Genetically modified crops may be the key to unlocking a sustainable future. According to a recent study, researchers have found that crops created through biotechnology are better equipped to deal with the changing climate and can help farmers make the most of their land. The research team studied the effects of rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns on crops and found that crops made through biotechnology were much better able to resist the effects of climate change.

Recent studies have revealed a promising new approach to treating antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections: photodynamic action. This method involves using light to activate a photosensitizer molecule, which, when combined with oxygen, produces reactive oxygen species that damage the bacterial cell membrane. The result is a weakened bacterial cell that is more susceptible to antibiotics. In a study published in the journal Science Advances, researchers found that the photodynamic action weakened the resistance of bacteria to antibiotics, making treatments more effective and potentially leading to improved outcomes.
Today, news broke that Jeff Bezos, the founder of Blue Origin, was in a tragic accident. Bezos was reportedly testing a new spacecraft when the accident occurred, and he did not survive. This is a heartbreaking moment for the space industry, as Bezos was a pioneer in the field and an advocate for space exploration. His work will live on, and his legacy will be remembered for years to come. Our thoughts are with his family, friends, and colleagues during this difficult time.

Today, Jeff Bezos unveiled his vision for a revolutionary new space venture, Blue Space. Blue Space is a research and development program that seeks to develop the technology necessary to make space exploration and habitation possible. The program will focus on developing innovative new space launch systems, renewable energy sources, and advanced materials. Bezos believes that with Blue Space, humanity will be able to “explore and enjoy the beauty and bounty of the solar system” and that “the solar system can and should become our second home.

Recently, scientists have made a breakthrough in machine learning that could change the way we interact with the environment. In a study published in Nature Communications, a team of researchers from the University of Oxford have developed a computer program that can recognize birds using plastic. The system was trained to recognize over 50 species of birds from photos of plastic collected from the beaches and seas of the UK and Europe.

A new technique developed by researchers has made it easier to safely manipulate molecules. This technique is expected to revolutionize the understanding of chemical processes and open up new possibilities for synthetic chemistry. The technique works by using a laser to quickly and precisely move molecules from one place to another. This means that molecules can be moved around in order to create complex chemical reactions without having to use hazardous materials or expose them to dangerous levels of heat or pressure.

NASA recently achieved a major milestone on its journey to explore the universe with its BurstCube mission! BurstCube is a small satellite launched in 2023 that will search for gamma-ray bursts, the most powerful explosions in the universe. Using the CubeSat form factor, BurstCube is an ultra-lightweight and highly capable instrument that will help scientists learn more about the nature of gamma-ray bursts, which are believed to be the origin of many of the elements in the universe.

In a recent discovery, scientists have found a bacterium that could have a big impact on the availability of rare earth elements. This newly found bacterium, called Paenibacillus sp. Y412MC10, can extract rare earth elements from ore with an efficiency that is previously unheard of. This could help to increase the availability of rare earth elements, which are used in a variety of modern technologies and are becoming increasingly scarce.
In a major breakthrough for the field of physics, a team of researchers from the University of Gothenburg have discovered a new type of molecule. The molecule – dubbed the “giant trilobite Rydberg molecule” – is the largest molecule ever created and has the potential to revolutionize research in a wide range of scientific fields.
This breakthrough was made possible through the use of a powerful technique called “cold molecule spectroscopy”.
An exciting new research team has just been formed with the goal of tackling antibiotic-resistant superbugs. This team, made up of scientists from around the world, is working on a new approach to combating these dangerous bacteria: sabotaging them from within. The researchers are creating and deploying a special type of bacteria that has been genetically modified to target and destroy antibiotic-resistant superbugs. By doing this, they hope to be able to outsmart the superbugs and restore the effectiveness of antibiotics.
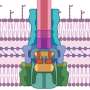
The future of global production is looking a lot closer to aquatic ecosystems. A new study from a team of researchers, published in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution, has revealed that the global production system is becoming increasingly reliant on the health of aquatic ecosystems. The study found that the majority of global production now takes place in, or near, aquatic ecosystems, such as rivers, lakes and oceans, and that this trend is expected to continue in the future.

A new study recently published in the journal Nature Communications has revealed some fascinating insights into the diets of early primates.
Researchers studied the fossil teeth of a species of early primate called Anchomomys that lived in what is now Southern Europe between 42 and 35 million years ago. The fossil teeth allowed them to reconstruct the diet of Anchomomys, and what they found was surprising.
Analysis of the teeth revealed that Anchomomys was an omnivore, meaning it ate both plant and animal material—something that was previously thought to be unique to humans.

A team of researchers from the University of California, Irvine recently made an incredible discovery – that certain insects may have the secret to a longer life. By using a technique called “targeted starvation,” the researchers were able to extend the lifespan of fruit flies up to 30%. This is a significant finding, as it could potentially open up new possibilities for human health and longevity.
The secret to longer life for these insects lies in a simple trick: skip a meal.

