
Scientists have made a major breakthrough in understanding how the deadly malaria parasite is transmitted between mosquitoes and humans. In a study published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers from the University of York have identified how the parasite alters the behaviour of its mosquito host, increasing its likelihood of biting humans and spreading malaria.
This is an incredibly important discovery that could help us better understand and combat the spread of malaria.

Repelling insects doesn’t have to be a stinky, bitter, and painful experience anymore. Scientists have developed a new way to repel bugs that is odorless and tasteless. This new insect repellent is a protein-based solution that is designed to be sprayed on clothing or skin. It is effective against mosquitoes, ticks, and other biting insects, and has been tested to last up to 8 hours. The best part is that it doesn’t cause any skin irritation or have a bitter taste, like many traditional repellents.
A new study from the University of California has discovered a mysterious and devastating disease affecting jujube trees around the world. The disease, known as “Witches’ Broom,” is caused by a fungal infection and has been reported in many countries, including the United States, China, India, and Pakistan. The disease causes the tree to produce numerous small shoots, making it look like a witch’s broom. These shoots are not only unsightly, but they also reduce yields and reduce the quality of the fruit, making it difficult for growers to make a profit.

Astronomers have recently made an incredible discovery: a supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy is emitting a powerful beam of light! This discovery is being heralded as a major breakthrough in our understanding of black holes and their behavior. The light beam, which has been dubbed the “Black Hole Sun,” is believed to be generated by the strong gravity of the black hole. This phenomenon could be used to study the properties of the black hole itself and could potentially provide insight into the behavior of other cosmic phenomena.

The future of drug delivery systems is here! Scientists have recently developed an innovative, self-assembled system for drug delivery: a unimolecular self-assembled hemicyanine-oleic acid conjugate. This system is made up of two cationic molecules, hemicyanine and oleic acid, connected by a covalent bond. The molecules have the ability to self-assemble into a nanostructure at physiological pH, allowing for the targeted delivery of drugs to specific tissues within the body. This groundbreaking technology could revolutionize the way we deliver medications and improve outcomes for patients!
Scientists have recently discovered a new way to combat the eucalyptus beetle, a destructive pest of eucalyptus trees. By using a bio-pesticide made from fungi, the beetle can be effectively controlled without the use of harsh chemical pesticides. This new method of pest control is believed to be the first of its kind, and could be a major breakthrough in protecting eucalyptus trees from the beetle. Not only is this method of pest control more environmentally friendly, but it is also much more effective in controlling the beetle population.

Scientists recently made a breakthrough discovery in ultrafast carrier diffusion visualization. By using a new technique in combination with a high-sensitivity microscope, they were able to observe and record a process that was previously too fast to be seen. This process, known as ultrafast carrier diffusion, is the movement of electrons in a semiconductor material and takes place in a matter of femtoseconds (one femtosecond is one quadrillionth of a second).
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) recently announced the successful launch of the Very Large Telescope (VLT) Exoplanet Hunter, a powerful new tool for detecting and studying exoplanets orbiting distant stars. The VLT Exoplanet Hunter uses a combination of adaptive optics and direct imaging to search for exoplanets around nearby stars, allowing for the study of distant planets in greater detail than ever before. This new telescope will be able to detect exoplanets as small as Jupiter, meaning that it can observe planets that were previously too small or faint to be detected by other methods.

Today, scientists have released a study that shows an increase in wildflower populations, along with an increase in insect pollinators. This is welcome news, as it indicates that environments are becoming more hospitable to these important species. The study found that wildflower populations were increasing in many parts of the world, in both temperate and tropical climates. This increase was accompanied by a proportional rise in the number of insect pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and flies.

In recent years, nanotechnology has been gaining traction in many industries, and now wood is the latest sector to benefit from this cutting-edge technology. Researchers at the University of Minho in Portugal have developed a nanotechnology-based approach to make wood more resistant to biodeterioration, which can occur due to insect attacks, fungal growth, and other biological agents. This new technology provides a viable alternative to traditional wood preservation methods, and could be the key to making wood a more sustainable building material.
In a new study published in the journal Nature Materials, researchers from the University of California, San Diego have identified the key mechanisms of materials that make them biologically compatible. The team studied how materials interact with biological systems, and identified the key molecular and physical properties that make them suitable for use in biomedicine. Their findings provide a foundation for medical device and drug development as well as for the development of new materials for use in biomedicine.
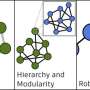
A strange coincidence between two different theories of physics has recently been observed. In what has been called the “AdS/CFT Correspondence,” the physics of gravity on one side of a theoretical universe appears to mirror the physics of particles on the other side. This strange coincidence, first proposed in 1997, has been called “one of the most remarkable in all of physics.”
The AdS/CFT Correspondence is based on two different theories of physics: string theory and quantum field theory.

