applications this new process could bring!

Today, scientists at CERN have announced that they have achieved a major breakthrough in the search for axions, mysterious particles that could hold the answers to some of the most fundamental questions of our universe. The scientists have developed a new detector, called ATLAS, that is able to detect axions in a way that was previously impossible. This is a huge step forward in our understanding of the fundamental laws of physics, and could lead to a better understanding of the nature of dark matter.

The world’s oceans are a source of valuable natural resources—and now, scientists have found a way to create useful materials from them. In a new study published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, researchers have developed a way to combine biopolymers derived from ocean-based sources with synthetic polymers to create a unique material with a range of potential applications. The new material is stronger than existing biopolymers-synthetic polymer combinations, and is more resistant to heat and humidity.
For those working in the field of protein and peptide analysis, the development of a new graphical user interface (GUI) could be a game changer. The GUI, developed by a team of researchers at the University of California, San Diego, is designed to provide scientists with an efficient way to analyze large datasets of proteins and peptides. With the GUI, researchers can quickly visualize the structure and composition of proteins and peptides, allowing for faster and more accurate analysis.
In a groundbreaking new study, scientists have revealed a new method for decoding gene expression with ‘deep terminators’ – an advanced machine learning algorithm. This new algorithm could revolutionize gene expression research, allowing for the identification of previously unknown patterns within a gene. Through the development of this new technique, researchers have a newfound ability to uncover the complexities of gene expression and how it relates to a variety of biological systems.
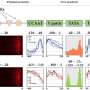
A new technique to study RNA-RNA interactions in microbial cells has been developed by researchers from the Netherlands Institute for Systems Biology. This technique, called RNA-RNA interaction profiling (RRI), uses a combination of machine learning and deep sequencing to identify, quantify and characterize interactions between RNA molecules in cells. The RRI technique allows researchers to study the mechanisms by which RNA molecules interact, which can provide insight into how microbial cells function and respond to changes in their environment.

NASA is set to launch an exciting new mission to explore Hot Jupiters, a unique class of exoplanets located close to their host stars. The spacecraft, named “TESS” (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite), will be the size of a 12-inch laptop and is expected to launch in 2023. This mission promises to revolutionize our understanding of Hot Jupiters, which are gas giant planets that orbit very close to their stars.
NASA is gearing up for an incredible mission that will revolutionize our understanding of Hot Jupiters.
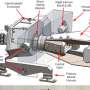
A recent study has revealed a previously unknown mechanism behind pressure-induced glass phase transition. In the study, researchers from the University of Tokyo and the Institute for Molecular Science in Japan have determined how the structure of glass changes under pressure.
The research team found that when pressure is applied to a glass, it undergoes a transition from an amorphous solid to a crystalline solid. This transition occurs due to the formation of a highly ordered structure of silicon-oxygen bonds, known as the SiO4 tetrahedron.
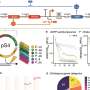
Synthetic biology is a rapidly advancing field that is revolutionizing the way we understand and manipulate living systems. By combining the principles of engineering and biology, synthetic biology is able to unlock the secrets of host physiology and engineer new biological systems. In this article, we will discuss the secrets of synthetic biology and how it is being used to create new biological systems.
One of the most exciting areas of synthetic biology is the ability to engineer new biological systems.
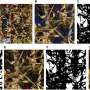
A groundbreaking new method for analyzing wheat yields has been developed by researchers at the University of Sydney. This method uses a combination of machine learning and satellite imagery to accurately and quickly assess how much wheat is being grown in a given region. This method can be used to predict disease outbreaks and yield losses due to extreme weather events. The research team hopes that their findings will help farmers better prepare for and minimize losses due to disease outbreaks and climate-related events.
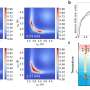
A new artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm has been developed by scientists that could help identify tiny particles in a ‘mile-long’ particle accelerator, allowing them to determine the health of the particles. The algorithm is based on a deep learning model and can detect and classify particles within the accelerator with remarkable precision. This could help scientists understand the behavior of particles that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, and is an important step towards understanding the physics of particle accelerators.

In a major breakthrough for plastic production, researchers have developed a way to harness microbes to produce sustainable plastic. This new process uses natural and renewable materials such as sugar, starch, and cellulose as the feedstock for plastic production, meaning that the plastic is biodegradable and does not rely on petroleum or other nonrenewable sources. This process is more cost-effective and environmentally friendly than traditional plastic production, and is a major step towards reducing plastic pollution.
It’s been said that we’re living in a golden age of science and technology. But what if we could look back and say that the 21st century was the true golden age of science and technology?
That’s the goal of a new project from the Augur Institute, which has set out to identify and develop new fields of science and technology over the next hundred years. The project, which is called “Augur Century,” is an effort to bring together experts from across the scientific and technological spectrum to brainstorm and create groundbreaking new fields of research and development.

Our Milky Way galaxy is about to experience something that has never happened before - a great galactic merger! Scientists have discovered that the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) and the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) will collide with the Milky Way in approximately 2 billion years. This will be a spectacular event that will cause a huge disturbance in our galaxy, and possibly even cause new stars to form. The collision of the two Magellanic clouds will also provide us with a unique opportunity to study the evolution of galaxies.

A recent study published in the journal Water, Air, and Soil Pollution has proposed a new method for treating animal manure that would be more efficient and less expensive than traditional methods. The method involves zapping the manure with a special electrode, which breaks down organic matter and reduces the amount of pollutants released into the environment. This process could potentially reduce the cost of manure treatment by up to 70%.

Today, researchers from the University of California San Diego have announced a breakthrough in optics technology. They have developed a new type of lens, called a hybrid achromat, which can reduce the size of optical systems by up to ten times. This opens the door to a new era of miniaturized optics, ushering in many potential applications including improved telescopes, microscopes, and cameras.
The hybrid achromat is composed of two microlenses, each having a different focal length.
Scientists have recently been able to answer a longstanding mystery about the composition of the Martian moons, Phobos and Deimos. Thanks to the successful Mars and Moonsand Mission, researchers were able to analyze samples from the moons and conclude their composition. The mission was able to bring back the first ever samples of the moons, which were studied in the laboratory. This groundbreaking research provides a better understanding of the formation and evolution of the Martian moons, and may have implications for future exploration and colonization of the planet.

