
Have you ever considered the impact that weird and wonderful animals can have on conservation efforts? In a recent study published in the Journal of Conservation Biology, researchers found that cute and unusual animals are often the focus of media attention, leading to an increased interest in conservation efforts. From the blobfish to the axolotl, these unique creatures are helping to raise awareness and support for important conservation initiatives. So next time you come across a strange and adorable animal, remember that they may be playing a bigger role in conservation than you think.

The collision of a black hole and a neutron star has long been a subject of fascination and mystery for scientists. However, a recent study has revealed that a collision detected in 2019 has defied expectations, with the resulting object having characteristics that challenge our current understanding of such events. This unexpected discovery has sparked a new wave of curiosity and inquiry among researchers, as they strive to unravel the complexities of these cosmic phenomena.

The universe is a vast and mysterious place, full of wonders that continue to amaze and astonish us. One such wonder is the recent image captured by the Hubble Space Telescope, which offers a breathtaking view of a galactic supernova. This rare event allows us to witness the explosive death of a massive star, shedding light on the complex processes that govern the cosmos. As we marvel at the sight of this celestial spectacle, we are reminded of the boundless beauty and majesty of the universe, and the countless secrets that remain waiting to be uncovered.

As concerns about environmental sustainability continue to grow, the spotlight has turned to one of Mexico’s most iconic products: tequila. A recent study has revealed that the cultivation of blue agave, the plant used to make tequila, could have significant environmental benefits. From water conservation to carbon sequestration, the potential positive impact of blue agave cultivation on Mexico’s environment is promising. Could this beloved beverage be the key to a more sustainable future for Mexico?

The world of technology and science continues to push boundaries and break new ground. Recently, a team of scientists has announced a groundbreaking development - the creation of a hair-thin optical fiber. This advancement holds immense potential for revolutionizing the fields of telecommunications, medical imaging, and beyond. One can’t help but wonder what incredible innovations and discoveries will be made possible by this remarkable feat of engineering and ingenuity.
Read Full Article Here

As pet ownership continues to rise, many people are curious about the potential health risks associated with living in close proximity to animals. Zoonoses, diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans, have been a concern for centuries. However, scientists are now actively researching ways to reverse zoonoses and prevent the spread of illness from pets to their human companions. In a world where pets are cherished members of the family, this research raises important questions about the future of human-animal health and safety.

The idea that machines can accurately predict molecular properties raises a host of interesting questions. How exactly do these machines work, and what makes them so effective? Are there limitations to their predictive capabilities, and if so, what are they? Furthermore, what implications does this technology have for fields such as drug discovery and materials science? As we continue to delve into the potential of machine learning in the realm of molecular properties, we find ourselves faced with a multitude of intriguing inquiries.
The recent study conducted on the International Space Station has brought to light the surprising resilience of microorganisms in extreme conditions. Scientists have discovered that certain bacteria and fungi are not only able to survive but also thrive in the microgravity environment of the ISS. This raises questions about the potential risks of these microorganisms posing a threat to astronaut health and equipment. It also opens up avenues for further research into the mechanisms that allow these organisms to adapt and persist in space, which could have implications for future long-duration space missions and the search for extraterrestrial life.

Have you ever wondered how microbes can change the acidity of your favorite foods? A recent study has found that feeding salt to microbes can actually turn acidic foods into a tasty culinary delight. This discovery opens up a world of possibilities for creating new and unique flavor profiles in pickles, sauerkraut, and other fermented foods. Could salt-fed microbes be the key to unlocking a whole new world of gastronomic experiences?

The possibility of human colonization on Mars has led scientists to explore ways to detoxify the planet’s soil and water. In a recent development, researchers have proposed the idea of a biocatalytic reactor that can utilize microorganisms to break down toxic compounds and make the environment suitable for sustainable living. This raises a plethora of questions: Can such a reactor be successfully engineered for the harsh conditions of Mars? How will it be powered and maintained?

Have you ever considered the potential power of embracing idiosyncrasies in the world of biotechnological optimization? A recent study published in the Journal of Biotechnology explores this very concept. Traditionally, researchers have sought to standardize and streamline processes to achieve optimal results. However, this new approach challenges that notion and instead encourages scientists to embrace the unique characteristics of individual systems. By recognizing and leveraging idiosyncrasies, researchers may be able to unlock new opportunities for enhancing biotechnological processes.

