Scientists have recently unveiled a new antioxidant made from a diverse mix of water-soluble lignin, carbohydrate, and phenolic compounds. This new antioxidant, found in the cell walls of plants, is the first of its kind and promises to revolutionize the antioxidant industry. The antioxidant has been tested to be highly effective at scavenging free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative damage, and promoting overall health. With its diverse and potent antioxidant properties, this new antioxidant could be used to supplement health and nutrition products, cosmetics, and even food.

A breakthrough in cancer research is here! A team of researchers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a new microfluidic magnetic method to accurately analyze tumor-derived exosomes. These exosomes are tiny vesicles that can be used to detect and monitor cancer. This new method allows for the rapid and accurate analysis of these exosomes, enabling researchers to gain a better understanding of the biology of cancer. The team believes their new method could lead to improvements in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment.
Did you know that your genetics play a role in hosting microorganisms? Recent research has shown that certain genetic variations determine how well a host can take in and interact with microorganisms. This research has implications for understanding how diseases and viruses are spread. By understanding the underlying genetics of the host, scientists can better determine how to contain the spread of disease. Additionally, this research can help us better understand how our genetic makeup affects the way our immune system responds to pathogens.

Today, researchers revealed a new strategy to reveal the full chemical complexity of any sample. This strategy, which involves using a novel combination of mass spectrometry and ion mobility spectrometry, can detect and identify molecules in complex matrices. The team demonstrated the new approach by using it to identify thousands of lipids in a pig liver sample, providing a snapshot of the organ’s chemical composition. The strategy could be used in the future to study the composition of any complex sample, providing a new way to analyze and better understand the chemical complexity of biological systems.

A new study has recently uncovered the mystery of black holes, and the secret may be in the form of holography! Researchers at the University of Cambridge have discovered that a holographic description of the interior of a black hole may be the answer to understanding how these mysterious phenomena work. This new breakthrough could revolutionize our understanding of space, time, and gravity, and has the potential to unlock the secrets of the universe.

A recent breakthrough in meteorology has uncovered a mysterious pattern in snowflakes. Scientists have discovered that snowflakes have an intricate design that follows a specific pattern. This pattern appears to be a combination of both radial and linear symmetry, making it one of the most unique snowflake patterns ever discovered. Researchers are now trying to understand why this pattern exists and how it could be used to better predict winter weather.

In the exciting new world of materials science, researchers have made a breakthrough that could revolutionize the way we create and manipulate materials. By combining atomistic simulations with machine learning, scientists have developed a new technique that could dramatically speed up the grain engineering process. This process involves manipulating the properties of grains of materials, such as metals, alloys, and ceramics, to achieve specific properties. This technique could pave the way for new materials with specific properties tailored to meet the needs of various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and energy.
In a world first, scientists have successfully used microwaves to detect and control soil-borne pests and diseases in an effort to help farmers fight crop losses. The study, published in Nature Plants, is the first to show how microwaves can be used to detect pests and diseases in soil, and could have major implications for sustainable agriculture.
Today, farmers are facing a growing challenge in dealing with pests and diseases that can decrease crop yields and increase their costs.

A breakthrough study has revealed that molecular jackhammers can be used to rupture melanoma cells in the body, providing a potential new approach to treating this deadly form of cancer. The research, conducted by scientists at the University of Washington and published in the journal Science Advances, shows that these tiny jackhammers can be used to break apart the walls of melanoma cells, killing the cancer cells and leaving healthy cells unharmed.

Space exploration is no longer just for men! In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have discovered that women can actually have more muscular strength than men during spaceflight. This could lead to the inclusion of more female astronauts in space exploration. The study, conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA), found that due to the effects of microgravity on the human body, women can have greater muscular strength than men during spaceflight.

A new method of utilizing nanomedicines in conjunction with X-ray vision may revolutionize the future of healthcare. Scientists have recently developed a new way to use mRNA-based nanomedicines to produce a powerful X-ray vision, enabling them to view the inner workings of cells in unprecedented detail. This technique could help doctors diagnose diseases, study drug efficacy, and more. The breakthrough was made possible by introducing a special kind of fluorescent protein into the nanomedicine, allowing it to be tracked within the cells.

In a breakthrough discovery, scientists have successfully created a new type of covalent framework using vapor deposition. This new method could help to create materials with unprecedented properties, paving the way for new applications in many industries.
The new technique stands out from other covalent framework creation methods due to its ability to create materials with different pore sizes. This allows for the creation of materials with different properties, such as increased strength or improved electrical conductivity.

A new antibiotic substance has been discovered in the human nose that could help combat the growing threat of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The substance, called lugdunin, is produced by the bacteria Staphylococcus lugdunensis, which is found naturally inside the human nose. Researchers at the University of Tübingen in Germany found that lugdunin is effective against a range of bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria which is responsible for a wide range of infections, including those that can cause sepsis.

