A new method has been discovered that could pave the way for the development of new and improved antibiotics. Scientists from the University of Oxford have created a method that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to identify the best combinations of different antibiotics that could be used to combat bacterial infections. This method could help scientists in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a growing global health problem. The new technique could provide a more effective way to target bacteria and reduce the risk of resistance.

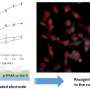
A new electrochemical chemosensor has been developed that promises faster and more effective diagnosis of serious diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease. The chemosensor is made from a single carbon nanotube coated with a polymeric material and an enzyme, which acts as a biological catalyst. This nanostructure is highly sensitive and can detect a wide range of organic molecules in the body. It can be used to identify diseases at the molecular level, which can lead to more accurate and timely diagnosis.
In recent years, Australia has seen an alarming increase in the spread of myrtle rust, a fungal disease that attacks native plants in the Myrtaceae family. This includes species such as eucalypts, bottle brushes and tea trees, all of which play an important role in the health of our forests. The disease has been devastating for Australia’s forests, causing extensive damage to the foliage and weakening trees, leading to their eventual death.

A revolutionary new wound-healing hydrogel, developed by researchers from the University of California, San Diego, could be a game-changer for medical care. The hydrogel, made from a combination of seaweed-derived polymers, is designed to be an environmentally friendly and sustainable alternative to existing hydrogels made from animal-derived materials. The seaweed-derived hydrogel has been tested and found to be just as effective at promoting wound healing as existing hydrogels, and its sustainability makes it an attractive option for medical professionals.

Scientists have developed a groundbreaking new method of scanning entire galaxies and their surroundings in an extremely short amount of time. This new technique, known as a “fast sky survey”, is capable of scanning a galaxy in just a few minutes, compared to the weeks or months a regular sky survey might take. This breakthrough technology will revolutionize the way we observe and study galaxies, allowing us to understand their structure and history much more quickly and efficiently.

Astronomers have recently discovered a new moon orbiting Jupiter, bringing the total number of Jovian moons to 79! This new moon, designated as S/2016 J2, is the smallest of all of Jupiter’s moons, measuring only 578 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by researchers from the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington, D.C., who used images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope to identify the new moon. S/2016 J2 is located in the outermost region of the Jovian system, and it orbits in a clockwise direction.
In a major breakthrough, researchers from the University of California, San Diego have successfully synthesized a new kind of semiconductor material that could lead to more advanced and efficient electronic devices. The team used a novel technique to create a material called a “monolayer semiconductor”, which consists of a single layer of atoms less than one nanometer wide. This material is highly conductive and could be used to design faster, more energy efficient transistors and other electronic components.
A new study has revealed that climate change is having a major impact on fish stocks around the world. The study, conducted by a team of scientists from the University of California, San Diego, has found that rising ocean temperatures and acidification are causing significant shifts in the distribution of fish populations, with worrisome implications for global food security. The researchers studied data from over 500 sites around the world, looking at the abundance and diversity of fish species and the impacts of climate change.

Today, scientists have announced a breakthrough development in photonic chip technology: a small photonic chip that can sense and control temperature with unprecedented accuracy and speed. This development has the potential to revolutionize industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and energy. The chip is made up of tiny optical structures that act as thermal sensors and actuators, allowing it to measure temperature, control thermal gradients, and respond quickly to temperature changes. The chip is incredibly small, measuring only a few hundredths of a millimeter in size, making it ideal for use in microscopic devices such as medical implants and robotic systems.

Astronomers have recently discovered a new type of galaxy, known as “extremely metal-poor galaxies” (XMPs), which could provide important clues to the earliest stages of galaxy formation. XMPs are galaxies with very low amounts of heavy elements, such as iron and oxygen, compared to other galaxies. This lack of metals could reveal the conditions of the early universe shortly after the Big Bang, when the first stars and galaxies began to form.

Astronomers have discovered something remarkable: for the first time, they have found that the color of galaxies depends on the type of stars they contain. In a new study, researchers have discovered that red galaxies are more likely to have older stellar populations, while blue galaxies are more likely to have younger stars. This discovery could help us better understand the formation and evolution of galaxies, and the universe as a whole.

In a recent study, a team of scientists from the University of Sydney have successfully analyzed a pre-colonial lineage of an extinct indigenous Australian population. By analyzing the DNA of a centuries-old Indigenous Australian mummy, the researchers were able to ascertain the genetic history of an ancient population. This research is groundbreaking in that it not only provides insight into the history of Indigenous Australians, but also sheds light on the ancestry of many Indigenous peoples across the world.

