China recently announced their ambitious plans to launch a spacecraft to explore the far side of the moon by 2023. This mission, the Chang’e-4, is part of the country’s growing space exploration program. It will be the first mission to ever land on the far side of the moon, and its success would mark a major milestone for China’s space exploration program. The mission will involve sending a rover to explore the lunar surface and gather data on the geology, terrain, and environment.

It’s no secret that cockroaches are amongst some of the most resilient creatures on the planet. But did you know that they could also be a source of antimicrobial resistance genes? A new study has shown that cockroaches can spread genes that can make bacteria resistant to antibiotics and other antimicrobial treatments. This is a major public health concern, as it could lead to a decrease in effectiveness of various treatments.

A new study from scientists at the University of Washington suggests that entropy – the measure of disorder – is the key to understanding the habitability of planets. The research team used mathematical models to show that planets that sustain life must be capable of dissipating entropy, or energy, over time. This is the first study to propose entropy as a primary factor in determining the habitability of a planet.

Today marks an incredible moment in history; Europe has just announced its commitment to protecting nature. This is a big deal, and a huge step forward in our fight to save the planet.
The European Union has unveiled its ambitious plan to protect 30% of the continent’s land and sea by 2030. This is an unprecedented move, and an incredibly bold one. This is not just a symbolic gesture, but a real commitment to protecting the environment and its inhabitants.

Today, we’re taking a look at an interesting question: does friction require a knowledge of the physics principles behind it in order to be understood? To answer this question, we must first define what we mean by friction. Friction is the force that resists the relative motion of two objects that are in contact with one another. This resistance can be caused by a variety of mechanisms, including the molecular adhesion between the two surfaces, the interlocking of their irregularities, and the air resistance between them.

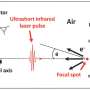
Cancer research has taken a huge leap forward with the development of ultrafast laser technology that can be used for cancer treatment. Research conducted at the University of Oxford has revealed the potential of this revolutionary technology to be used in the fight against cancer. The ultrafast laser pulses can be precisely tuned to target cancer cells without damaging surrounding tissue, leading to the potential for more targeted and effective cancer treatments.
A new method of bacteria identification has been developed that could revolutionize disease diagnosis. This new method, developed by researchers at the University of Maryland, uses a combination of machine learning and gene sequencing to quickly and accurately identify bacterial species. This method has the potential to greatly improve the speed and accuracy of disease diagnosis, which is essential for patient care. The researchers are hopeful that this new method could help reduce the time it takes to identify bacterial infections, allowing for more accurate and timely diagnosis and treatment.

In a breakthrough in energy storage technology, scientists have developed a new type of battery that can harness power from its environment and store it indefinitely. This revolutionary new battery could provide an almost limitless source of energy and revolutionize the way we power our devices. The new battery uses a combination of advanced materials and techniques to absorb ambient energy from its surroundings, allowing it to store energy without the need for a traditional power source.
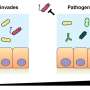
A recent study has discovered that more diverse gut bacteria communities are better at protecting humans from pathogens than less diverse communities. The findings, published in the journal Nature Microbiology, suggest that a diverse gut microbiome is more capable of competing with and eliminating harmful bacteria.
The research team found that when the gut microbiome was diverse, it was able to produce compounds that inhibited the growth of pathogenic bacteria. Additionally, the researchers discovered that the more diverse the gut microbiome, the more successful the defense against pathogens.
NASA has just announced a revolutionary new form of communication that could revolutionize space exploration. The new technology, called Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD), will be tested on the International Space Station (ISS) in 2023. This technology utilizes laser beams to send and receive data, allowing for faster and more reliable communication between the space station and Earth. This new method of communication could potentially revolutionize the way astronauts, spacecraft, and satellites interact with one another.

Recent research has revealed that Neanderthals were “morning people” and preferred to be active during the day, suggesting they had similar sleep patterns to modern humans. The study, conducted by an international team of researchers, was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Are you a morning person? It turns out that Neanderthals were too! A new study has found that Neanderthals were “morning people” who preferred to be active during the day.

A recent study published in Nature Communications has unlocked some of the mysteries of a chicken virus known as Gammacoronavirus. By analyzing ancient DNA from chickens, the study’s authors were able to trace the virus back to the early days of domestication, more than 8,000 years ago. This groundbreaking discovery offers insight into the evolution of Gammacoronavirus and how it has adapted over the centuries. The findings also suggest that the virus could have been introduced to chickens through contact with humans, rather than through a wild bird source.
Today, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery in space: the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has detected icy complex molecules in protostars. This discovery suggests that some of the most crucial ingredients for the formation of life may have been present since the dawn of the universe.
The JWST, which is set to launch next year, is the most powerful space telescope ever built. It is capable of detecting both light and infrared radiation, allowing scientists to observe objects in the universe that are too faint or too far away to be seen by other telescopes.

