We all know how important it is to conserve energy, but did you know that a new strategy has been developed to make the process even more efficient? Researchers from the University of Maryland have recently developed a new strategy for creating highly efficient resonant absorption of light. This new technique is based on using nanostructures that are designed to interact with light in a special way, allowing them to absorb higher amounts of energy than traditional materials.

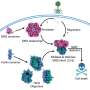
A recent breakthrough in software engineering could revolutionize the way we tackle bacteria-related diseases. Scientists at the University of California, San Francisco, have developed a software program that can identify and construct bacteriophages—viruses that infect and kill bacteria—which could pave the way to a much more effective form of antibiotic treatment.
The software program is able to quickly identify phages that have already been discovered and construct new ones from scratch.

The highly anticipated launch of the Vulcan Centaur rocket has been delayed until January 2024. This rocket, which is the next generation of space launch vehicles, was originally scheduled to launch this year but has been pushed back due to a variety of factors.
The delay is reportedly due to a combination of technical and regulatory issues. Engineers have identified some potential design flaws that need to be addressed before the rocket can be cleared for launch.

For a few weeks in 2023, ‘LK-99 superconductor mania’ swept the internet. The discovery of this unique material with its remarkable properties sparked excitement amongst scientists and the general public alike. This new superconductor had the potential to revolutionise the energy industry and could even open up a new era of space exploration. It could be used to create powerful engines and even to build space elevators. The possibilities were endless!

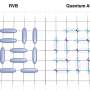
Recently, researchers at the University of Tokyo have made an incredible discovery: a magnetic liquid crystal quadrupole. This breakthrough opens up new possibilities for materials with unique optical and electrical properties. The research team was able to identify a new structure in which four magnetic liquid crystal molecules are arranged in a square-like shape, forming a stable quadrupole. This quadrupole can be used to control the flow of electricity and light.
Nanodiamonds have been used in research for years, but a recent breakthrough could revolutionize the field of quantum computing. Researchers at the University of Chicago have developed a method of embedding nanodiamonds in a polymer to create a device that can store large amounts of quantum information. This technique could help advance the development of quantum computers, which are expected to be faster and more powerful than current computers. The nanodiamonds are embedded in a polymer that is made up of organic molecules, allowing for the nanodiamonds to be precisely and securely embedded in the material.
A recent breakthrough in AI technology promises to revolutionize the way archaeologists analyze and understand the artifacts of prehistoric times. A team of researchers at the University of Manchester has developed a sophisticated system that can recognize and categorize artifacts from the Paleolithic era with an accuracy that surpasses human experts. The AI system is trained on a database of over 10,000 artifacts, which it uses to accurately identify objects like flint tools, pottery shards, and animal bones.

A new method to fabricate optical devices with precise specifications has been developed by researchers at the Institute of Photonic Sciences (ICFO). The team has developed a method that allows for the fabrication of optical devices with far greater precision than the current state-of-the-art. This new method could drastically reduce the cost and time needed to create high-precision devices, making them more accessible for researchers and industry. The method uses a combination of optical lithography and 3D printing to achieve the desired level of precision.

Have you ever wanted to be an astronomer but never knew where to start? We’ve got some exciting news for you! A new astronomy toolkit is set to be released in 2023 that will make astronomy accessible and fun for everyone. This toolkit will provide users with a plethora of tools to explore and learn about the sky and its weirdest features. With the help of this toolkit, users will be able to observe stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects in real time, and even hunt for exoplanets!

A new study published in Nature Genetics has identified a genetic vulnerability to a common herbicide found in sweet field corn. The researchers from the University of California, Riverside (UCR) found that a single gene variant in sweet field corn was linked to a decreased tolerance for the herbicide glyphosate. This means that plants with this gene variant are more likely to suffer from glyphosate toxicity, leading to reduced yields and increased vulnerability to weed infestations.
NASA’s Voyager mission has been a source of fascination and admiration for decades. Recently, a new issue has arisen that will require some serious thought and ingenuity to solve. The nuclear-powered spacecrafts are running out of energy.
Without energy, the Voyager spacecrafts won’t be able to continue transmitting the data and images that have captivated us for years. Scientists have been working tirelessly to find a solution to this issue, and now they may have an answer.

Recent advances in nanoscale carrier-based approaches to enhancing drug efficacy have shown promise for the treatment of a wide range of diseases, from cancer to HIV. Nanoscale carriers are nano-sized particles designed to transport therapeutic agents to specific sites within the body. By delivering these agents directly to the target site, nanoscale carriers can improve the efficacy of drugs, reduce side effects, and increase drug bioavailability. This is particularly beneficial for treating complex diseases, such as cancer, where traditional drug delivery methods may be ineffective.
The Geminids meteor shower is one of the most spectacular meteor showers of the year, and it’s peaking this week! The shower is visible all over the world, and it will reach its maximum visibility on Tuesday, December 13th and Wednesday, December 14th. The Geminids are known for being one of the most active meteor showers, producing up to 120 meteors per hour during its peak activity. So if you’re looking for a beautiful night sky show, mark your calendars for this week and get ready to be amazed by the Geminids!