As technology continues to advance, the possibility of small solar giant interplanetary travel becomes more of a reality. What are the potential implications of this groundbreaking advancement? What are the challenges that researchers and engineers may face in making this a viable option? Join us as we delve into the future of interplanetary travel and the potential of small solar giants to revolutionize space exploration as we know it.
Read Full Article Here
The discovery of superconductivity in certain transition metal dichalcogenides has opened up a world of possibilities in the field of material science. Scientists are eager to understand the underlying mechanisms of these materials and harness their potential for various applications. How do these materials behave under different conditions? What are the implications of this discovery for future technologies? There is much to explore and uncover in the realm of superconducting transition metal dichalcogenides.
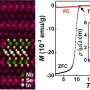
The idea of bacteria boosting their own immune systems might seem counterintuitive, but a recent study has shown that it can actually increase the effectiveness of antibiotics. This discovery raises the question: how exactly does this process work? Is there a way to harness this natural immune boost to improve antibiotic treatments for human illnesses? These findings open up a world of possibilities for improving our understanding and utilization of antibiotics in the fight against bacterial infections.
Have you ever wondered how the energy levels within our cells impact their overall quality? According to a new study from researchers, the energy available to human cells can significantly influence their function and health. This begs the question: what are the implications of this finding for human health and disease? It’s fascinating to think about how something as fundamental as cellular energy can play a crucial role in our well-being.
The latest news of Japan’s plans to send a moon lander have sparked a lot of curiosity. With discussions of the spacecraft being significantly smaller than previous ones, many are left wondering if this is a step in the right direction. Is it a strategic move to focus on smaller, more agile technology? Or is Japan aiming too small for an ambitious mission to the moon? It will be interesting to see how this development unfolds and what it means for the future of lunar exploration.

The successful use of a new laser instrument on NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) has opened up new possibilities for lunar research. The instrument, called the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA), has provided highly detailed topographic maps of the moon’s surface, shedding light on lunar geology and potential landing sites for future missions. This breakthrough raises the question: could laser technology be the key to unlocking even more discoveries about the moon and beyond?

NASA’s Artemis program has people buzzing with excitement about the prospect of returning to the moon. However, recent reports indicate that the rocket intended for this groundbreaking mission may be overheating. What could this mean for the future of lunar exploration? Is there a solution in sight, or will this setback leave us grounded on Earth for the foreseeable future? These developments certainly raise many questions about the feasibility and timeline of the Artemis mission.

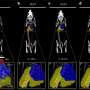
The use of positron emission particle tracking (PEPT) technology has revolutionized the way scientists study animal behavior. By injecting animals with tracers and using advanced imaging techniques, researchers are able to track the movement of particles within the animal’s body, providing valuable insights into their behavior and physiology. But is this technology the future of animal behavior studies? How will it impact our understanding of animal biology and ecology? These are questions that only time will answer as PEPT continues to evolve and be utilized in new and exciting ways.
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) has announced its plans to send a spacecraft to the moon in 2024. The spacecraft, called SLIM, will be the first in a series of lunar missions aimed at exploring the moon’s surface and conducting scientific research. With advancements in technology, what new discoveries could SLIM uncover about the moon’s geology, natural resources, and potential for future human exploration? As we eagerly await the launch of this lunar spacecraft, we can only wonder what secrets it will uncover on the surface of the moon.

The race to find effective treatments for cancer continues to push the boundaries of medical research. A recent article on Phys.org discusses the development of an AI-driven platform that aims to accelerate the discovery of a PHD inhibitor, a promising new avenue for combating certain types of cancer. How exactly does this platform work? What makes PHD inhibitors significant in the fight against cancer? Let’s delve into the details and explore the potential impact of this groundbreaking development in cancer treatment.

The recent breakthrough in molecular engineering has opened up a world of possibilities for the future of mechanical systems. The development of a clutch stack driven by molecular gears has the potential to revolutionize industries that rely on precise and efficient mechanical operation. How will this advancement impact the fields of automotive, aerospace, and robotics? What other applications could benefit from this cutting-edge technology? The possibilities seem endless, and the implications are truly exciting.
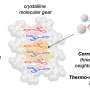
Have you ever heard of bacteria acting like kamikaze soldiers? In a fascinating new study, researchers have discovered that certain bacteria have the ability to effectively act as soldier cells, conferring resistance to their peers. This phenomenon raises a myriad of questions: How do these kamikaze bacteria function? What advantages do they provide to the bacterial community? And could their behavior hold potential for future scientific or medical applications? The intersection of biology and warfare has never been more intriguing.

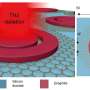
The recent development of a carbon-based tunable metasurface absorber has sparked excitement in the world of materials science. This innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize how we harness and manipulate light and heat. With the ability to fine-tune the absorbance properties of the metasurface, researchers are hopeful that this breakthrough could lead to advancements in a wide range of applications, from solar energy harvesting to stealth technology. As we look toward the future, the possibilities for this carbon-based metasurface absorber are endless, and we can’t help but wonder what new breakthroughs and opportunities it will bring.
As we look towards 2024, the use of cash for conservation efforts in South Africa is being called into question. With a changing economic landscape and new challenges facing the environment, conservationists are struggling to maintain their efforts. How will this impact the future of wildlife preservation and environmental protection in the region? It’s a pressing concern that demands our attention.
Read Full Article Here
source: Phys.org

