
As parents, we want to capture the natural joy our children experience during the holiday season. A great way to do this is to have your child draw and write about their holiday experience. Drawing and writing can be a powerful way to help children express their emotions, and it can be a great way to document their holiday memories and create lasting keepsakes. Drawing and writing can also be a fun and creative activity for the entire family to enjoy.

Today, scientists at the University of Texas announced a revolutionary new development in the field of space exploration. They have created a fleet of miniaturized robots that can be used to explore the surface of asteroids. These robots are incredibly small, measuring only several millimeters in size. They can operate in the weightlessness of space, and they can move around using the asteroid’s own gravitational field. This is an incredibly exciting breakthrough, as it opens up the possibilities of exploration to much smaller, more agile spacecraft.
The rise of antibiotic resistance has been a growing threat to global health in recent years. Now, researchers have discovered a new way to combat the phenomenon: by understanding the behavior of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. In a new study, published in the journal Science, researchers from the University of Washington have developed a method to observe and track the behavior of antibiotic-resistant bacteria during the process of drug resistance. By doing so, they can identify patterns in the bacteria’s behavior that can be used to develop new strategies for combating antibiotic resistance.

A new study published in the journal Nature Communications has revealed an exciting development in the field of paleopathology. Paleopathology is a speciality of paleontology which focuses on the study of diseases in ancient fossils and their relation to evolution. The study has centered on the bacteria known to cause tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and has found evidence that the bacteria has been present in the human species for at least 6,000 years.

Astronomers have recently discovered a distant galactic nucleus located 12 billion light-years away. This is the largest and most distant structure ever observed in the universe. Using the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST), astronomers were able to detect this galactic nucleus, which is located in an area of space previously thought to be empty. By studying the nucleus, scientists will be able to learn more about the structure and evolution of galaxies.

Astronomers have discovered that the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), one of the Milky Way’s closest galactic neighbors, is surrounded by an extended family of smaller galaxies. The research, conducted by an international team of astronomers, provides new insight into the structure of the SMC and its role in the evolution of galaxies.
Recently, a team of astronomers from around the world have discovered that the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), which is one of the Milky Way’s closest galactic neighbors, is actually surrounded by an extended family of smaller galaxies.
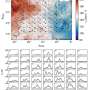
In a groundbreaking new study, researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics have revealed how images hidden in noise can be revealed using a quantum-inspired approach. The team applied this approach to a variety of noisy images, such as images of stars or galaxies distorted by noise, and were able to successfully recover the hidden images. The team demonstrated that their technique was able to achieve excellent reconstruction of images with noise levels as high as 50%.
Recent research has revealed a radical new way to reuse plastic that could kickstart a circular economy and help reduce our reliance on virgin plastics. By combining the properties of plastic and metal, a team of researchers have developed a new process that can convert used plastic bottles into metal parts. The process, which uses a combination of gasification, the temperature of metal, and a special cooling process, could revolutionize the way we recycle plastic materials and keep them out of landfills.
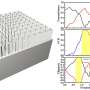
A breakthrough study has given us an exciting new tool to play with: all-dielectric metamaterials for controlling the polarization state of light. Researchers have developed a new type of optical device called a dielectric metasurface, which is made up of layer upon layer of dielectric materials. By carefully controlling the structure of the metasurface, researchers can control the polarization state of light in the near-field and far-field regions. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize the way we control and manipulate light, with a wide range of applications from imaging to communication.
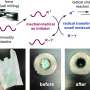
Recent research has uncovered a way to use the lethal toxin from anthrax to treat certain kinds of cancer. The toxin, known as lethal factor (LF), has been found to be effective in treating tumors that are resistant to current treatments. In a study published in the journal Science, researchers showed that LF was able to kill tumor cells that were resistant to both chemotherapy and radiation. The study also found that LF was able to trigger tumor necrosis, a process where the tumor cells die off and are replaced by healthy tissue.
A recent study by leading astronomers has revealed the surface of a distant exoplanet through studying its atmosphere. The findings are a breakthrough for exoplanet observation, as this is the first time the surface of an exoplanet has been revealed in such detail. Scientists were able to study the atmosphere of the exoplanet by analyzing the light from its star as it passed through the atmosphere of the exoplanet. This groundbreaking technique allowed them to determine the chemical composition of the planet’s atmosphere and the temperatures at different levels in the atmosphere.

For many people, traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) can be a life-altering experience. The physical, emotional, and cognitive effects of a TBI can be devastating, and the search for treatments and solutions is ongoing. Now, researchers have taken a major step forward in the quest to alleviate the debilitating effects of TBIs. After years of study, researchers have developed a new device that uses noninvasive electrical stimulation to stimulate the brain’s natural healing process.
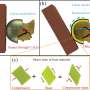
New research has discovered that the Tatooine meteorite, famously seen in Star Wars: The Phantom Menace, is actually much older than previously thought. This meteorite, known as the Tatahouine Meteorite, was found in 1931 in the Tatahouine region of Tunisia and is now believed to be around 4.5 billion years old. This makes it one of the oldest meteorites ever found and could provide us with new insights into the early formation of our solar system.