The European Space Agency (ESA) is set to launch an ambitious mission to explore the X-ray vision capabilities of the common European lobster. Over the next four years, the ESA’s Lobster Eye X-ray Mission (LEXM) will investigate the unique visual system of the lobster and how it is adapted to both bright and dark environments. This mission will involve fitting lobsters with tiny cameras and sending them up to the International Space Station to study their responses to X-rays in microgravity.

A new study from scientists at the University of California, Davis, has revealed a surprising evolutionary timeline for the diminished production of boric acid. Boric acid, a naturally-occurring compound found in soils, is essential for the development of plants and animals. The research team discovered that boric acid production in plants and animals has been diminishing over the last million years, leading to a decrease in the amount of boric acid available in the environment.

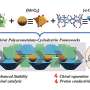
In a recent study, scientists have announced the successful development of a chiral polyoxometalate-based framework with unprecedented levels of stability. This framework has the potential to revolutionize the field of chemical engineering, as it is both robust and versatile enough to be used in a variety of applications. Furthermore, the researchers have noted that this framework is also able to self-assemble, meaning it can be used to create materials with specific properties.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have been making waves in the agriculture industry, and now, a team of scientists has reported a breakthrough that brings this technology one step closer to helping farmers detect and diagnose crop diseases. The team has developed a vision-based deep neural network that can identify and classify crop diseases with an accuracy of around 95%. This could give farmers a powerful tool to address crop diseases quickly and efficiently, ensuring better yields and higher profits.

A new behavior curriculum is set to be implemented in Australian schools in 2023, with the aim of teaching students the importance of good behavior. The curriculum will focus on teaching students about responsible decision making, respectful communication, and self-awareness. It is hoped that the curriculum will help students to develop a better understanding of their own behavior and how it impacts those around them. The curriculum will also provide strategies for managing emotions, dealing with difficult situations, and developing positive relationships with peers and teachers.

A few years ago, the idea of a space elevator was little more than science fiction. Now, thanks to the hard work of NASA and SpaceX, the concept is becoming a reality. On December 20th, NASA announced that four astronauts will be testing a new space elevator concept developed by SpaceX. The mission, which is set to launch next year, will be the first of its kind and will be a major step forward in furthering our understanding of space transportation.

Ho-Ho-Ho! It’s that time of year again! That’s right, it’s time for Santa Claus to take off on his magical journey! According to recent reports, Santa Claus is set to take off on December 24th, 2023. Santa will be traveling around the world delivering presents to all the good boys and girls. He will be assisted by his team of elves and reindeer as he makes his way across the globe.

In a recent study, researchers from the UK have uncovered the complex microbial interactions that contribute to the flavor of cheddar cheese. With the help of sophisticated DNA sequencing techniques, the team identified a range of bacteria that help give cheddar cheese its unique taste. Among them were various species of lactic acid bacteria, which are known to produce flavor compounds. The team also identified a range of other bacteria, including yeast and mould, that play a role in the flavor development of the cheese.
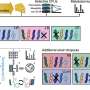
Today, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have announced the discovery of a critical piece of the puzzle in understanding Lassa virus. A new study reveals the structure of the ribonucleoparticle (RNP) complex of Lassa virus, providing insight into how the virus replicates, and paving the way for the development of new therapeutic treatments. The RNP complex of Lassa virus is a complex of proteins and RNA that allows the virus to replicate inside the host cell.
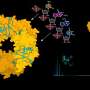
Astronomers have made an exciting discovery that could change how we understand the history of the universe. In a survey of ancient galactic remnants, they have discovered seismic ripples that provide evidence of the early stages of galactic formation.
These seismic ripples, known as “ripples of resonance”, are caused by the gravitational pull of unseen dark matter. This interaction creates a pattern of ripples that can be detected by astronomers. By studying these ripples, astronomers can learn more about the formation and evolution of galaxies.

Nanoscale patterns within materials have been revealed by scientists using a new technique, which can help develop new materials for applications such as energy storage devices and sensors.
The breakthrough technique, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge, uses a variation of electron microscopy to observe the ‘matrix’ of atoms or molecules within a material.
The technique, called Matrix Electron Diffraction Tomography (MEDT), enables scientists to observe nanoscale patterns within materials, such as the arrangement of atoms or molecules, as well as their chemical composition.
Scientists have recently made a major breakthrough in understanding the molecular function of a key G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). This receptor, called GPCR12, is part of a family of receptors that are found in virtually all animals and play an important role in many physiological processes. By combining X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy, the researchers were able to determine the three-dimensional structure of GPCR12 and its interaction with its partner protein, Gα.

In a new breakthrough, astronomers have captured an unprecedented image of the Chicken Nebula, with an incredible resolution of 12 billion pixels. This stunning image was taken using the recently upgraded Large Millimeter Telescope (LMT) in Mexico, and shows a remarkable level of detail never seen before. The Chicken Nebula is an area of star formation in the constellation Taurus, and the new image shows a large number of protostars, young stars, and jets of gas being ejected from them.