Are you interested in learning more about virtual reality and its potential applications in nuclear particle physics? In this article, we’ll be taking a closer look at how virtual reality (VR) could be used to better understand and study nuclear particles. We’ll be answering questions such as: What is virtual reality? How can it be used to study nuclear particle physics? What are the benefits of using VR in this field?

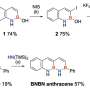
In recent years, scientists have been working to develop methods for non-destructive root Situ analysis (RSNA), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been a crucial tool in this endeavor. In a paper published recently in the journal Vacuum, researchers showed how they used AI to develop an automated system for accurately analyzing root Situ samples.
The team demonstrated the accuracy of their system by using it to classify root Situ samples into two categories—healthy and unhealthy.
It’s been estimated that by 2023, the average taxpayer in the United States could be facing a tax spike of up to 10%—and that could drive many taxpayers into bankruptcy. This skyrocketing of taxes is due to several factors, but the most significant one is the federal government’s increasing need for revenue. With national debt reaching record highs, the federal government is turning to tax increases to make up the difference.

A new study has revealed that pollinators have a much bigger impact on edamame yields than previously thought. This news has huge implications for our agricultural future.
The study, conducted by researchers at the University of California, Davis, was designed to understand the importance of pollinators in edamame production. The team found that when pollinators were excluded, yields dropped by an average of 43%. This is a staggering figure that shows just how crucial pollinators are to this particular crop.

Reindeer have always been known for their incredible vision, but now researchers have discovered how they evolved to have such keen eyesight. It turns out that their vision has adapted to help them spot their favorite food in the snow. By studying the genetic basis of reindeer vision, scientists have discovered how the animals evolved to be able to spot moss, their favorite source of food, within the snowy landscape. The findings were recently published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution.

Recently, it was discovered that Rembrandt van Rijn, one of the greatest painters of the Dutch Golden Age, was way ahead of his time when it came to art preservation. Archaeologists have found evidence that Rembrandt used a lead-based impregnation technique to preserve his artworks. This method, which has been used by conservators in recent years, was used by Rembrandt more than 400 years ago. This was a groundbreaking discovery, as it has allowed us to gain insight into the techniques used by artists of the past.

Today, scientists have discovered a unique way to measure the distance between stars: by listening to the music they emit. In a recent study, researchers used a special instrument to detect the sound waves created by stars and then used the frequency of these waves to calculate the distance between them. By combining this method with other existing techniques, astronomers are now able to measure the distance between stars more accurately and quickly than ever before.

Today, President Joe Biden is hosting a special event in the White House Rose Garden to celebrate the first all-female NASA astronaut crew. This historic event marks the first time in history that an all-female crew will be launched into space. This groundbreaking mission is scheduled to launch from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20th, 2023.
The event will feature astronauts Christina Koch, Shannon Walker, and Kayla Barron, who will be the first ever all-female crew to travel to the International Space Station.

Today marks a huge milestone in the world of astronomy - a major discovery has been made! Scientists have discovered a planetary system with two planets orbiting around a sun-like star, located in a stellar cluster approximately 3,000 light years away from Earth. This is the first known instance of a planetary system like this being discovered within a stellar cluster, and it has the potential to change the way we think about the formation of stellar systems.

Today, Rocket Lab, the first orbital-class launch provider, announced a successful launch of a Japanese satellite into space. This mission marks the first time Rocket Lab has launched an orbital payload from Japan - a landmark moment for the company. The mission was a collaborative effort between Rocket Lab and satellite operator Synspective, and saw the successful deployment of Synspective’s Synspective Stardust satellite into a sun-synchronous orbit from the Mahia Peninsula in New Zealand.

Today, scientists have revealed a remarkable molecular complex that has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about bacterial viruses, or bacteriophages. Using state-of-the-art imaging and computational methods, researchers from the University of California San Diego and the University of California Los Angeles were able to create a 3D reconstruction of the bacteriophage’s outer shell, or capsid. This reconstruction provided a detailed view of the bacteriophage’s structure, which could open up new avenues of research into the way bacteriophages infect and interact with bacterial cells.

Today marks a historic day in the study of solar flares. Scientists have discovered that the sun is capable of producing the largest solar flare ever recorded, temporarily powering up the sun’s magnetic field. This solar flare is over ten times more powerful than any other recorded in the past decade and has the potential to create a solar storm of epic proportions. This new research will help us better understand the sun’s activity and its impact on Earth’s environment.

A recent discovery has been made that could revolutionize the reproductive process. Scientists have discovered a way to create eggs from stem cells that could be used to fertilize a baby. This means that for the first time, men and women could both produce viable gametes (eggs or sperm) for reproduction. This could open the door to new possibilities for same-sex couples, as well as those who are unable to produce viable gametes due to medical issues.