The United Kingdom is staying true to the metric system! Following a public consultation which ran from May to July of this year, the UK government has announced that it will retain its metric measurements. With an overwhelming majority of the respondents in favor of keeping the metric system, the government concluded that it is the best way to measure distances, volumes, and temperatures. The UK is now firmly committed to the internationally accepted metric system and will continue to adhere to it in the future.

Scientists have recently made a groundbreaking discovery about the moon: a large, ice-covered ocean lies hidden beneath its south pole! This is the first time such an ocean has been found on any celestial body other than Earth. This discovery has huge implications for our understanding of our solar system, and could even mean that we may one day be able to explore this ocean ourselves. This means that the moon, once thought to be a desolate wasteland, could now be a potential home for life.

Recently, scientists have discovered a new pathway for the ionization and dissociation of molecules. This new pathway, called Interatomic Coulombic Decay (ICD), is incredibly efficient at breaking apart molecules and enabling researchers to gain a better understanding of the structure of matter on an atomic level. ICD has already been used to help explain the behavior of molecules in a variety of chemical and biological processes, providing a new layer of insight into the inner workings of molecules.
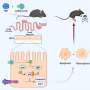
In a recent study, researchers at the University of California, Davis, have identified a gene that helps tuberculosis (TB) bacteria to persist in the body for long periods of time, even in the absence of treatment. This gene, called Rv1733c, is able to turn on dormant TB bacteria in the body, allowing them to remain in a state of low-level infection without causing any symptoms. This could explain why some people who have been infected with TB are able to remain asymptomatic for years, even though they may not be receiving treatment.
Terahertz (THz) waves, which are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between 0.3 and 30 THz, have attracted much attention in recent years due to their potential applications in various fields such as medical imaging, security, and communication. Now, a team of researchers from China and the US have developed a new type of THz transistors based on two-dimensional (2D) plasmons. This new device has an extremely high sensitivity and a broad operation bandwidth, which could open up new possibilities for THz wave applications.

A recent breakthrough in chemistry has enabled researchers to precisely control the chemical attributes of spice compounds. This breakthrough means that scientists can now precisely control the flavor, scent, and texture of spices, allowing them to create the most flavorful, aromatic, and texturally-pleasing spice blends possible. This new capability could revolutionize the way we experience spices, allowing us to create custom spice blends that are tailored to our own personal tastes and preferences.

Recent research has demonstrated that organic-inorganic perovskites can be used to achieve high-efficiency photovoltaic (PV) devices. This breakthrough in material science has opened up exciting possibilities for the future of renewable energy. The photovoltaic effect is the process of converting light into electricity, and organic-inorganic perovskites have been proven to be extremely efficient at this task. With the potential to be used as a low-cost, highly efficient solar cell material, organic-inorganic perovskites could revolutionize the renewable energy sector.
We are now entering a new era in materials science with the development of a new elastomeric material with ultrahigh strain-induced crystallization. Recent research conducted by a team of scientists from the University of Michigan has revealed that a novel elastomeric material with high elasticity and strength can be created through strain-induced crystallization. This material is capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, pressures, and corrosive environments. It is also extremely lightweight and durable, making it ideal for use in a wide range of applications, from aerospace parts to medical implants.

Today, researchers have developed a new technique that could revolutionize the way quantum technology is developed. The technique, called “logical magic state fidelity distillation”, can greatly reduce the amount of resources needed to perform certain quantum operations, while achieving higher fidelity results than ever before. This could have major implications for the development of future quantum computers, as well as other quantum devices. With this new technique, quantum computing could become more accessible and reliable than ever before.
Recent research has revealed a new way to obtain high quality DNA from marine samples. Scientists have developed a new method to purify DNA from marine sediment cores, which can provide important insights into the history and evolution of marine ecosystems. This new method involves a combination of mechanical and chemical treatments, which helps to eliminate contaminants while preserving the integrity of the DNA. The results of this research will allow scientists to better understand the genetic diversity of the marine environment and its effects on the overall health of the oceans.

Today, scientists announced a breakthrough in the field of quantum optics. By using a pair of lasers and a crystal lattice, they’ve discovered a way to control the vibrations of a lattice with unprecedented accuracy. This new technique opens the door for a range of applications, from quantum computing to medical imaging. With this discovery, scientists are one step closer to unlocking the secrets of the quantum world.
Read Full Article Here
Did you know that the fiber content of a material can affect its mechanical properties? A new study conducted by researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder has found that the fiber content of a material affects its mechanical properties such as strength, stiffness, and toughness. The study analyzed the mechanical properties of a variety of different types of fiber-reinforced materials. The results showed that materials with higher fiber content had better mechanical properties than materials with lower fiber content.