A new material has been discovered that is ultra-hard and rivals the hardness of diamond, making it one of the hardest materials ever measured. This material, called “ultrahard Fullerite”, was synthesized in a laboratory at the University of Science and Technology of China and is made of carbon and hydrogen atoms. The team behind this discovery has said that the material is as hard, if not harder, than diamond and is much more resistant to wear and tear than any other known materials.

A new study by molecular biologist Dr. Annabelle Jones has found that a drug-resistant fungus is on the rise worldwide. This fungus, called Candida auris, is a type of yeast that can cause serious infections in humans and is particularly dangerous to people with weakened immune systems. Dr. Jones and her team monitored the spread of the fungus in hospitals and healthcare facilities across the globe. They found that cases of C.
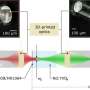
A revolutionary new hybrid laser technology is now available to create three-dimensional (3D) micro-optics with unprecedented accuracy and stability. Developed by a team of scientists at the University of California, Santa Barbara, this new technology could revolutionize the way micro-optics are created, allowing for more precision and longer-lasting 3D micro-optic parts. The team combined two different laser sources to create a new hybrid laser system that is capable of producing extremely accurate 3D parts.
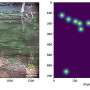
Recent advances in artificial intelligence have enabled us to make a major breakthrough in the conservation of endangered species. A team of researchers, using an AI-based method, have successfully identified a large population of manatees in the Caribbean Sea. This is a significant milestone in our efforts to protect these vulnerable species from extinction. The AI-based method used by the team was able to detect the presence of manatees and distinguish them from other aquatic life by analyzing their distinctive movements in the water.
Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in the field of evolutionary biology: a team of researchers has developed an artificial “embryo-like” device that is able to simulate the early development of human blood. This new device is the first of its kind and could provide unprecedented insight into human evolution, helping us to better understand our past and prepare for our future. The device consists of two layers of stem cells, in a similar structure to a real embryo, and is able to replicate the process of blood formation in a human body.
The James Webb Space Telescope is set to make a groundbreaking discovery. Scientists have recently discovered the tiniest free-floating brown dwarf ever seen! This brown dwarf, located 200 light-years from Earth, is only two-thirds the size of Jupiter, making it the smallest of its kind. This discovery provides a valuable insight into the formation of stars and planets. The team of astronomers used the Webb Telescope to observe the brown dwarf’s atmosphere and measure its temperature.

A new study suggests that there may be icy exoplanets located beyond our solar system that could host vast oceans beneath their frozen surfaces - and maybe even geysers! The study, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, suggests that these exoplanets could be habitable and that they could have oceans up to 100 kilometers (62 miles) deep. This could provide an exciting opportunity to explore the potential for life in these distant worlds.

The future of fuel cells just got brighter! A research team from Pennsylvania State University have developed a new pathway to electrochemically convert ‘clean’ hydrogen into a liquid fuel. This breakthrough could provide an efficient and cost-effective way to store and transport hydrogen as a fuel source. The team’s method uses a combination of two chemical processes to convert hydrogen into a liquid fuel that can be used in a combustion engine.
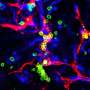
The way our cells work can often be mysterious. But, a recent study has found that even within groups of cells that appear to be identical, there can be significant differences in their behavior. Researchers from the University of Edinburgh have discovered that cells of the same type can respond differently to their environment depending on the group they belong to.
This study highlights the importance of considering the context cells are in when attempting to understand their behavior.
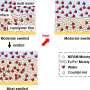
A recent study has revealed a surprising discovery: microscopic algae can form a glassy shell in order to survive environmental stress. This shell, which is made of glass-like silica, is incredibly thin yet strong enough to protect the tiny algae from heat, cold, and other extreme conditions. The study, conducted by scientists from the University of Bremen, provides insights into how these microscopic creatures survive and adapt to their changing environment.

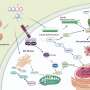
Recent advances in chemical methods have opened up new possibilities for the development of RNA medicine. RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is an important molecule involved in many cellular processes including gene expression and protein synthesis. In recent years, scientists have been exploring the potential of using RNA-based therapies as a way to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Now, a team of researchers led by the University of Tokyo have developed a new chemical method that could further advance the use of RNA-based therapies.
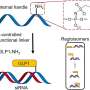
Recently, scientists have made a remarkable discovery about a certain enzyme in bacteria. In a study published in Nature, researchers have revealed that the enzyme has a crucial role in the bacteria’s ability to survive and grow. This enzyme, known as YdaH, is a protein-based enzyme found in many species of bacteria. What makes this enzyme so special is that it can break down and recycle a variety of proteins. This enables the bacteria to obtain energy from the proteins they consume, giving them the ability to grow and survive.