In a recent study published in Nature, researchers have discovered a unique evolutionary event in a binary system known as HM Sagittae. This binary system consists of two stars - a white dwarf and a red dwarf - that orbit each other and are locked in a symbiotic relationship. What makes this system particularly interesting is that it is the first of its kind to show evidence of a binary evolution process that has resulted in an increase in the mass of the white dwarf.

The future of medical treatment is here: CRISPR gene editing therapy is now a reality! Scientists have successfully used CRISPR technology to modify the genes of human cells in a laboratory setting. This breakthrough could be a game-changer for treating diseases and disorders that have long been considered incurable. CRISPR works by targeting specific genes responsible for a disease or disorder and using a “molecular scissors” to edit them, allowing for precise genetic modifications.

In recent years, the debate over the use of high-stakes exams in education has become increasingly contentious. The proponents of high-stakes exams claim that they are necessary for ensuring accountability and providing an objective measure of student achievement. However, the evidence does not necessarily support these arguments. Studies have shown that high-stakes exams often fail to accurately measure student achievement, are highly susceptible to cheating, and can lead to an emphasis on rote memorization over meaningful learning.

In recent years, cancer immunotherapy has become a promising new approach for treating certain types of cancer. Now, researchers have found a way to enhance the potential of cancer immunotherapy with nanoparticles. In a new study, researchers at the University of Texas at Austin have developed a novel nanoparticle-based system that can amplify the immune response to a cancer vaccine. The nanoparticles are designed to target specific immune cells, stimulating an enhanced immune response to the cancer vaccine and potentially leading to better therapeutic outcomes.
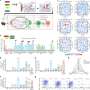
For those of us who have studied biology, we are all familiar with the concept of the ribosome - the essential cellular machine responsible for protein synthesis in all known living organisms. However, what is less well known is how this remarkable organelle has evolved over time.
Researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have recently made a fascinating discovery about ribosomal proteins - the key components of the ribosome. Using a novel method of mapping the evolutionary history of these proteins, the team was able to trace the evolutionary development of a single ribosomal protein back to a common ancestor shared by all three domains of life - bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes.
Scientists recently discovered a new species of bacteria that has the ability to eat plastic! This amazing new discovery could have a major environmental impact and could eventually lead to a solution to the global plastic pollution crisis. The bacteria, called Ideonella sakaiensis 201-F6, was discovered by a team of researchers in Japan. The bacteria is capable of breaking down and metabolizing a type of plastic known as poly(ethylene terephthalate) or PET.

A new study has uncovered a shocking truth about poaching: it is far more widespread than previously thought. Using genomic analyses, scientists have identified poaching hotspots in previously unknown areas. The research, published in the journal Nature, reveals that poaching is occurring in places that were previously thought to be relatively safe. This indicates that urgent action needs to be taken to protect these species from extinction. The findings of this study provide invaluable information for conservationists, allowing them to target their efforts more effectively and combat poaching in a timely manner.

Chia seeds have been gaining popularity for their health benefits, and now researchers have discovered that they may have even more nutritional benefits than previously thought. A new study has found that chia seeds contain higher levels of some key nutrients than previously thought, including omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and calcium. This news could be especially beneficial for those looking to incorporate more plant-based sources of nutrition into their diets. By adding just a small amount of chia seeds to your meals, you could be getting more of the essential nutrients your body needs.

Recently, scientists have been able to use a new synchrotron-based analysis to study the composition of asteroid Bennu. This analysis has allowed us to gain a better understanding of the asteroid’s composition and how it formed. By using the synchrotron’s X-ray beam, scientists were able to measure oxygen isotopes in Bennu’s mud-like surface material. This data will help us to better understand the asteroid’s origin and its potential to seed organic molecules to Earth.

A new fast energy-saving synthesis method for electrocatalysts has been developed by researchers from the National Institute of Chemical Physics and Biophysics. This new method utilizes a microwave-assisted synthesis process to produce electrocatalysts at a significantly reduced energy cost compared to traditional methods. This cutting-edge method is expected to reduce the energy cost of electrocatalyst synthesis by up to 50%, while also increasing the number of catalysts that can be produced in a given period of time.

Today, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery: they have successfully sequenced the genome of the threatened whitebark pine tree. This tree species is found in the high-altitude forests of the Rocky Mountains and is an important part of the ecosystem, providing food for wildlife and helping to regulate the local environment. Knowing the genetic makeup of the whitebark pine tree is essential to understanding the species, and to preserving it for generations to come.

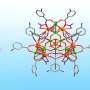
A recent breakthrough in the field of inorganic chemistry has the potential to revolutionize chemical reactions involving carbon-carbon bonds. Researchers at the Tokyo Institute of Technology have developed a method for controlling the size of inorganic clusters, which can be used to catalyze reactions between carbon-carbon bonds. This discovery could lead to more efficient and cost-effective ways of producing various chemical compounds, including medicines and polymers. The researchers’ findings, published in Nature, are the first to show that inorganic clusters can be used to catalyze the formation of carbon-carbon bonds.