A new study has revealed a breakthrough method for detecting and preventing disease in wildlife populations. Researchers from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health have developed a novel approach to detect pathogens in wild animals that could help preserve endangered species and protect humans from zoonotic diseases. The method involves monitoring the levels of antibodies in wild animals, which can indicate the presence of a pathogen before it manifests into a full-blown outbreak.

Artificial intelligence (AI) has been making strides in many areas, from autonomous driving to speech recognition. Now, researchers have developed an AI algorithm that can generate proteins with exceptional strength. In a paper published in Nature Communications, the researchers explain how their algorithm can generate proteins with up to 10 times the strength of natural proteins. This breakthrough could have major implications for drug development, biotechnology, and materials science.
AI is revolutionizing the way we design proteins.

In a groundbreaking move, the UK will be introducing special schools at both the beginning and end of the educational system. These schools will be dedicated to helping children with special educational needs (SEN) who are not adequately served in mainstream schools. The hope is that these specialized schools will provide an environment where students can access the right amount and type of support to successfully progress through their education. This is an exciting development that could have a profound effect on the lives of many children with SEN and their families.

Researchers have made a breakthrough in photonic crystals that could revolutionize the development of interstellar space missions. Known as Starshot, the project aims to develop laser-propelled spacecraft that could reach Alpha Centauri, our nearest stellar neighbor, in just 20 years.
The breakthrough in photonic crystals is a major step forward for the Starshot project. Photonic crystals are extremely efficient at storing and transmitting light energy, meaning they could be used to power spacecraft with laser propulsion.
The world’s largest telescope mirror is set to become even larger! It will be made up of 12 segments, giving it an unprecedented power that will allow us to observe the universe in greater detail than ever before. This new telescope is being developed by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). It is known as the European Extremely Large Telescope (E-ELT) and will be the largest optical-infrared telescope ever built. The mirror will measure 39 meters in diameter, making it the world’s largest telescope mirror.

In a new study published in the journal Biology of Consciousness, researchers explored a groundbreaking theory that consciousness could be a product of cellular activity in the brain. This theory, known as cell-based consciousness, proposes that the cells in the brain have an “awareness” of their surroundings and thus contribute to the overall consciousness of an individual. The research team conducted experiments to test this theory, and their results provide strong evidence in favor of cell-based consciousness.

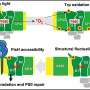
A new study has shed light on the role of oxidized tryptophan (Trp) residues in proteins. Scientists from the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) in Austria have characterized the oxidation state of Trp residues in proteins, allowing them to better understand their role in protein folding and stability.
The scientists studied the oxidation state of Trp residues in several proteins, and found that oxidation of the Trp residues impaired protein folding and stability.
Recent research has revealed that the metabolism of living organisms is much more complicated than previously understood. Scientists have discovered a new type of metabolism, dubbed ‘cryptic metabolism’, that is playing an important role in the functioning of cells. Cryptic metabolism refers to the utilization of small molecules, such as amino acids, to generate energy and perform other vital cellular functions. This new finding is shaking up the field of metabolism and may open up new avenues for research.
Scientists have recently announced a major breakthrough in the field of particle physics - the IceCube Neutrino Observatory at the South Pole will be expanded to create the even bigger IceCube-Gen2. This new and improved observatory will be 10 times larger than the current observatory, with the goal of detecting and studying elusive particles known as neutrinos. Neutrinos are incredibly difficult to detect because they pass through matter unimpeded and interact very weakly with other particles, so the larger observatory will be a major step forward in particle physics research.

It’s the most wonderful time of the year! The James Webb Space Telescope has officially spotted a new holiday season planet orbiting around Uranus! This new planet, named “Uranus-X”, is the first ever to be discovered around the eighth planet in our Solar System and has been deemed an exciting discovery by scientists. It’s estimated to be about the size of Neptune and is believed to be composed of ice and rock.

Astronomers have discovered a distant cluster of galaxies, called the Pandora Cluster, that has been hiding in plain sight for billions of years. Located about 7.5 billion light-years away from Earth, the cluster is the most massive and luminous cluster of galaxies ever seen at such a great distance. With its incredible size and brightness, the Pandora Cluster is giving astronomers a unique glimpse into the universe’s distant past.
Astronomers have just discovered a distant cluster of galaxies that has been hiding in plain sight for billions of years!

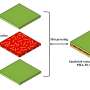
In a recent study, researchers from the Institute of Materials Science and Engineering at the University of Technology in Berlin have developed a new type of composite biopolymer that can be used for a variety of applications. This sandwich-structured composite biopolymer consists of a flexible core layer surrounded by two outer layers of a more rigid material. This composite material can be used for a range of applications, including as an envelope material for drugs, as a material for medical implants, and in food packaging.