The search for exoplanets capable of sustaining life has been a topic of intense interest for years now. Scientists have made remarkable progress in recent years, uncovering a number of Earth-like exoplanets that may have the potential to host life. The latest breakthrough in this endeavor comes from a team of researchers from the University of Washington, who have discovered a group of exoplanets that may be able to maintain a habitable climate in spite of being located in an area of space known as the “hellish” region.

This week, scientists announced that they have made a major breakthrough in understanding the history and contents of the universe. Using a fleet of radio telescopes, they have been able to create the most detailed map of the universe ever made. This map has allowed them to observe the evolution of the universe over the past 13 billion years, and to detect matter that had previously been undetectable. This is a huge step forward in our understanding of the universe and its development!
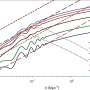
In a recent study, researchers have developed a new mathematical language to help scientists better understand how biological networks work. This new language can help scientists identify patterns in complex networks of proteins and other molecules, which are essential for life. By using this language, scientists can better understand how changes in the network structure can affect the functioning of the entire network. This breakthrough could lead to discoveries in areas such as cancer research and drug design.

The possibilities of medical botulinun toxin A (BTX-A) are seemingly endless. From wrinkle-reducing injections to treating chronic medical conditions, this powerful neurotoxin is being used in new and exciting ways. Recently, researchers have begun to explore its potential in treating a variety of neurological and psychological conditions. From reducing tics and spasms associated with Tourette’s Syndrome to treating depression and anxiety, BTX-A has been found to have dramatic effects on patients.
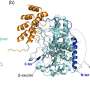
Have you ever heard of a bacterium that can power its own locomotion? Scientists have recently announced the discovery of a giant bacterium that has the unique ability to generate its own energy and use it to move around! This giant bacterium, which is approximately 5 micrometers in size, is one of the first bacteria ever discovered to use its own energy to move. Researchers have found that this bacterium uses a type of self-generated energy, known as a proton motive force, which is generated by its own metabolism to power its movement.

In a major milestone for physics, scientists have developed a strategy for creating higher temperature superconductors. Superconductors are materials that can conduct electricity without resistance at very low temperatures and are used in a wide range of applications, from MRI machines to maglev trains. Until now, the highest temperature at which superconductivity has been achieved is around -140°C. But the new strategy, developed by an international team of researchers, could enable superconductivity at temperatures as high as -50°C.
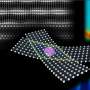
Nanotechnology has the potential to revolutionize cancer treatments and the way we understand tumor behavior. A new study has found that nanotechnology can be used to develop artificial materials that can interact with tumor cells. These materials can be used to track and manipulate tumor behavior, providing researchers with an unprecedented level of insight into the behavior of tumors. By understanding how cancer works on a microscopic level, scientists can develop more targeted treatments, with fewer side effects, and improve patient outcomes.
Today, CountShoots, a leading provider of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), unveiled its newest UAV, the CountShoots X2, a revolutionary drone designed with advanced artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities. The X2 offers unprecedented performance and ease of use with its AI-powered flight control system, allowing users to get the most out of their UAVs. The X2 is designed to be the perfect tool for commercial applications, giving operators the ability to capture stunning aerial footage with ease.

This Saturday, scientists are set to introduce the world to “woolly cats,” a new breed of domesticated cats created by splicing together the genes of cats and dogs. Woolly cats will be the first of their kind, and will have a unique combination of traits from both species. They will have the fluffy fur of a dog, combined with the playful nature of a cat. This revolutionary breakthrough in science is sure to have pet owners everywhere excited to get their hands on one of these unique animals.

Scientists have recently identified twelve gaps in the genome sequence of the model organism Arabidopsis thaliana. This discovery is a major breakthrough as it gives researchers the potential to uncover thousands of new genes that could provide insights into important biological processes. Arabidopsis thaliana has long been a model organism for scientists studying plant biology. With the completion of its genome sequence in 2000, scientists have been able to study the genetic basis of many plant traits.

In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers at the University of Cambridge have uncovered a new electronic pathway that links atomic vibrations to magnetism. This new pathway has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of how matter behaves at the atomic level. The research team found that when atoms vibrate, they can cause electrons to move in ways that can affect the magnetic properties of materials. This could lead to new materials with properties which could be used in a variety of applications, from sensing to energy production.

A new image-capturing technique has been developed by researchers from the University of Cambridge that can take pictures of fluids in motion. The technique, called Liquid Lace-Medusa, allows researchers to capture incredibly detailed images of fluids without disrupting their natural movement. This could be used to study phenomena such as turbulence and fluid-structure interactions, and could provide important insights into many scientific fields.
The Liquid Lace-Medusa technique works by using a device that is able to project laser light into a tank of fluid and capture the resulting image.